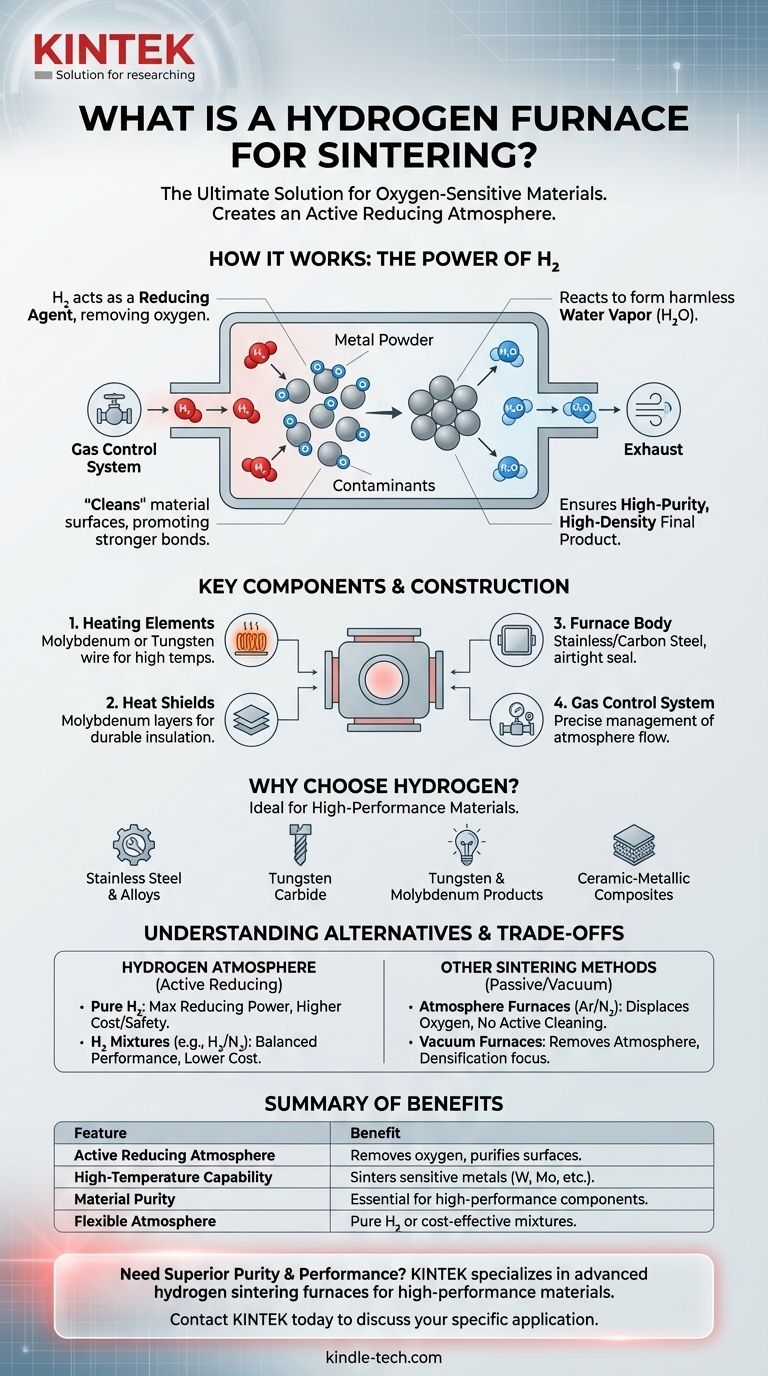
In essence, a hydrogen furnace is a specialized piece of high-temperature equipment used for sintering materials that are highly sensitive to oxygen. It uses hydrogen gas not just as a heating medium, but as an active, protective atmosphere that prevents oxidation and purifies the material's surface during processing.
The critical function of a hydrogen sintering furnace is its ability to create a "reducing" atmosphere. This means the hydrogen actively removes oxygen and other contaminants at extreme temperatures, a capability essential for producing high-purity, high-performance metal and ceramic components.
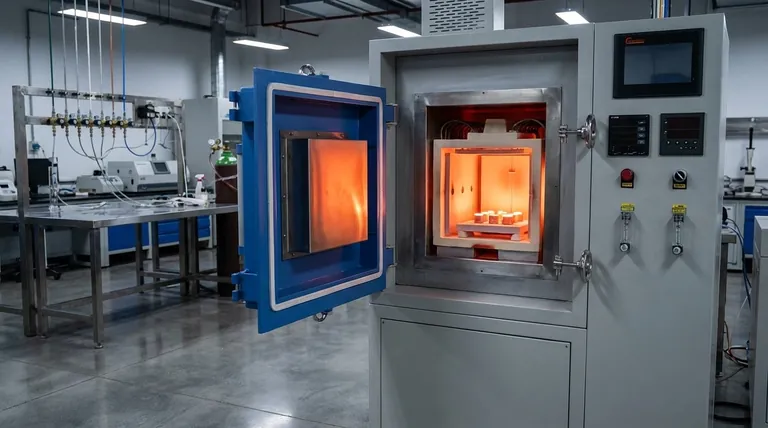

How a Hydrogen Furnace Works
To understand its value, we must look beyond simple heating and focus on the chemical environment it creates. The furnace's design is entirely centered on controlling this atmosphere.
The Role of the Hydrogen Atmosphere
The core principle is using hydrogen (H2) as a reducing agent. At the high temperatures required for sintering (fusing powder particles together), most metals would rapidly form oxides, compromising their structural integrity.
Hydrogen actively prevents this by reacting with any oxygen present, forming harmless water vapor (H2O) that is vented away. This process effectively "cleans" the surfaces of the material particles, promoting stronger bonds and a denser final product.
Key Components and Construction
A typical hydrogen furnace is built to withstand extreme heat and manage a controlled gas environment.
Its main components include:
- Heating Elements: Often made of molybdenum or tungsten wire, which can operate at very high temperatures without degrading in the hydrogen atmosphere.
- Heat Shields: Layers of molybdenum are used for insulation instead of traditional fiber, as they are more durable in this specific environment.
- Furnace Body: The chamber is constructed from stainless steel or carbon steel, designed to be sealed airtight to contain the hydrogen atmosphere.
- Gas Control System: A sophisticated system manages the flow of hydrogen and any inert gases, ensuring the correct atmospheric composition throughout the sintering cycle.
Why Choose Hydrogen for Sintering?
The decision to use a hydrogen furnace is driven entirely by the material being processed. It is not a general-purpose tool but a solution for specific, demanding applications.
Sintering High-Performance Materials
Hydrogen is the required choice for materials whose final properties depend on extreme purity and the absence of oxides.
Common applications include the sintering of stainless steel, tungsten carbide, and other high-performance alloys. It is also essential for producing pure tungsten and molybdenum products and certain specialized ceramic-metallic composites.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While powerful, a hydrogen furnace is not the only option for sintering. Understanding its place relative to other technologies is key to making an informed decision.
Pure Hydrogen vs. Hydrogen Mixtures
Operating a furnace with pure hydrogen provides the maximum reducing capability but also carries higher operational costs and safety considerations.
For many applications, a hydrogen mixture that combines H2 with an inert gas like nitrogen or argon is a practical compromise. This approach lowers costs while retaining enough reducing power for the task.
Comparison to Other Sintering Methods
- Atmosphere Furnaces: These use inert gases like argon or nitrogen. Their goal is simply to displace oxygen and prevent reactions. They do not actively clean or reduce the material surface as hydrogen does.
- Vacuum (Hot Press) Furnaces: These remove the atmosphere entirely, creating a vacuum to prevent oxidation. Some also apply high pressure during the cycle to help densify the material, which is particularly useful for certain ceramics. The choice depends on whether the material benefits more from a vacuum or an active reducing environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Material
Selecting the correct sintering technology requires matching the furnace's capabilities to the material's chemical needs.
- If your primary focus is high-purity metals sensitive to oxygen (e.g., tungsten, molybdenum): A pure hydrogen furnace is the industry standard for achieving the necessary reduction and density.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective sintering of stainless steel or other alloys: A furnace using a hydrogen-nitrogen mixture often provides the ideal balance of performance and operational cost.
- If your primary focus is advanced ceramics that require densification under pressure: A hot press sintering furnace operating under a vacuum is likely the more appropriate technology.
Ultimately, choosing a hydrogen furnace is a decision to leverage chemistry to achieve superior material properties that are unattainable with other methods.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Atmosphere | Actively removes oxygen, prevents oxidation, and purifies material surfaces. |
| High-Temperature Capability | Sinters sensitive materials like tungsten, molybdenum, and stainless steel. |
| Material Purity | Essential for producing high-performance, high-density metal and ceramic components. |
| Atmosphere Control | Can use pure hydrogen or cost-effective hydrogen-inert gas mixtures. |
Need to achieve superior purity and performance in your metal or ceramic sintering process?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including hydrogen sintering furnaces designed for high-performance materials like tungsten, molybdenum, and stainless steel. Our experts can help you select the right furnace configuration—whether pure hydrogen or a gas mixture—to meet your specific material and budget requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sintering application and discover how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary benefits of using hydrogen firing for sintering parts? Achieve Peak Density & Corrosion Resistance
- Why must a hydrogen-reducing atmosphere be maintained for tungsten annealing? Ensure Purity in High-Temp Processing
- What are hydrogen furnaces used for? Achieve Purity and Speed in High-Temperature Processing
- What is hydrogen atmosphere heat treatment? Achieve Superior Surface Purity & Brightness
- What is the use of hydrogen in furnace? A Key to Oxygen-Free High-Temperature Processing



















