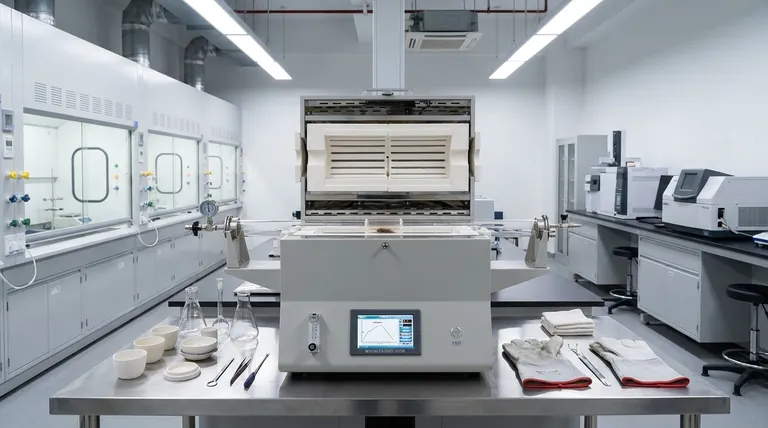
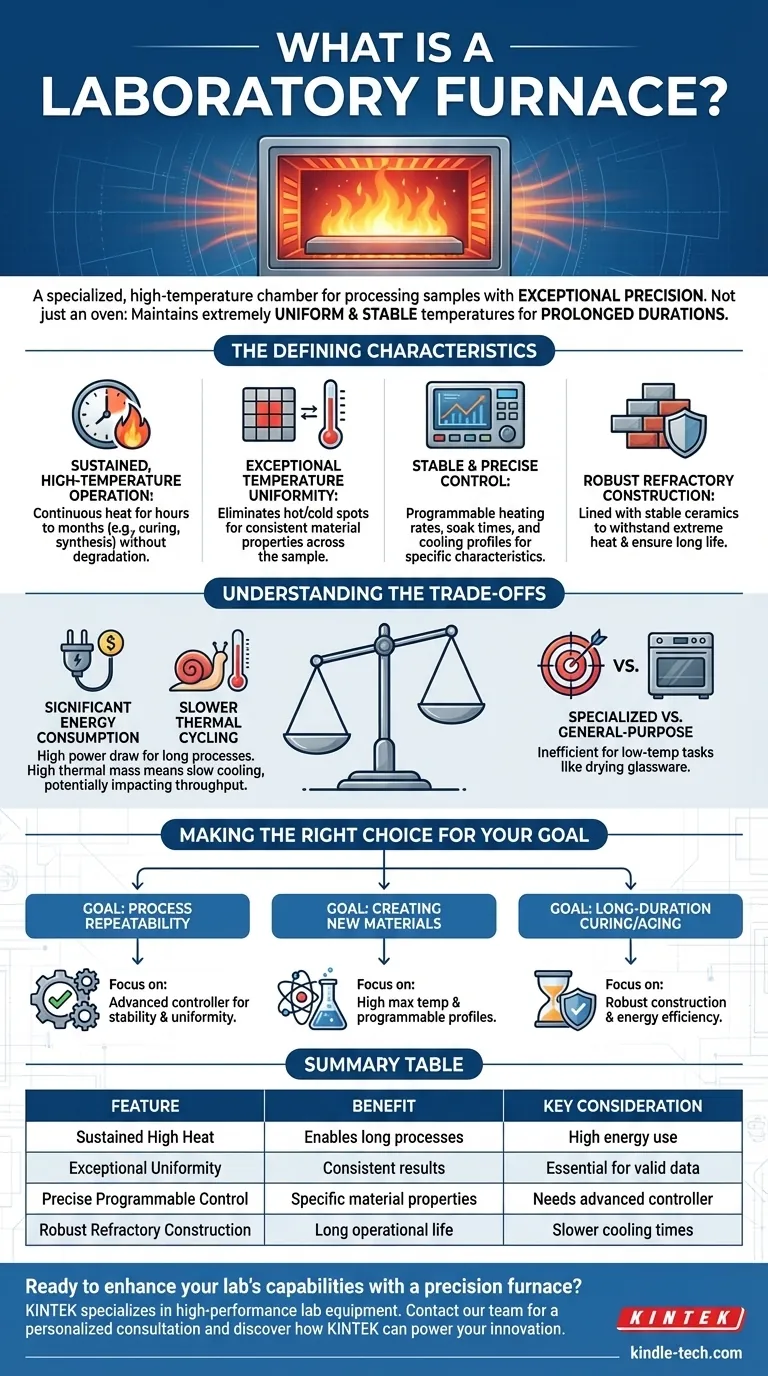
At its core, a laboratory furnace is a specialized high-temperature chamber designed for processing samples and materials with exceptional precision. These devices provide continuous, uniform heat for extended periods and are essential tools in fields ranging from materials science and engineering to chemical synthesis and geological research.
A laboratory furnace is not simply a high-heat oven. Its primary value lies in its ability to maintain extremely uniform and stable temperatures for prolonged durations—a capability made possible by its construction from robust, heat-resistant refractory materials.

The Defining Characteristics of a Laboratory Furnace
To understand the role of a furnace, it's essential to recognize the features that distinguish it from other heating equipment. These characteristics are engineered specifically for the demands of scientific and industrial processing.
Sustained, High-Temperature Operation
A key function of a laboratory furnace is to provide continuous heat. Many material processes, such as curing ceramics or complex chemical syntheses, require high temperatures to be maintained for hours, days, or even months to complete successfully.
The furnace is built to handle this thermal stress without degradation, ensuring the process can run to completion without interruption.
Exceptional Temperature Uniformity
For scientific results to be valid and repeatable, every part of a sample must be treated identically. Laboratory furnaces are designed to create an extremely uniform temperature zone within the heating chamber.
This uniformity ensures that there are no hot or cold spots, guaranteeing consistent material properties throughout the entire sample.
Stable and Precise Control
Modern furnaces feature sophisticated controllers that allow for precise management of the thermal process. This includes the heating rate (how fast it gets to temperature), the soak time (how long it stays at temperature), and the cooling profile.
This stable, programmable control is critical for creating materials with specific, desired characteristics.
Robust Refractory Construction
The ability to withstand extreme temperatures is due to the furnace's internal construction. It is lined with refractory materials, which are ceramics and other compounds that are chemically and physically stable at high heat.
This robust build not only contains the heat effectively but also ensures the furnace has a long operational life despite the demanding conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, laboratory furnaces come with inherent trade-offs that are important to understand for proper application and management.
Significant Energy Consumption
Maintaining high temperatures for long periods requires a substantial amount of energy. The power draw of a laboratory furnace is a significant operational consideration, especially for continuous-use processes.
Slower Thermal Cycling
The very same refractory materials that make a furnace excellent at holding high temperatures also give it significant thermal mass. This means that while it may heat up quickly, it will often take a very long time to cool down, which can slow down high-throughput workflows.
Specialized vs. General-Purpose Use
A laboratory furnace is a highly specialized piece of equipment. It is not a general-purpose laboratory oven. Using it for low-temperature applications like drying glassware is inefficient and impractical due to its slow cooling and high-power design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a furnace requires matching its capabilities to your specific scientific or production objective.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: Prioritize a model with an advanced digital controller that guarantees exceptional temperature stability and uniformity across the chamber.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials: Look for a furnace that can reach the specific high temperatures your synthesis requires and offers programmable heating and cooling profiles.
- If your primary focus is long-duration curing or aging: Emphasize robust refractory construction and documented energy efficiency to manage operational costs over time.
Ultimately, a laboratory furnace is an investment in process control, enabling research and production outcomes that would otherwise be impossible.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Sustained High Heat | Enables long-duration processes like curing and synthesis. | High energy consumption. |
| Exceptional Uniformity | Guarantees consistent, repeatable results across samples. | Essential for valid scientific data. |
| Precise Programmable Control | Allows for specific heating/cooling profiles to create desired material properties. | Requires an advanced digital controller. |
| Robust Refractory Construction | Withstands extreme temperatures for long operational life. | High thermal mass leads to slower cooling times. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a precision furnace?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces designed for the exacting demands of materials science, chemical synthesis, and research. Our experts can help you select the ideal model for your specific application, ensuring superior temperature control, uniformity, and durability.
Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can power your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction and temperature control mechanism of a laboratory tube furnace? Master Precision Heating for Your Lab
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance



















