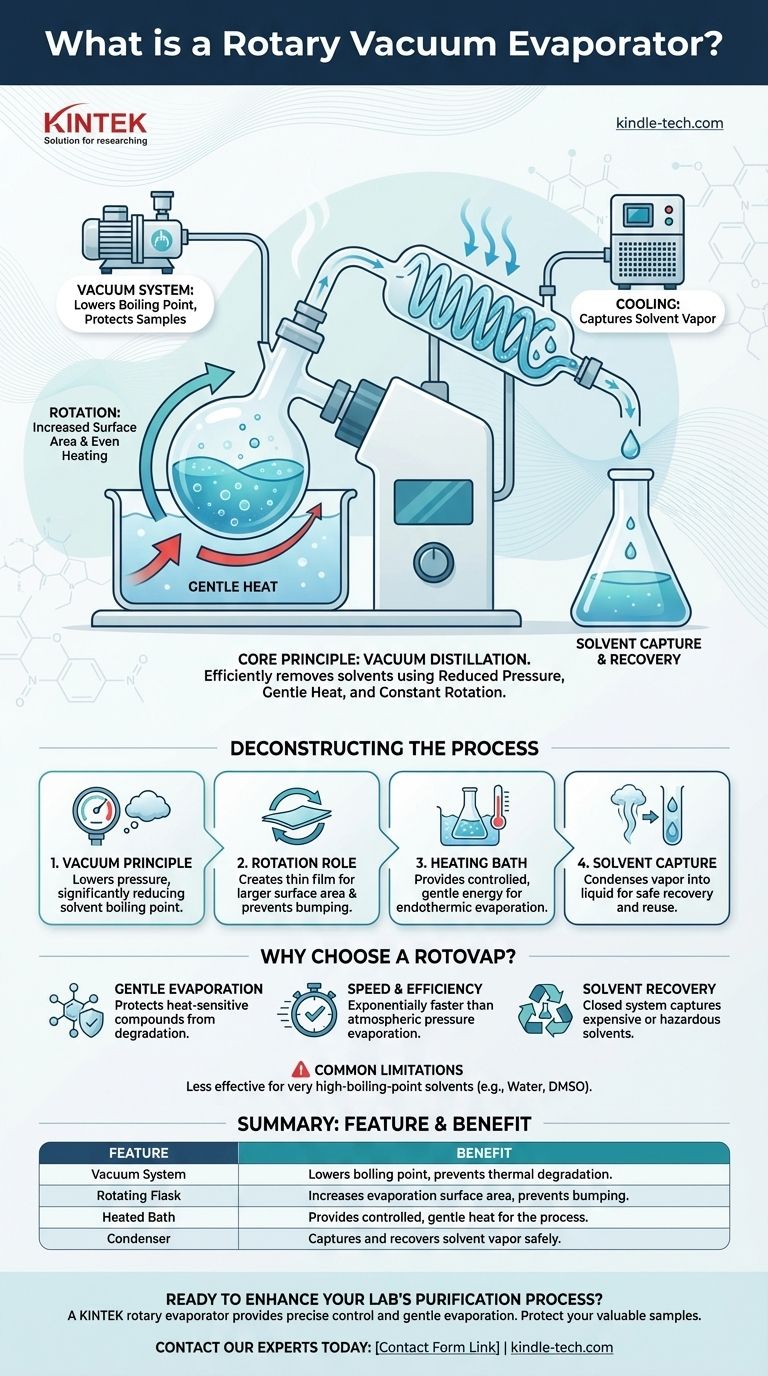
At its core, a rotary vacuum evaporator—often called a "rotovap"—is a laboratory instrument designed to efficiently and gently remove solvents from a sample. It accomplishes this through a process known as vacuum distillation, combining reduced pressure, gentle heat, and constant rotation to separate a volatile solvent from a non-volatile compound of interest.
The central challenge in chemical purification is removing a solvent without destroying the sample you want to keep. A rotary evaporator solves this by lowering the solvent's boiling point with a vacuum, allowing for rapid evaporation at a low, safe temperature.

Deconstructing the Process: How a Rotovap Works
To understand the rotovap's value, you must first understand the scientific principles that make it so effective. Each component plays a critical role in achieving gentle and rapid solvent removal.
The Principle of Vacuum Distillation
The defining feature of a rotovap is the vacuum. By lowering the pressure inside the system, the boiling point of the solvent is significantly reduced.
This is the same reason water boils at a lower temperature at high altitudes. The rotovap exploits this principle to make solvents boil at temperatures as low as room temperature, preventing thermal degradation of sensitive samples.
The Role of Rotation
The rotating flask, which holds the sample, is the most visually distinct part of the apparatus. This rotation is not for show; it serves two crucial functions.
First, it constantly spreads the liquid into a thin film on the inner surface of the flask, dramatically increasing the surface area available for evaporation. Second, it provides constant agitation, ensuring the sample is heated evenly and preventing violent bumping or boiling.
The Importance of the Heating Bath
The evaporation of a solvent is an endothermic process, meaning it requires energy in the form of heat. The rotovap uses a heated fluid bath, typically filled with water, to provide this energy in a controlled and gentle manner.
The bath temperature is carefully set to be warm enough to facilitate evaporation at the reduced pressure but low enough to avoid damaging the sample.
Capturing the Solvent
As the solvent evaporates, the vapor travels into a condenser. This component uses a cooled surface (from circulating water or a chiller) to turn the solvent vapor back into a liquid.
This recaptured liquid, known as the distillate, is collected in a separate receiving flask. This prevents the release of potentially hazardous solvent fumes into the lab and allows the solvent to be recycled.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Why Choose a Rotovap?
While powerful, a rotary evaporator is a specific tool for a specific job. Understanding its advantages and limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Primary Advantage: Gentle Evaporation
The main reason to use a rotovap is to protect heat-sensitive compounds. Traditional distillation often requires high temperatures that can decompose or alter the chemical structure of the desired product. A rotovap removes this risk entirely.
Speed and Efficiency
Compared to simply letting a solvent evaporate at atmospheric pressure, a rotovap is exponentially faster. The combination of increased surface area, gentle heat, and reduced pressure creates the ideal conditions for rapid evaporation.
Common Limitations
A rotovap is less effective for removing very high-boiling-point solvents, such as water or DMSO. While possible, the process can be extremely slow even under a strong vacuum. For these applications, other techniques like freeze-drying (lyophilization) are often preferred.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding when to use a rotary evaporator depends entirely on your sample and your objective.
- If your primary focus is purifying a heat-sensitive product: The rotovap is the standard and safest method for removing a volatile solvent without degrading your compound.
- If your primary focus is quickly processing a large volume of solvent: A rotovap is far more efficient and faster than open-air evaporation or other passive methods.
- If your primary focus is solvent recovery and safety: The closed system with a condenser is ideal for capturing and reusing expensive solvents or preventing the release of hazardous vapors.
Mastering the use of a rotary evaporator is a fundamental skill for efficient and safe chemical purification in any modern laboratory.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Vacuum System | Lowers solvent boiling point to prevent thermal degradation. |
| Rotating Flask | Increases evaporation surface area and prevents bumping. |
| Heated Bath | Provides controlled, gentle heat for the evaporation process. |
| Condenser | Captures and recovers solvent vapor safely and efficiently. |
Ready to enhance your lab's purification process?
A KINTEK rotary evaporator provides the precise control and gentle evaporation needed to protect your valuable, heat-sensitive samples. Whether you're concentrating compounds, recovering solvents, or purifying products, our rotovaps are designed for reliability and efficiency.
Contact our lab equipment experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs. Get in touch via our Contact Form to discuss your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rotary Vane Vacuum Pump for Lab Use
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How do you inspect a vacuum pump? A Step-by-Step Guide to Ensure Peak Performance
- What are the advantages of rotary vane pumps? Unlock Cost-Effective, High-Performance Vacuum
- What are the safety issues with vacuum pumps? Avoid Chemical, Mechanical, and Implosion Risks
- How to select the best rotary vane pump for specific needs? Match Your Application's Requirements
- What are the disadvantages of rotary vane vacuum pumps? Understand the Oil-Related Trade-offs



















