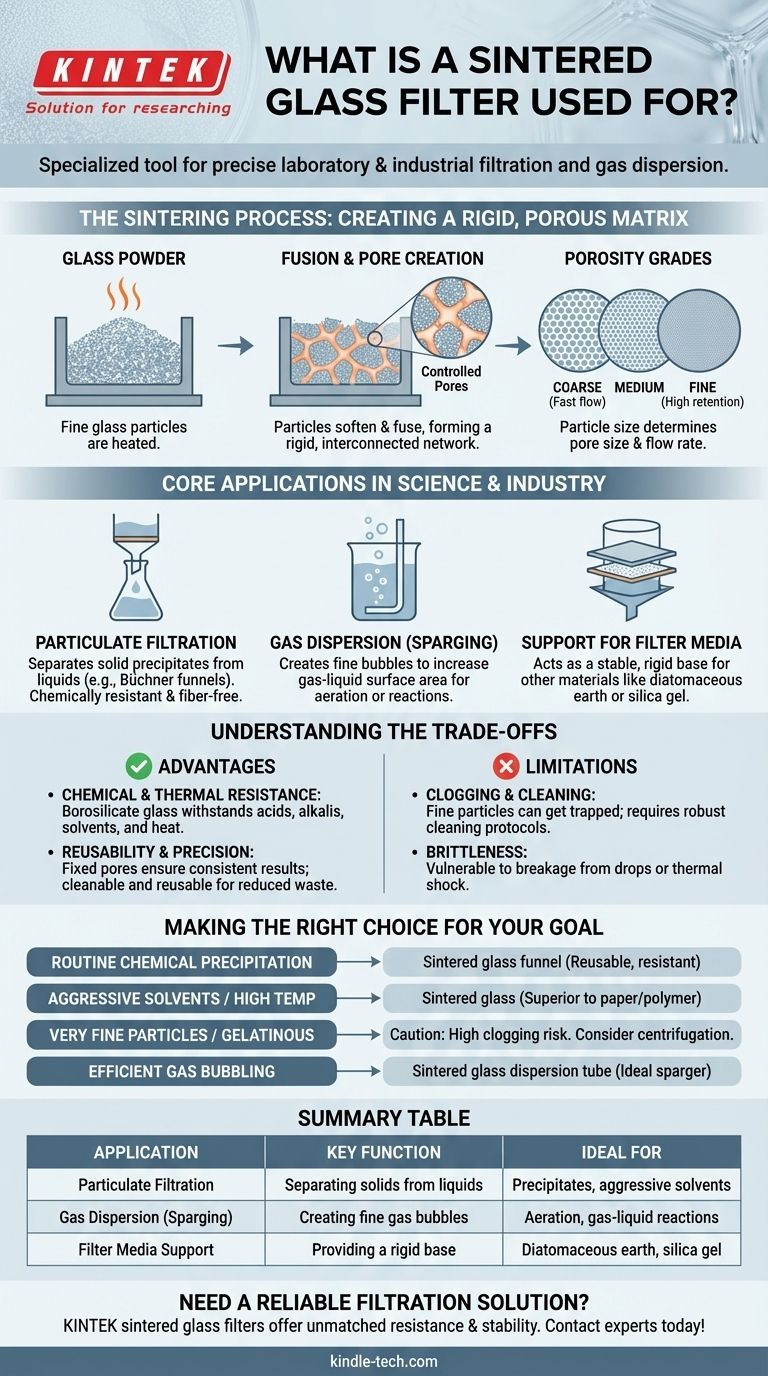
In laboratory and industrial settings, a sintered glass filter is a specialized tool used to separate solid particles from a liquid or to disperse a gas into a liquid. Made by fusing (sintering) crushed glass particles into a solid but porous disc, its primary function is filtration, especially in applications where chemical resistance and thermal stability are required.
The true value of a sintered glass filter lies not just in what it does, but how it's made. The sintering process creates a rigid, chemically inert filter with precisely defined pores, making it a reusable and robust alternative to paper or polymer filters for demanding scientific work.

The Principle Behind the Filter: The Sintering Process
To understand the filter's applications, you must first understand its construction. The unique properties of the filter are a direct result of the sintering process.
From Glass Powder to a Solid Disc
Sintering involves taking a fine glass powder, placing it in a mold, and heating it to a temperature where the particles begin to soften and fuse at their contact points. The material is not heated to its melting point; rather, the particles are just hot enough to stick together, forming a single, solid piece.
Creating a Controlled Porous Network
This fusion process creates a rigid matrix with a network of tiny, interconnected channels running through it. These channels are the pores that allow liquid or gas to pass through while trapping solid particles that are larger than the pore size.
The Critical Role of Porosity Grade
By using glass powders of different particle sizes, manufacturers can produce filters with different average pore sizes. These are categorized by a porosity grade, ranging from coarse (large pores for fast filtration of large particles) to very fine (small pores for capturing tiny particles).
Core Applications in Science and Industry
The combination of a fixed porous structure, chemical resistance, and thermal stability makes sintered glass ideal for several key tasks.
Particulate Filtration from Liquids
This is the most common use. Sintered glass funnels (often called Büchner funnels) are used to separate a solid precipitate from a solution after a chemical reaction. Unlike filter paper, the glass is non-reactive with most chemicals and won't shed fibers into the filtrate.
Gas Dispersion (Sparging)
Forcing a gas through the fine pores of a sintered glass disc into a liquid creates a stream of very small bubbles. This dramatically increases the surface area of the gas in contact with the liquid, which is highly effective for processes like aeration or for bubbling a reactive gas through a solution.
A Support for Other Filter Media
In some applications, the rigid sintered disc acts as a stable, flat support bed for other filtration materials, such as a layer of diatomaceous earth or silica gel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintered glass filters are not the right tool for every job. Understanding their limitations is key to using them effectively.
Advantage: Chemical and Thermal Resistance
The filter is typically made of borosilicate glass, which is highly resistant to acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. It can also be heated in an oven to dry the collected solids directly on the filter, a task impossible with polymer or paper filters.
Advantage: Reusability and Precision
Because the pores are fixed within a rigid structure, they do not change size under pressure, leading to very consistent results. They are designed to be cleaned and reused hundreds of times, reducing long-term waste.
Limitation: Clogging and Cleaning
The primary drawback is that fine particles can become permanently lodged deep within the filter's pores. While they can be cleaned with strong acids or back-flushing, severe clogging can render a filter unusable. They are not disposable and require a cleaning protocol.
Limitation: Brittleness
Like all glassware, sintered glass filters are brittle. They can be broken if dropped or subjected to rapid, extreme temperature changes (thermal shock).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct filtration method depends entirely on your specific objective and constraints.
- If your primary focus is routine chemical precipitation: A sintered glass funnel is an excellent, reusable choice due to its superior chemical resistance.
- If you need to filter aggressive solvents or perform filtrations at high temperatures: Sintered glass is the superior choice over paper or polymer membrane filters.
- If you are working with very fine particles or gelatinous precipitates: Be aware of the high risk of clogging and have a robust cleaning plan, or consider an alternative method like centrifugation.
- If you need to bubble a gas into a reaction mixture efficiently: A sintered glass gas dispersion tube (or sparger) is the ideal tool for the job.
By understanding its fundamental construction, you can leverage the unique strengths of a sintered glass filter for precise and demanding scientific applications.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Particulate Filtration | Separating solids from liquids | Chemical precipitates, aggressive solvents |
| Gas Dispersion (Sparging) | Creating fine gas bubbles in liquids | Aeration, gas-liquid reactions |
| Filter Media Support | Providing a rigid base for other materials | Diatomaceous earth, silica gel layers |
Need a reliable, reusable filtration solution for your lab?
Sintered glass filters from KINTEK offer unmatched chemical resistance and thermal stability for your most demanding applications. Whether you're filtering aggressive solvents, performing high-temperature separations, or need precise gas dispersion, our lab equipment ensures consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sintered glass filter for your specific porosity and chemical resistance needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Longpass Highpass Filters for Optical Applications
- Shortpass Filters for Optical Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Sampling Filters
- Narrow Band Pass Filters for Precision Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
People Also Ask
- What is the acceptable pressure drop across a filter? Master Your System's Health and Efficiency
- What is the purpose of sintered glass? A Guide to Precision Filtration and Chemical Resistance
- What are the advantages of centrifuge filter? Achieve Fast, Gentle Sample Prep for Your Lab
- What are the applications of optical coating? Unlock Advanced Light Control for Your Industry
- What is the use of thin film in optics? Mastering Light Control for Lenses, Mirrors, and Filters
















