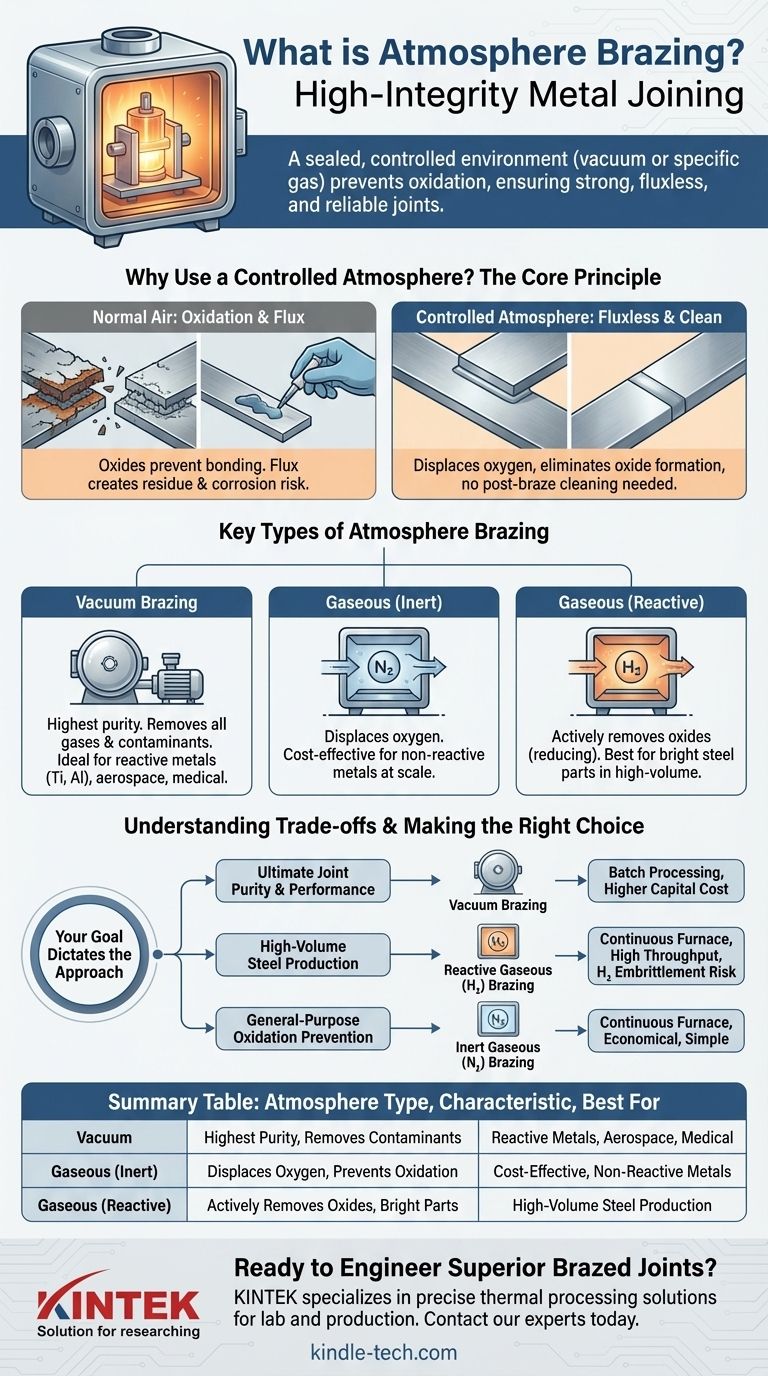
In essence, atmosphere brazing is a high-integrity metal-joining process performed inside a sealed furnace where the air has been replaced by a carefully controlled gas or a vacuum. This controlled environment is the key to the process; it prevents the formation of oxides at high temperatures, which ensures the filler metal can flow freely and create a strong, clean, and reliable joint without the need for chemical fluxes.
The crucial takeaway is that the "atmosphere" in atmosphere brazing is not a passive element—it is an active tool. The choice of atmosphere, whether a vacuum or a specific gas, directly determines the cleanliness, strength, and material properties of the final brazed joint, making it a critical engineering decision.

Why Use a Controlled Atmosphere? The Core Principle
Brazing requires heating metals to high temperatures, often over 800°F (427°C). In normal air, this heat would cause oxygen to rapidly react with the metal surfaces, creating a layer of oxide.
### Eliminating Oxidation
Oxides are brittle, non-metallic layers that prevent the brazing filler metal from "wetting" or bonding properly with the base materials. A controlled atmosphere displaces the oxygen, eliminating this primary cause of joint failure.
### Achieving a "Fluxless" Braze
In traditional brazing, a chemical flux is applied to clean the metal and prevent oxidation. Controlled atmospheres make this step unnecessary. This "fluxless" process results in cleaner parts, no post-braze cleaning to remove corrosive flux residue, and a more streamlined manufacturing operation.
Key Types of Atmosphere Brazing
The term "atmosphere brazing" covers several distinct methods, each defined by the environment created inside the furnace.
### Vacuum Brazing
This is often considered the highest-purity form of atmosphere brazing. Parts are loaded into a furnace, which is then sealed and pumped down to a very low pressure, creating a near-vacuum.
The vacuum actively removes not only oxygen but also other volatile contaminants and impurities from the metal surfaces. This makes it ideal for joining reactive metals like titanium and aluminum, or for mission-critical aerospace and medical components where joint integrity is paramount.
### Gaseous Atmospheres
Instead of a vacuum, these processes use a specific gas or mixture of gases to control the environment. This is often performed in a continuous furnace where parts move along a conveyor belt.
An inert atmosphere, typically using pure nitrogen, works by simply displacing the oxygen. It is a cost-effective way to prevent oxidation for many common materials.
A reactive (or active) atmosphere, most commonly using hydrogen, goes a step further. Hydrogen not only displaces oxygen but also actively reacts with and removes existing surface oxides (a process called "reducing"). This is particularly effective for steels and results in exceptionally bright, clean parts post-brazing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right atmosphere involves balancing cost, complexity, and desired final quality. There is no single "best" method for all applications.
### Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces represent a significant capital investment and have more complex operational cycles (pumping down, heating, cooling). Gaseous atmosphere furnaces, especially continuous models, can offer higher throughput but require precise gas flow and safety management, particularly with flammable gases like hydrogen.
### Material Compatibility
While excellent for steels, a hydrogen atmosphere can cause hydrogen embrittlement in certain metals, making them brittle and prone to failure. Vacuum brazing avoids this risk and is superior for reactive metals that would form undesirable compounds even in a trace-gas environment.
### Process and Throughput
Continuous brazing with a gaseous atmosphere is ideal for high-volume production of smaller, uniform parts. Batch brazing in a vacuum furnace is better suited for large, complex assemblies, lower production volumes, or when multiple parts with different geometries need to be processed together.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your goal dictates the correct approach. The selection of an atmosphere is a technical decision that should be driven by the performance requirements of the final product.
- If your primary focus is ultimate joint purity and performance: Vacuum brazing is the superior choice for its unmatched ability to create clean, high-integrity joints in sensitive or reactive materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of steel parts: A continuous furnace with a hydrogen-rich atmosphere provides an excellent balance of oxide reduction, high throughput, and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose oxidation prevention at scale: An inert nitrogen atmosphere in a continuous furnace is often the most economical and straightforward solution for non-reactive metals.
By understanding the role of the atmosphere, you move from simply joining parts to engineering a superior, reliable final product.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Key Characteristic | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Brazing | Highest purity, removes all gases and contaminants | Reactive metals (titanium, aluminum), aerospace, medical components |
| Gaseous (Inert) | Uses nitrogen to displace oxygen, prevents oxidation | Cost-effective brazing of non-reactive metals at scale |
| Gaseous (Reactive) | Uses hydrogen to actively remove oxides, creates bright parts | High-volume production of steel parts |
Ready to Engineer Superior Brazed Joints for Your Lab or Production Line?
Atmosphere brazing is a critical process for achieving clean, high-integrity metal assemblies without the drawbacks of flux. The right furnace and atmosphere are essential for your success.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise thermal processing solutions your laboratory needs. Whether you are developing new components or scaling up production, our expertise can help you select the ideal brazing system for your materials and throughput requirements.
Let's discuss your project. Contact our experts today to find the perfect brazing solution for stronger, more reliable results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What are the stages of sintering? A Guide to Mastering the Powder-to-Part Process
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the boiling point of THC under a vacuum? A Guide to Safe Distillation
- What metal Cannot be brazed? Overcoming Surface Chemistry for Strong Joints











