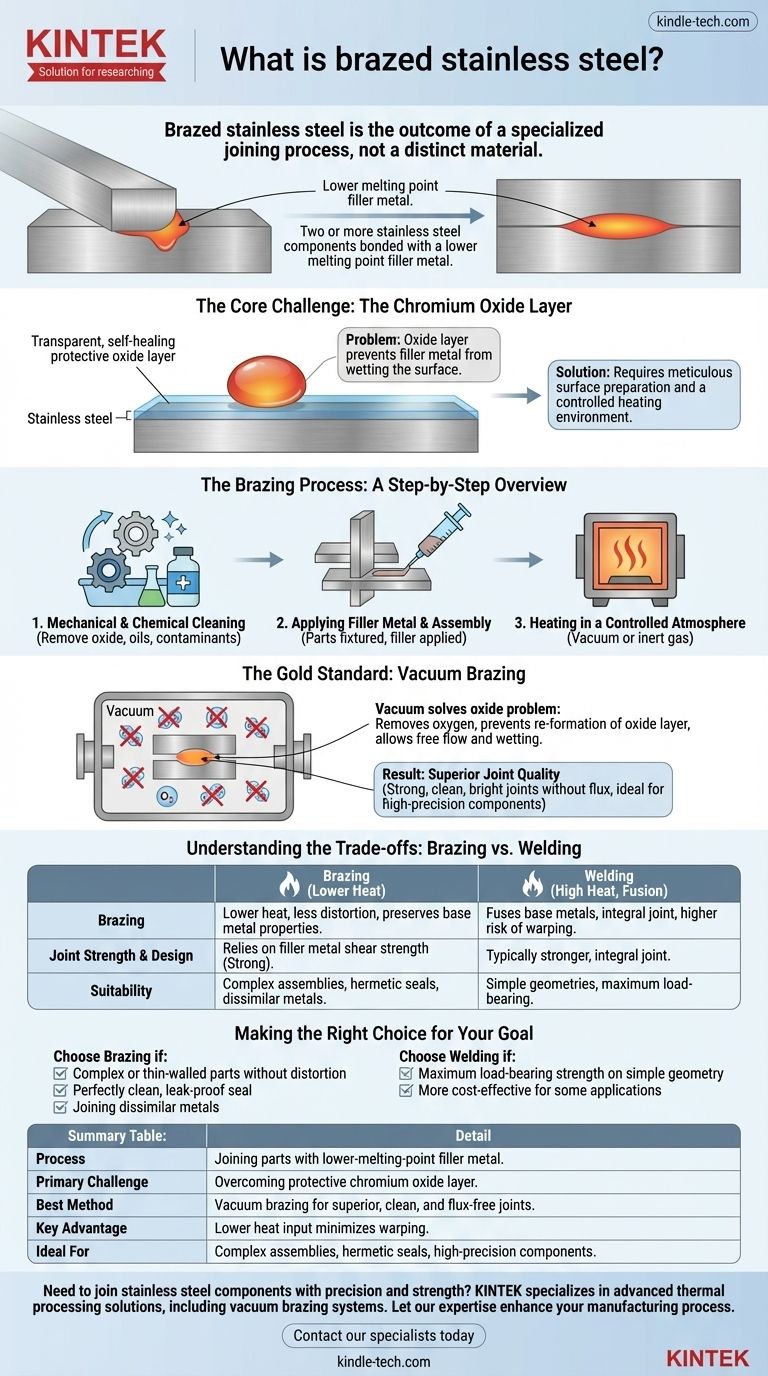
Brazed stainless steel is not a distinct type of material, but rather the outcome of a specialized joining process. It refers to two or more stainless steel components that have been bonded together using a filler metal with a lower melting point than the steel itself. The process involves heating the assembly so the filler metal melts and flows into the joint by capillary action, creating a strong, clean bond upon cooling without melting the base steel.
The core challenge—and primary focus—of brazing stainless steel is overcoming its naturally protective oxide layer. This layer prevents the filler metal from properly adhering, meaning successful brazing depends entirely on meticulous surface preparation and a controlled heating environment to achieve a sound joint.

The Central Problem: The Chromium Oxide Layer
The very property that makes stainless steel "stainless" is also its greatest obstacle during brazing.
Why is this layer a problem?
All stainless steel is protected by a thin, transparent, and self-healing layer of chromium oxide. This passive film is what gives the material its exceptional corrosion resistance.
However, for brazing, this oxide layer prevents the molten filler metal from "wetting" the surface of the steel. The filler metal will bead up, much like water on a waxed car, rather than spreading evenly to form a bond.
The Brazing Process: A Step-by-Step Overview
Successfully brazing stainless steel is a multi-stage process designed to meticulously manage the oxide layer.
Step 1: Mechanical and Chemical Cleaning
Before heating, the existing oxide layer must be removed. This is often done through mechanical methods like sandblasting or shot blasting.
This is immediately followed by chemical cleaning to remove any oils or contaminants. Workpieces are cleaned in solvents like acetone or alcohol, often using an ultrasonic bath to ensure all surfaces are perfectly clean.
Step 2: Applying Filler Metal and Assembly
The filler metal, often in the form of a paste, wire, or pre-formed shim, is applied to the joint. The parts are then fixtured together to maintain their precise alignment during the heating cycle.
Step 3: Heating in a Controlled Atmosphere
This is the most critical step. The assembly must be heated in an environment that prevents the chromium oxide layer from instantly re-forming on the hot steel. The most common and effective method for this is vacuum brazing.
The Gold Standard: Vacuum Brazing
For high-quality stainless steel components, vacuum brazing is the preferred industrial method.
How a Vacuum Solves the Oxide Problem
By placing the assembly in a high-vacuum furnace, nearly all oxygen is removed from the environment. As the part is heated, there is no oxygen available to re-form the oxide layer, allowing the brazing filler metal to flow freely and wet the clean steel surfaces.
The Result: Superior Joint Quality
This process results in extremely strong and clean brazed joints. Because no flux is used and no oxidation occurs, the finished part emerges from the furnace bright and clean, often requiring no post-process cleaning. This makes it ideal for medical, aerospace, and electromechanical components.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brazing vs. Welding
Brazing is not always the right choice. It is crucial to understand how it compares to welding, the most common alternative for joining steel.
Lower Heat and Less Distortion
Brazing occurs at a much lower temperature than welding, as you are only melting the filler metal, not the stainless steel itself. This significantly reduces the risk of warping, distortion, or altering the material properties of the parent metal, which is critical for delicate or high-precision parts.
Joint Strength and Design
A welded joint fuses the base metals, making the joint an integral part of the components. A brazed joint, by contrast, relies on the shear strength of the filler metal adhering to the surfaces. While very strong, a properly designed welded joint is typically stronger than a brazed one.
Suitability for Complex Assemblies
Brazing excels at joining complex, multi-part assemblies or dissimilar metals in a single furnace cycle. It is also ideal for creating leak-tight, hermetic seals in components like pipe fittings, housings, and HVAC system parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct joining method depends entirely on the design, material, and performance requirements of your component.
- If your primary focus is joining complex or thin-walled parts without distortion: Brazing is the superior choice due to its lower heat input.
- If your primary focus is achieving a perfectly clean, leak-proof seal for a finished part: Vacuum brazing delivers exceptional aesthetic and hermetic quality right out of the furnace.
- If your primary focus is maximum load-bearing strength on a simple geometry: Traditional welding may provide a stronger and more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, brazing is a powerful technique for creating precise, clean, and strong assemblies that preserves the integrity of the stainless steel.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Joining stainless steel parts using a lower-melting-point filler metal. |
| Primary Challenge | Overcoming the protective chromium oxide layer on the steel. |
| Best Method | Vacuum brazing for superior, clean, and flux-free joints. |
| Key Advantage | Lower heat input minimizes warping and distortion. |
| Ideal For | Complex assemblies, hermetic seals, and high-precision components. |
Need to join stainless steel components with precision and strength? KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including vacuum brazing systems. Our lab equipment and consumables are designed to help you achieve flawless, high-integrity joints for medical, aerospace, and electromechanical applications. Let our expertise enhance your manufacturing process—contact our specialists today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- What metals can be joined by brazing? Discover the Versatility of Modern Brazing Techniques
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- What is the process of vacuum brazing? Achieve High-Purity, Strong Metal Joining
- Why would you braze instead of weld? Preserve Material Integrity and Join Dissimilar Metals



















