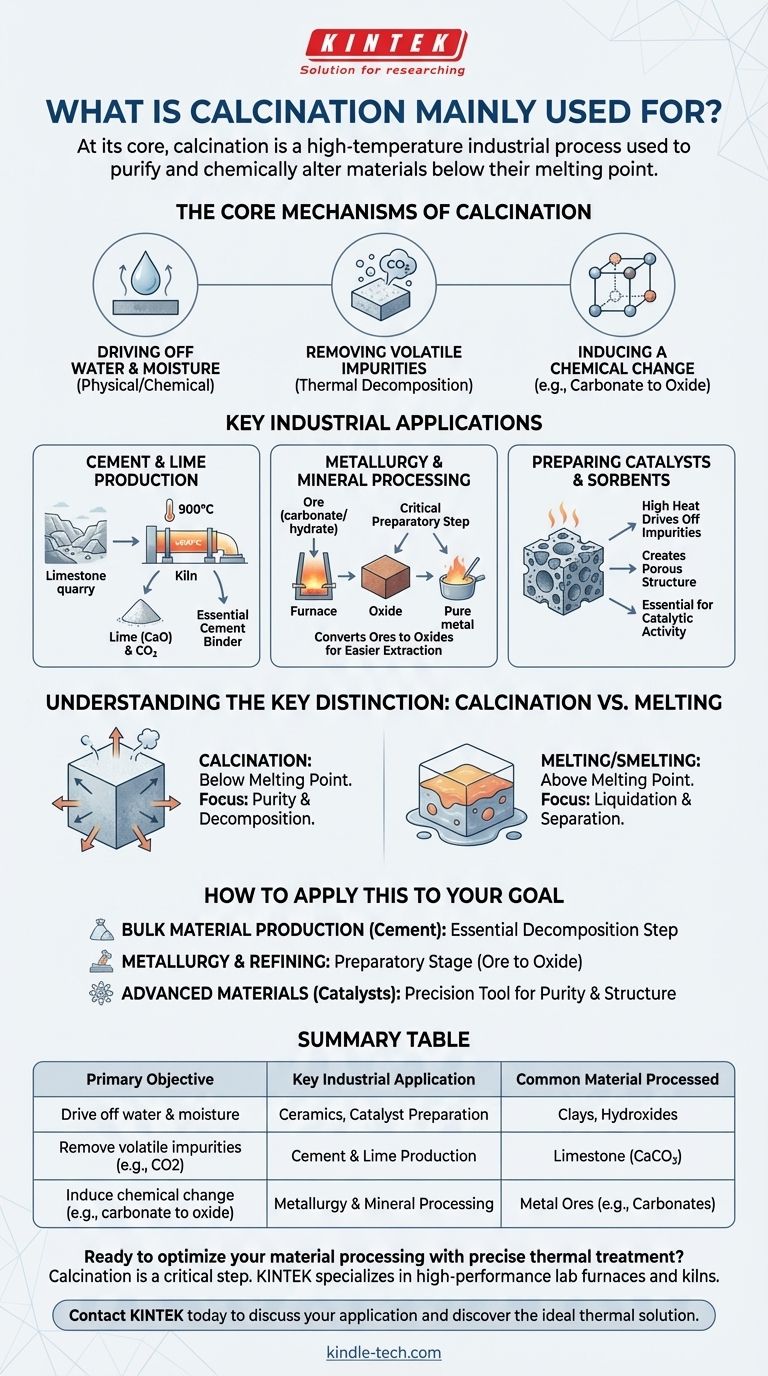
At its core, calcination is a high-temperature industrial process used to purify and chemically alter materials. Its most widespread and historically significant application is the thermal decomposition of limestone (calcium carbonate) into lime (calcium oxide) and carbon dioxide, a reaction that is fundamental to manufacturing cement.
Calcination is not about melting a substance, but rather heating it to a high temperature below its melting point. This controlled thermal treatment is designed to drive off volatile components like water and carbon dioxide, causing a fundamental chemical or physical change in the material.

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
To understand its applications, you must first understand what calcination achieves on a chemical and physical level. The process serves a few primary objectives.
Driving off Water and Moisture
Calcination is highly effective at removing all forms of water from a solid. This includes both physically absorbed surface moisture and chemically bonded water molecules within the material's crystal structure.
Removing Volatile Impurities
The most important function is removing volatile substances. This is achieved through thermal decomposition, where heat breaks down compounds. The most common example is driving off carbon dioxide (CO2) from carbonate minerals.
Inducing a Chemical Change
By removing these components, calcination changes the chemical makeup of the substance. For instance, converting a metal carbonate into a metal oxide prepares it for the next stage of processing.
Key Industrial Applications
The principles of calcination are applied across several major industries, each leveraging the process for a specific outcome.
Cement and Lime Production
This is the single largest use of calcination. Limestone (CaCO3) is heated in massive kilns to approximately 900°C, causing it to decompose into lime (CaO) and CO2. This lime is the essential binding agent in cement.
Metallurgy and Mineral Processing
Calcination is a critical preparatory step in extracting metals from their ores. Many ores are mined as carbonates or hydrates. Calcining them converts them into oxides, which are much easier to reduce into pure metal through a process like smelting.
Preparing Catalysts and Sorbents
In the chemical industry, calcination is used to activate materials like catalysts. The high heat drives off impurities and can create a porous structure with a high surface area, which is essential for catalytic activity.
Understanding the Key Distinction: Calcination vs. Melting
A common point of confusion is how calcination differs from other high-temperature processes like smelting or sintering. The distinction is critical.
The Goal is Transformation, Not Liquidation
The entire process is conducted at a temperature below the material's melting point. The solid-state of the substance is maintained. If the material were to melt, it would be a different process with a different outcome.
The Focus is on Purity and Decomposition
Calcination aims to remove unwanted parts of a compound (like water or CO2) or change its crystalline structure. In contrast, smelting uses temperatures above the melting point to liquefy and separate components, such as separating metal from slag.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding the purpose of calcination allows you to recognize its role in various industrial value chains.
- If your primary focus is bulk material production (like cement): View calcination as the essential decomposition step that creates your primary chemical building block.
- If your primary focus is metallurgy and refining: Use calcination as a preparatory stage to convert ores into oxides, which simplifies the subsequent metal extraction.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced materials (like catalysts): Treat calcination as a precision tool for controlling purity and crystal structure to achieve specific performance properties.
Ultimately, calcination is the foundational industrial technique for using heat to purify and transform solid materials without melting them.
Summary Table:
| Primary Objective | Key Industrial Application | Common Material Processed |
|---|---|---|
| Drive off water & moisture | Ceramics, Catalyst Preparation | Clays, Hydroxides |
| Remove volatile impurities (e.g., CO2) | Cement & Lime Production | Limestone (CaCO₃) |
| Induce chemical change (e.g., carbonate to oxide) | Metallurgy & Mineral Processing | Metal Ores (e.g., Carbonates) |
Ready to optimize your material processing with precise thermal treatment?
Calcination is a critical step for industries ranging from cement production to advanced materials development. KINTEK specializes in providing the robust, high-performance lab furnaces and kilns needed to achieve the perfect calcination process for your specific materials.
Whether you are refining ores, developing catalysts, or producing construction materials, our equipment ensures the purity and chemical transformation your work demands.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and discover the ideal thermal solution for your laboratory or pilot plant.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products



















