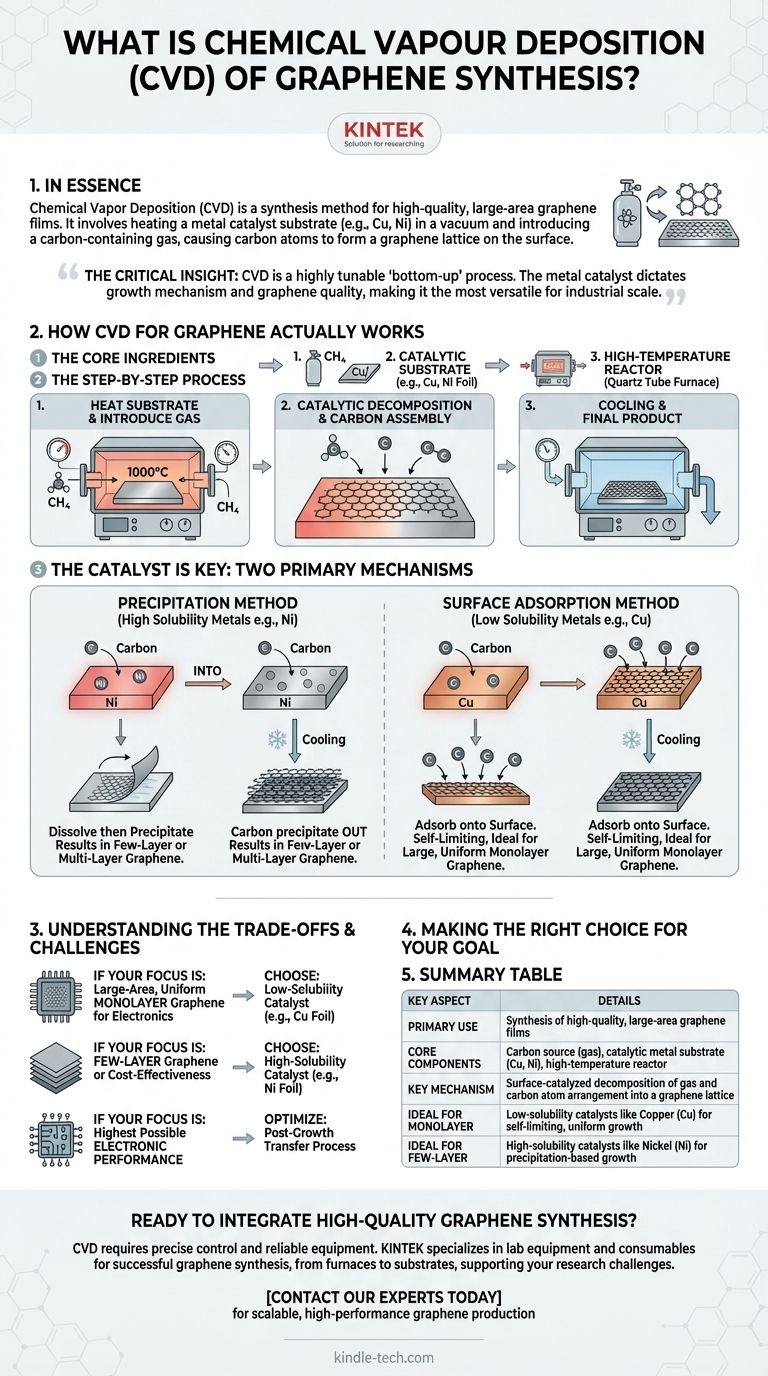
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a synthesis method used to grow high-quality, large-area films of graphene. The process involves heating a substrate, typically a transition metal foil like copper or nickel, in a vacuum chamber and introducing a carbon-containing gas. At high temperatures, the gas decomposes and the carbon atoms arrange themselves into the honeycomb lattice of graphene on the metal surface, which acts as a catalyst.
The critical insight is that CVD is not a single technique, but a highly tunable "bottom-up" process. The choice of metal catalyst fundamentally dictates the growth mechanism and, therefore, the quality and number of graphene layers produced, making it the most versatile method for industrial-scale graphene synthesis.

How CVD for Graphene Actually Works
To understand CVD, it's best to think of it as a controlled, high-temperature assembly line for atoms. The entire process hinges on creating the perfect conditions for carbon atoms to build themselves into a graphene sheet.
The Core Ingredients
The process requires three key components:
- A carbon source, which is typically a hydrocarbon gas like methane (CH₄).
- A catalytic substrate, most often a thin foil of a transition metal like copper (Cu) or nickel (Ni). This substrate provides the surface for growth and lowers the energy required for the reaction.
- A high-temperature reactor, usually a quartz tube furnace that allows for precise control of temperature, pressure, and gas flow.
The Step-by-Step Process
While specifics vary, the general steps are consistent. First, the metal substrate is heated to a high temperature (around 1000°C) inside the reactor. Then, the hydrocarbon gas is introduced.
The hot metal surface catalyzes the decomposition of the gas molecules into carbon atoms or "radicals." These active carbon atoms then diffuse and arrange themselves on the metal surface, bonding together to form the hexagonal structure of a graphene film. After the growth is complete, the system is cooled down, and the graphene film is ready for use or transfer.
The Catalyst is Key: Two Primary Mechanisms
The most important factor determining the outcome of the synthesis is the metal catalyst's ability to dissolve carbon. This leads to two distinct growth mechanisms.
The Precipitation Method (High Solubility Metals)
Metals like nickel (Ni) have a high solubility for carbon at elevated temperatures. During the process, carbon atoms from the gas first dissolve into the bulk of the hot metal, much like sugar dissolving in water.
When the system is cooled, the metal's ability to hold carbon decreases sharply. The dissolved carbon atoms then "precipitate" back out onto the surface, forming graphene layers. Because the carbon comes from the bulk metal, this process can easily lead to the formation of few-layer or multi-layer graphene and can be harder to control precisely.
The Surface Adsorption Method (Low Solubility Metals)
In contrast, metals like copper (Cu) have a very low carbon solubility. Carbon atoms do not dissolve into the metal. Instead, they adsorb directly onto the surface and arrange themselves into a graphene lattice.
This process is largely self-limiting. Once the copper surface is covered by a complete single layer of graphene, the catalytic activity of the surface is shut down, and further graphene growth stops. This makes copper the ideal substrate for producing large, uniform sheets of monolayer graphene.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While CVD is the most promising method for large-scale production, it is not without its technical hurdles. Achieving perfect results requires deep expertise and control.
The Transfer Process is Delicate
Graphene is grown on a metal foil but is almost always used on an insulating substrate, like silicon dioxide. This requires a transfer process where the metal is etched away, and the fragile, one-atom-thick graphene sheet is moved to its final destination. This step can introduce wrinkles, tears, and contamination that degrade the graphene's exceptional properties.
Quality is Not Guaranteed
The final quality of the graphene film is extremely sensitive to process parameters. Small fluctuations in temperature, gas pressure, or cooling rate can introduce defects into the crystal lattice, create unwanted multi-layer patches, or result in incomplete coverage.
Substrate Purity Matters
The cleanliness and crystal structure of the metal foil itself have a significant impact on the resulting graphene. Impurities on the substrate can act as nucleation sites for defects, disrupting the formation of a perfect, continuous sheet.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of CVD parameters should be driven entirely by the final application you have in mind for the graphene.
- If your primary focus is large-area, uniform monolayer graphene for electronics: Your best choice is a low-solubility catalyst like copper (Cu) foil to leverage its self-limiting growth mechanism.
- If your primary focus is producing few-layer graphene or cost-effectiveness is paramount: A high-solubility catalyst like nickel (Ni) can be a viable option, as the process can be less sensitive and the materials potentially cheaper.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible electronic performance: You must dedicate significant resources to optimizing the post-growth transfer process, as this is the most common source of performance-killing defects.
Ultimately, Chemical Vapor Deposition stands as the most scalable and powerful platform for engineering graphene films to meet specific demands.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Synthesis of high-quality, large-area graphene films |
| Core Components | Carbon source gas (e.g., methane), catalytic metal substrate (e.g., Cu, Ni), high-temperature reactor |
| Key Mechanism | Surface-catalyzed decomposition of gas and carbon atom arrangement into a graphene lattice |
| Ideal For Monolayer Graphene | Low-solubility catalysts like Copper (Cu) for self-limiting, uniform growth |
| Ideal For Few-Layer Graphene | High-solubility catalysts like Nickel (Ni) for precipitation-based growth |
Ready to integrate high-quality graphene synthesis into your research or production line?
The CVD process requires precise control and reliable equipment to achieve optimal results. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables essential for successful graphene synthesis, from high-temperature tube furnaces to high-purity substrates. Our expertise supports laboratories in overcoming the challenges of CVD, such as temperature control and contamination prevention.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you achieve scalable, high-performance graphene production tailored to your specific application, whether for electronics, composites, or advanced materials research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings



















