In advanced manufacturing, debinding and sintering are the two critical, sequential steps that transform a fragile, powder-based component into a solid, dense metal part. Debinding is the process of carefully removing a temporary binding agent from the molded part, and sintering is the subsequent process of heating the remaining pure powder so the particles fuse together into a strong, final object.
The core challenge in powder-based manufacturing is turning loose powder into a solid object. Debinding and sintering solve this by first using a temporary "glue" (binder) to create the shape, then removing that glue (debinding), and finally heating the material to permanently weld the powder particles together (sintering).

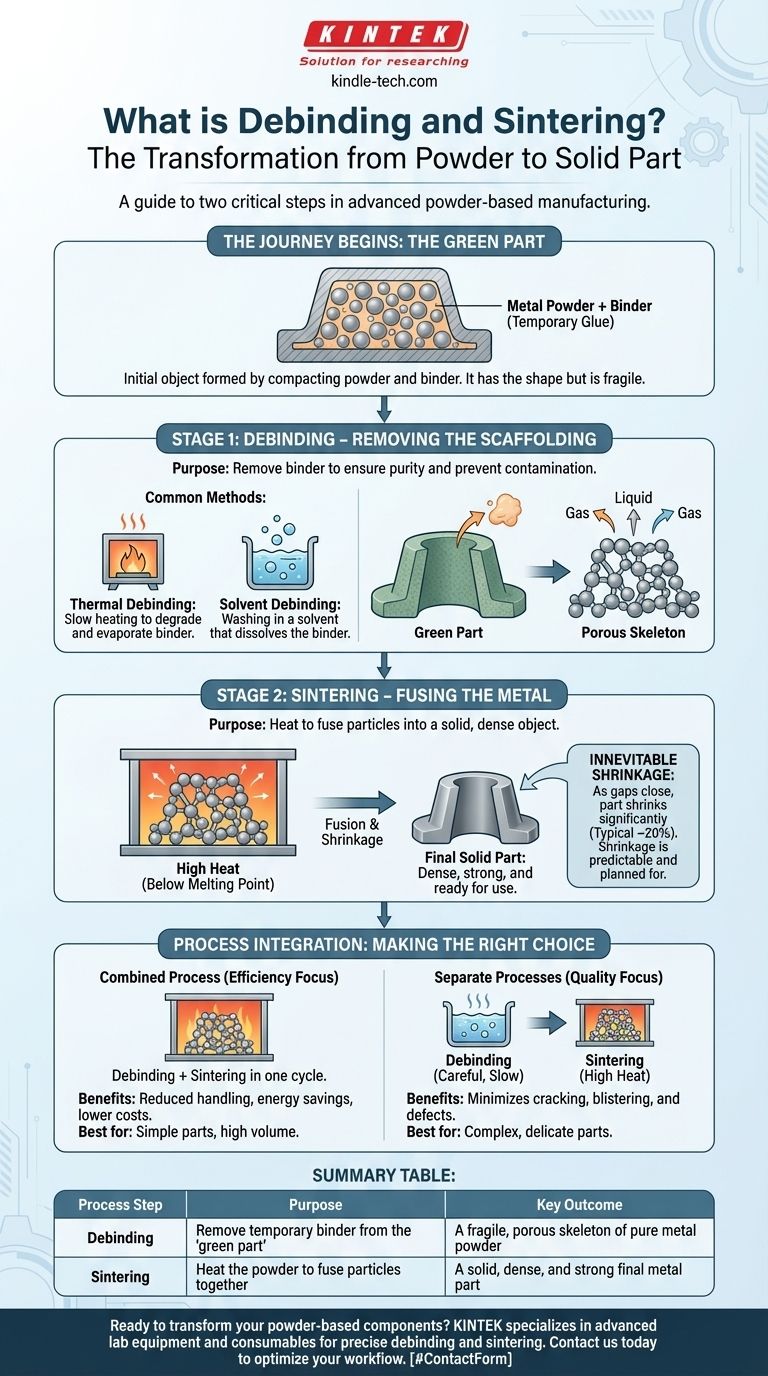
The Journey from Powder to a Solid Part
To understand debinding and sintering, you must first understand the state of the component before these processes begin. This initial component is known as a "green part."
What is a "Green Part"?
A green part is the initial object formed by compacting metal powder mixed with a binder. It has the desired shape but is mechanically weak and porous.
The binder acts as a temporary scaffold, holding the metal powder particles in place so the part can be handled without crumbling.
Why the Binder is Essential (and Temporary)
This binding agent is necessary to form the complex geometry of the part during the molding or compaction phase.
However, this same binder becomes an undesirable impurity that would interfere with creating a strong, pure metal structure. It must be removed before the final fusion step.
Stage 1: Debinding – Removing the Scaffolding
Debinding is the methodical process of removing the binder from the green part. The goal is to eliminate as much of this temporary material as possible without damaging the fragile component.
The Purpose of Debinding
Complete binder removal is critical for two reasons. First, it ensures the final sintered part is pure and structurally sound. Second, it prevents the binder from evaporating uncontrollably in the furnace, which can contaminate the equipment and ruin other parts.
Common Debinding Methods
The removal method depends entirely on the type of binder used. The most common approaches include:
- Thermal Debinding: The part is slowly heated to degrade and evaporate the binder.
- Solvent Debinding: The part is washed in a chemical solvent that dissolves the binder.
Stage 2: Sintering – Fusing the Metal
After debinding, the part is now a porous skeleton of loosely-connected metal particles. Sintering is the process that converts this fragile skeleton into a dense, solid object.
How Sintering Creates a Solid
The part is heated in a controlled-atmosphere furnace to a temperature below the metal's melting point. This high heat energizes the atoms, causing them to diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, effectively welding them together.
The Inevitable Shrinkage
As the binder is removed and the gaps between the metal particles close during sintering, the part shrinks significantly.
This shrinkage is predictable and is accounted for in the initial design of the mold. A shrinkage of around 20% is typical, though the exact value depends on the material and the specific process parameters.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Process Integration
A key decision in manufacturing is whether to perform debinding and sintering in separate steps or within a single, continuous furnace cycle.
The Case for a Combined Process
Combining both stages into one furnace cycle is a common strategy to increase efficiency. This approach reduces part handling, saves energy, and lowers equipment costs.
It is particularly effective for high-volume production where the part geometry is relatively simple and poses no specific debinding challenges.
When to Keep the Processes Separate
For highly complex or delicate parts, a separate, dedicated debinding process is often safer. It allows for slower, more precise binder removal, which minimizes the risk of the part cracking, blistering, or distorting before it gains strength in the sintering phase.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your manufacturing strategy depends on the balance between speed, cost, and final part quality.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for simple parts: A combined debind-and-sinter process is the most direct path to reducing operational overhead.
- If your primary focus is part quality for complex geometries: A separate, carefully controlled debinding step is critical to prevent defects before sintering.
- If your primary focus is final material integrity: Your process must ensure near-total binder removal to prevent the internal pores and surface flaws that compromise a part's strength.
Ultimately, mastering this two-stage transformation from a powder-and-binder mix to a solid object is fundamental to achieving high-quality, net-shape metal components.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Purpose | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Debinding | Remove temporary binder from the 'green part' | A fragile, porous skeleton of pure metal powder |
| Sintering | Heat the powder to fuse particles together | A solid, dense, and strong final metal part |
Ready to transform your powder-based components into high-performance metal parts? The precise control of debinding and sintering is critical to your success. At KINTEK, we specialize in the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to master these processes, ensuring your laboratory achieves superior material integrity and part quality. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your manufacturing workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the effect of temperature on sintering process? Mastering Thermal Control for Superior Materials
- What is the significance of using high-temperature furnaces for 12% Cr steel? Optimize Microstructure & Reduce Ferrite
- What is the study of biomass pyrolysis? Transforming Waste into Valuable Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas
- Why is a vacuum environment system necessary for SEP of CuAlMn alloys? Achieve High-Purity Porous Structures
- What are the different types of heat transfer in a furnace? Mastering Conduction, Convection & Radiation
- What is quenching in casting process? A Guide to Achieving Superior Metal Hardness
- What applications are brazing used in? Joining Metals for Aerospace, Automotive & Medical Devices
- What is quenching heat treatment on aluminum? Unlock Maximum Strength and Precision



















