At its core, metal forming with a hydraulic press is a manufacturing process that uses the immense, controlled force generated by pressurized fluid to shape, bend, or cut metal. This method is fundamental to producing a vast range of parts, especially for high-volume applications like deep drawing and stamping in the automotive industry.
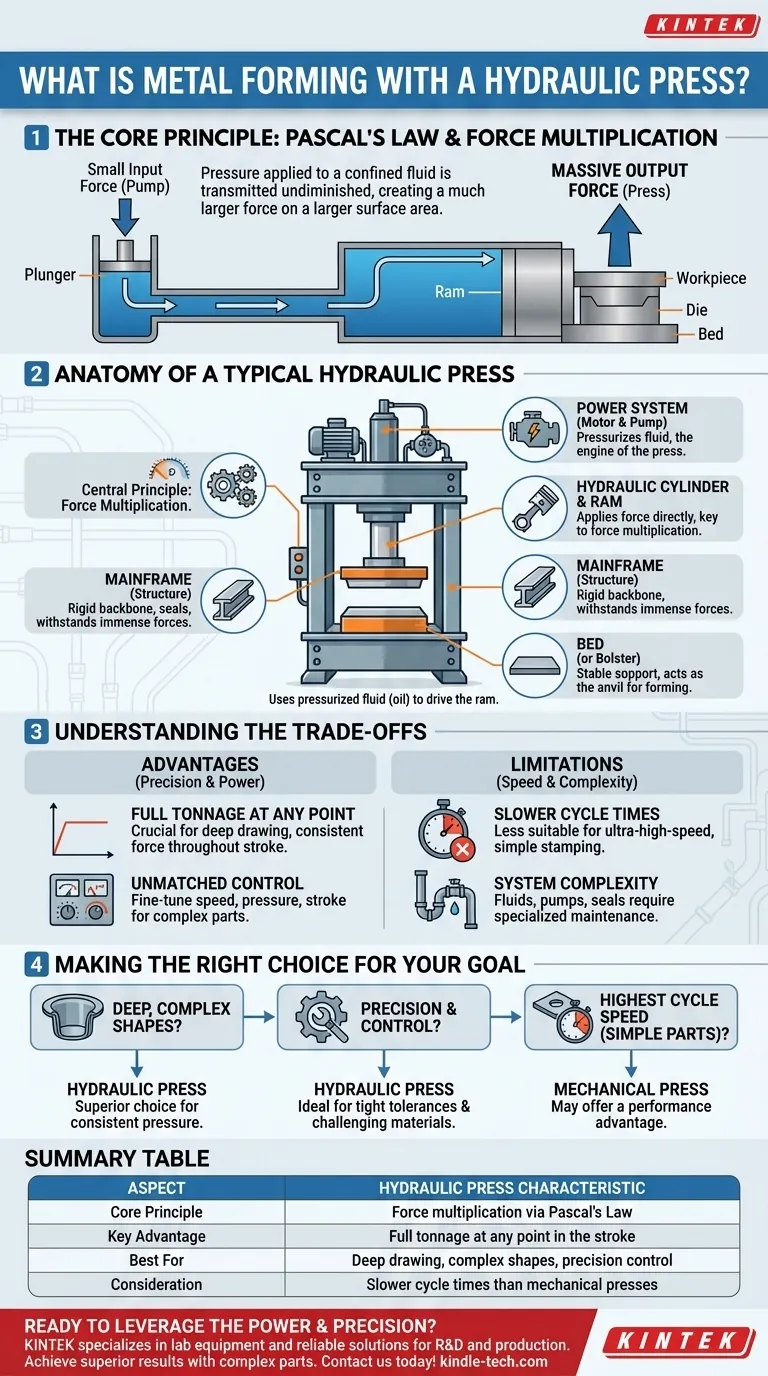
The central principle is force multiplication. A hydraulic press uses a confined, incompressible fluid—typically oil—to convert a small mechanical force from a pump into a massive, evenly applied compressive force, allowing it to reshape strong metals with precision.
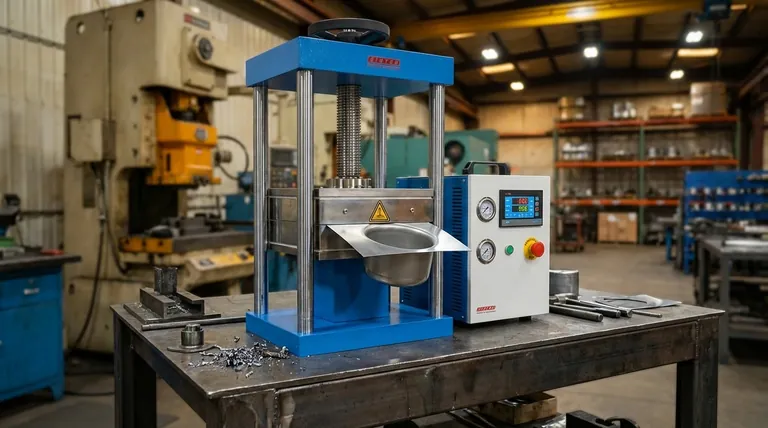

How a Hydraulic Press Achieves Force
The effectiveness of a hydraulic press comes from its ability to generate significant force from a simple and reliable mechanism based on fluid dynamics.
The Core Principle: Pascal's Law
A hydraulic system operates on Pascal's Law, which states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished throughout the fluid.
The press consists of two interconnected cylinders of different sizes: a small one called the plunger and a much larger one called the ram.
When a pump applies a small amount of force to the fluid in the plunger cylinder, it creates pressure. This same pressure acts on the larger surface area of the ram, resulting in a much larger output force.
The Role of the Pump and Fluid
The process begins with a pump, which is the power system of the press. The pump forces hydraulic fluid (oil) into the cylinder system.
This pressurized fluid is what drives the ram downward with a constant and controlled force, pressing the workpiece against a die or bed.
Anatomy of a Typical Hydraulic Press
While designs vary, nearly all hydraulic presses for metal forming share four fundamental components that work in concert.
The Mainframe
The frame is the structural backbone of the press. It must be incredibly strong and rigid to withstand the immense forces generated during operation without flexing or failing.
The Hydraulic Cylinder and Ram
The hydraulic cylinder houses the ram (or piston), which is the primary moving component that applies force directly to the workpiece. Its large surface area is key to force multiplication.
The Power System
This consists of the motor and pump responsible for pressurizing the hydraulic fluid. The power system is the engine of the press, creating the energy needed to perform the work.
The Bed (or Bolster)
The bed is the flat, stable surface that supports the die and the workpiece. It acts as the anvil against which the ram's force is applied, ensuring the metal is formed correctly and consistently.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Hydraulic presses are powerful tools, but they are not the universal solution for every metal forming task. Understanding their inherent advantages and limitations is critical.
Advantage: Full Tonnage at Any Point
Unlike a mechanical press that only delivers maximum force at the bottom of its stroke, a hydraulic press can deliver its full rated force at any point in the ram's travel. This is a crucial advantage for deep drawing processes.
Advantage: Unmatched Control
Hydraulic systems offer exceptional control over speed, pressure, and stroke length. This allows for fine-tuning the process to prevent material tearing or wrinkling, especially with complex parts.
Limitation: Slower Cycle Times
Generally, hydraulic presses have slower cycle times compared to their mechanical counterparts. This can be a drawback in extremely high-speed, high-volume stamping operations where simple parts are produced by the second.
Limitation: System Complexity
Hydraulic systems involve fluids, pumps, hoses, and seals that can be susceptible to leaks and require specialized maintenance. This can introduce more potential points of failure than a purely mechanical system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct forming method depends entirely on the requirements of the final part and the production environment.
- If your primary focus is deep, complex shapes: A hydraulic press is the superior choice due to its consistent pressure throughout the entire stroke.
- If your primary focus is precision and control: The ability to finely tune pressure and speed makes a hydraulic press ideal for parts with tight tolerances or challenging materials.
- If your primary focus is the absolute highest cycle speed for simple parts: A mechanical press may offer a performance advantage worth considering.
By understanding the fundamental principles of hydraulic force, you can effectively leverage this technology to form metal with both power and precision.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hydraulic Press Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Force multiplication via Pascal's Law |
| Key Advantage | Full tonnage at any point in the stroke |
| Best For | Deep drawing, complex shapes, precision control |
| Consideration | Slower cycle times than mechanical presses |
Ready to leverage the power and precision of a hydraulic press for your metal forming projects? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with reliable solutions. Whether you're in R&D or production, our expertise can help you achieve superior results with complex parts. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your manufacturing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- What is the advantage of KBr? Unmatched IR Transparency for Precise Spectroscopy
- What is the pellet technique in IR? Master Solid Sample Preparation for Clear Spectroscopy
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- What is the use of KBr? Master Sample Prep for Accurate IR Spectroscopy



















