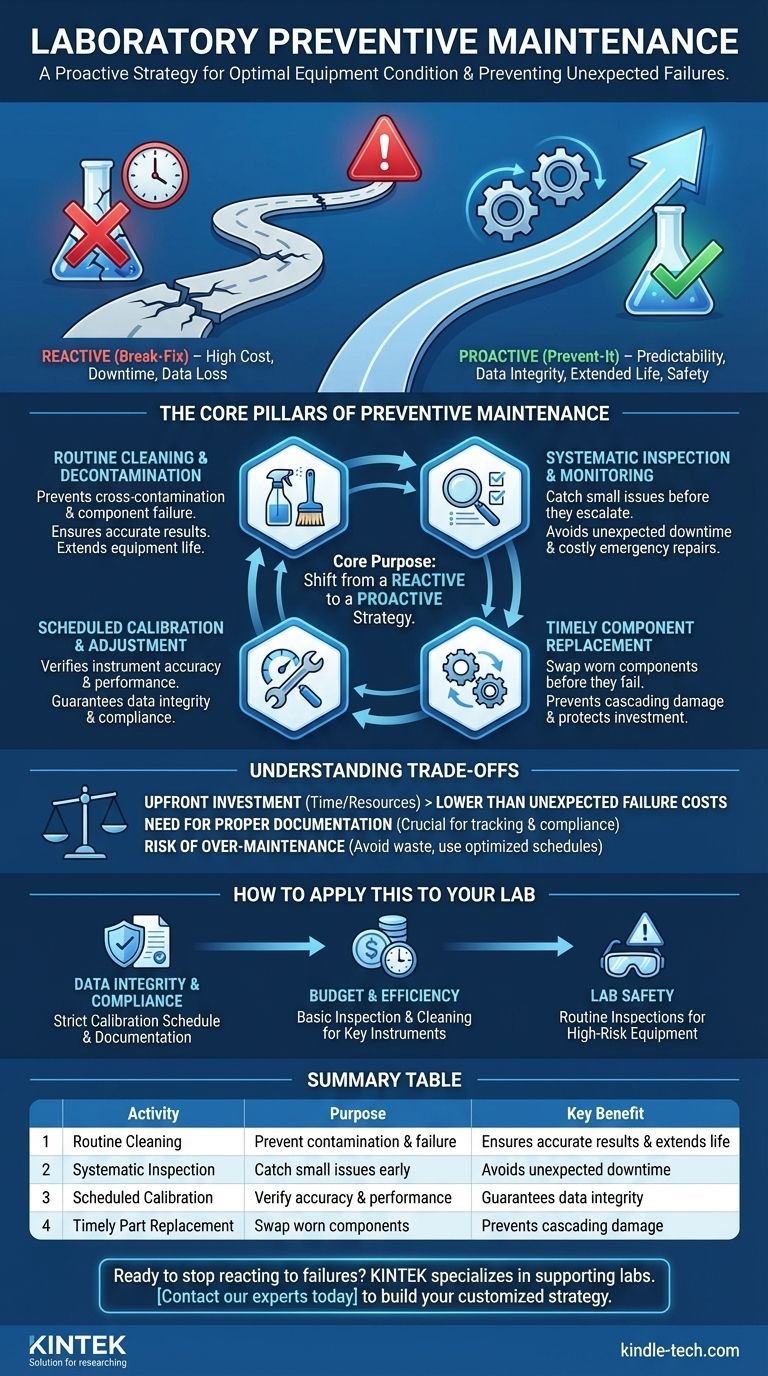
In a laboratory, preventive maintenance is a proactive strategy designed to keep equipment and instruments in optimal working condition to prevent unexpected failures. It involves a scheduled regimen of routine cleaning, inspection, calibration, and timely replacement of components that show wear. This systematic approach ensures the reliability and accuracy of your lab's most critical assets.
The core purpose of laboratory preventive maintenance is to shift from a reactive "fix-it-when-it-breaks" model to a proactive "prevent-it-from-breaking" strategy. This protects against catastrophic data loss, expensive downtime, and critical safety hazards.

The Core Pillars of a Preventive Maintenance Program
A robust preventive maintenance (PM) program is built on several key, recurring activities. It is not a one-time event but a continuous cycle of care.
Routine Cleaning and Decontamination
Proper cleaning is the first line of defense. It goes beyond simple tidiness to prevent sample cross-contamination and ensure sensitive components, like optical sensors or thermal blocks, function correctly.
A buildup of dust or chemical residue can insulate parts, cause overheating, and lead to premature failure.
Systematic Inspection and Monitoring
Regularly inspecting equipment is essential for catching small problems before they become major failures. This includes looking for signs of physical wear, listening for unusual noises, and checking for error codes or performance drifts.
This visual and functional monitoring allows you to identify a failing part and schedule a replacement on your terms, not during a critical experiment.
Scheduled Calibration and Adjustment
For a laboratory, maintenance is not just about mechanical function; it is about accuracy. Scheduled calibration verifies that an instrument is performing within its specified tolerances.
Without regular calibration as part of a PM plan, you cannot trust the data your instruments produce, invalidating results and research.
Timely Component Replacement
Many instrument components have a known, finite lifespan. A good PM program involves replacing parts like seals, filters, lamps, and electrodes based on manufacturer recommendations or observed wear, before they fail.
This avoids the cascading damage a single failed part can cause to the rest of the instrument.
From Reactive to Proactive: A Fundamental Shift
The difference between preventive and reactive maintenance is the difference between controlling your environment and being controlled by it. Many labs, as the saying goes, overlook this basic but powerful approach.
The High Cost of Reactive Maintenance
Simply waiting for equipment to break—often called "break-fix"—is a high-risk, high-cost strategy. It results in unplanned downtime, which can destroy irreplaceable samples, delay projects, and invalidate weeks of work.
Emergency repairs are almost always more expensive than planned ones and often occur at the most inconvenient times.
The Long-Term Value of Proactive Maintenance
A proactive PM program creates predictability. Maintenance is scheduled during non-critical hours, minimizing disruption to lab workflow.
This approach extends the lifespan of expensive equipment, improves the consistency and integrity of your data, and fosters a safer working environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly beneficial, implementing a preventive maintenance program is not without its own considerations. Objectivity requires acknowledging them.
The Upfront Investment
Preventive maintenance requires an investment of both time and resources. Staff must be allocated to perform the checks, and a budget is needed for stocking spare parts and potential service contracts.
This upfront cost, however, is almost always lower than the cost of unexpected failure and emergency downtime.
The Need for Proper Documentation
A PM program without meticulous records is ineffective. You must document every inspection, cleaning, calibration, and part replacement.
Without a log, you cannot track trends, prove compliance for audits, or know if the maintenance schedule is effective or needs adjustment.
The Risk of Over-Maintenance
It is possible to be too aggressive with maintenance. Replacing components far too early can be wasteful and add unnecessary cost to the program.
The goal is to find an optimized schedule based on manufacturer guidelines, instrument usage levels, and historical failure data, not to replace parts indiscriminately.
How to Apply This to Your Lab
Implementing a preventive maintenance program should be a deliberate, structured process. Start by prioritizing your most critical assets and expand from there.
- If your primary focus is data integrity and compliance: Begin by creating a strict calibration schedule and documentation procedure for all measurement-critical instruments.
- If your primary focus is budget and operational efficiency: Identify your most expensive or heavily used instruments and build a basic inspection and cleaning schedule to prevent the costliest failures.
- If your primary focus is lab safety: Immediately implement routine inspections for high-energy or high-risk equipment, such as centrifuges, autoclaves, and fume hoods.
Ultimately, a well-executed preventive maintenance program gives you control over your laboratory's operations, reliability, and results.
Summary Table:
| Activity | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Routine Cleaning | Prevent contamination & component failure | Ensures accurate results and extends equipment life |
| Systematic Inspection | Catch small issues before they become big problems | Avoids unexpected downtime and costly emergency repairs |
| Scheduled Calibration | Verify instrument accuracy and performance | Guarantees data integrity and compliance |
| Timely Part Replacement | Swap worn components before they fail | Prevents cascading damage and protects your investment |
Ready to stop reacting to equipment failures and start preventing them?
A proactive preventive maintenance plan is key to protecting your lab's productivity, data, and budget. KINTEK specializes in supporting laboratories with reliable equipment and consumables, ensuring your instruments perform at their best.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you build a customized maintenance strategy that fits your lab's unique needs and goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- 30L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 50L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
People Also Ask
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition











