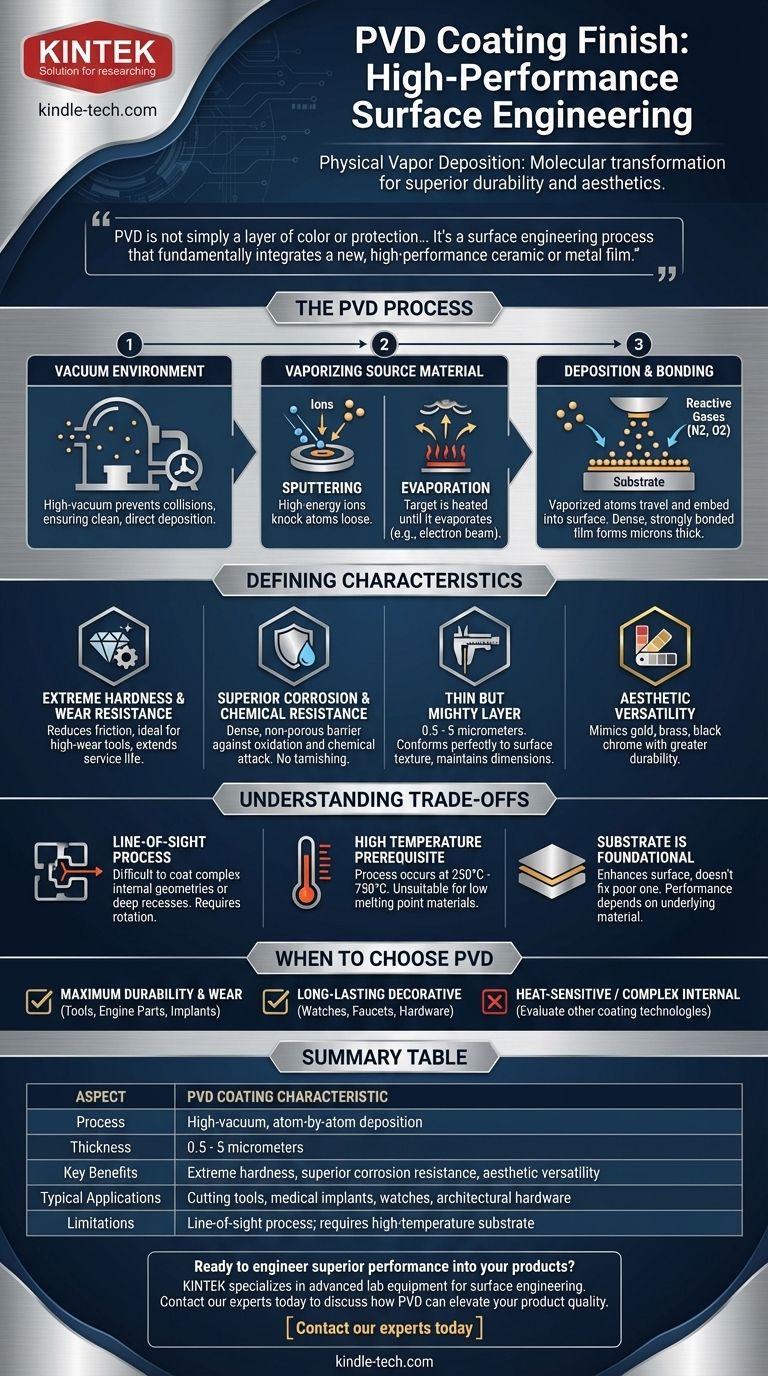
At its core, a PVD coating is a high-performance finish created through a process called Physical Vapor Deposition. In a high-vacuum chamber, a solid material is vaporized, and its molecules are then deposited atom-by-atom onto a surface, forming an extremely thin, hard, and strongly bonded layer. This isn't a wet paint or plating process; it's a molecular transformation of the object's surface.
PVD is not simply a layer of color or protection sitting on top of a product. It's a surface engineering process that fundamentally integrates a new, high-performance ceramic or metal film with the underlying material, enhancing its properties from the outside in.

How the PVD Process Works
To understand the unique qualities of a PVD finish, you must first understand the process. It is a sophisticated technique that happens within a controlled, high-tech environment.
The Vacuum Environment
The entire process takes place in a vacuum chamber. Removing nearly all the air is critical because it prevents vaporized coating particles from colliding with air molecules, ensuring a clean and direct path to the object being coated.
Vaporizing the Source Material
A solid piece of the coating material, known as the "target," is vaporized into a plasma state. This is typically achieved through one of two primary methods:
- Sputtering: The target is bombarded with high-energy ions, which physically knock atoms loose.
- Evaporation: The target is heated until it boils and evaporates, often using a cathodic arc or an electron beam.
The Deposition and Bonding
The vaporized atoms travel across the vacuum chamber and embed themselves into the surface of the component. To create specific compounds with unique properties (like titanium nitride for a gold color), reactive gases like nitrogen or oxygen are precisely introduced into the chamber. This results in a dense, strongly bonded film that is mere microns thick.
The Defining Characteristics of a PVD Finish
The unique application process gives PVD coatings a distinct set of advantages over traditional finishing methods like painting, powder coating, or electroplating.
Extreme Hardness and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings are exceptionally hard and significantly reduce friction. This makes them ideal for high-wear applications, such as cutting tools, where they can dramatically increase service life and performance.
Superior Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
The deposited film is dense and non-porous, creating a robust barrier against oxidation, corrosion, and chemical attack. A PVD-coated item will not tarnish or fade like many traditional metal finishes.
A Thin but Mighty Layer
Coatings typically range from just 0.5 to 5 micrometers. This extreme thinness means the finish conforms perfectly to the original surface texture without softening sharp edges or filling fine details. The underlying part's dimensions remain essentially unchanged.
Aesthetic Versatility
Beyond its functional benefits, PVD can produce a wide spectrum of colors and finishes. By changing the source material and reactive gases, it's possible to create finishes that mimic gold, brass, black chrome, and many other materials with far greater durability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PVD is not a universal solution. Being objective about its limitations is key to using it effectively.
It's a Line-of-Sight Process
Because the coating particles travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate, it is difficult to coat complex internal geometries or deep, hidden recesses. Parts are typically rotated on complex fixtures to ensure even coverage on all exposed surfaces.
High Temperature is a Prerequisite
The PVD process must be performed at high temperatures, often between 250°C and 750°C, to ensure proper film adhesion and structure. This makes it unsuitable for materials with low melting points, such as most plastics or certain alloys.
The Substrate is Foundational
A PVD coating enhances a surface; it does not fix a poor one. The final hardness, adhesion, and overall performance of the coating are directly dependent on the properties and preparation of the underlying substrate material.
When to Choose a PVD Finish
Selecting the right finish depends entirely on your project's specific goals. PVD excels in applications where performance cannot be compromised.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and wear resistance: PVD is the superior choice for high-performance components like industrial tools, engine parts, and medical implants.
- If your primary focus is a long-lasting decorative finish: PVD provides a far more durable and tarnish-resistant alternative to traditional plating for items like watches, faucets, and architectural hardware.
- If your primary focus is coating a heat-sensitive material or a complex internal shape: You may need to evaluate other coating technologies, as PVD's heat and line-of-sight requirements could be a limitation.
Ultimately, choosing a PVD finish is a strategic decision to engineer a surface for superior performance and longevity.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD Coating Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Process | High-vacuum, atom-by-atom deposition |
| Thickness | 0.5 - 5 micrometers (extremely thin) |
| Key Benefits | Extreme hardness, superior corrosion resistance, aesthetic versatility |
| Typical Applications | Cutting tools, medical implants, watches, architectural hardware |
| Limitations | Line-of-sight process; requires high-temperature substrate |
Ready to engineer superior performance into your products?
A PVD coating can provide the extreme durability, wear resistance, and long-lasting aesthetic appeal your application demands. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering, helping you achieve the perfect finish for your high-performance components.
Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD coating can solve your specific challenges and elevate your product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















