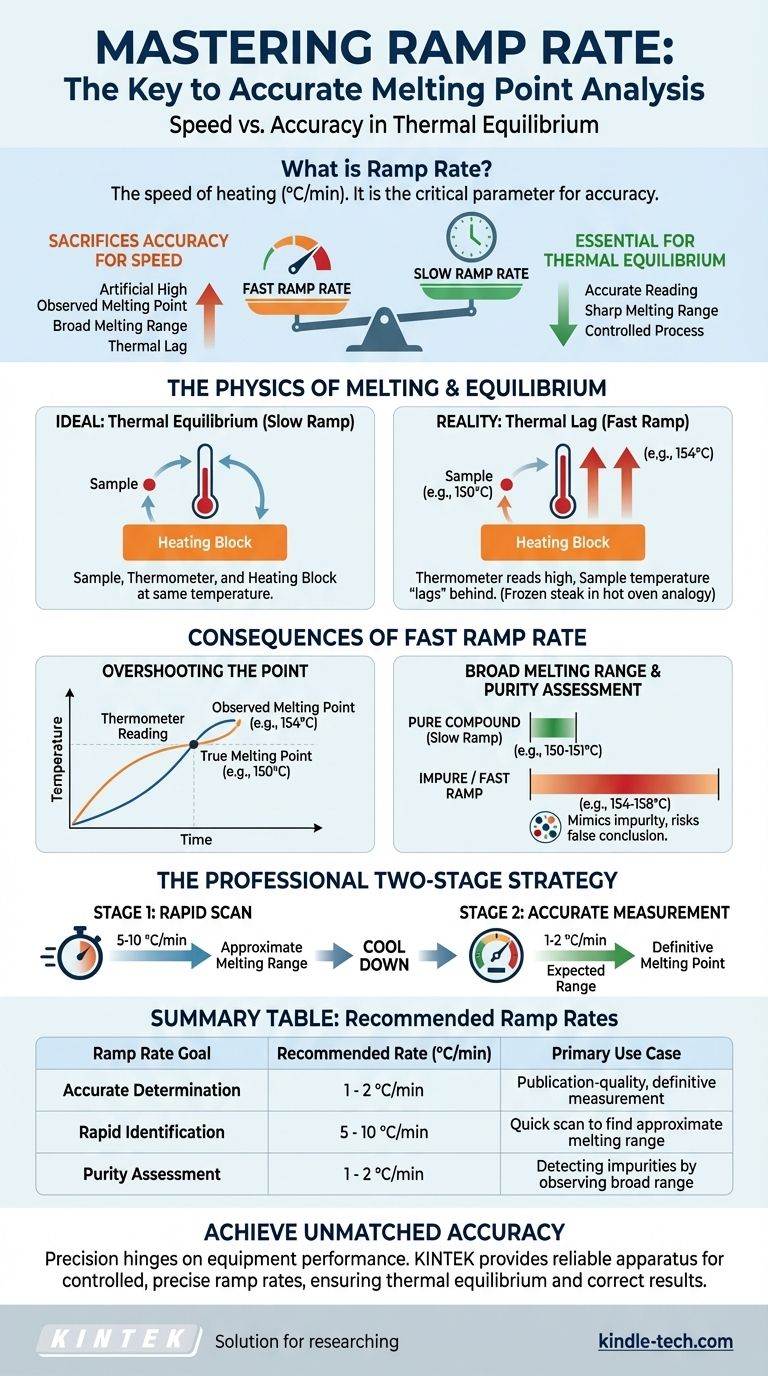
In melting point analysis, ramp rate is the speed of heating, and it is the single most critical parameter for ensuring accuracy. The ramp rate is the rate at which the temperature of the heating apparatus increases, measured in degrees Celsius per minute (°C/min). A ramp rate that is too fast will cause the observed melting point to be artificially high and the melting range to appear broader than it truly is, because the sample's temperature cannot keep up with the thermometer's reading.
The core challenge in melting point measurement is a fundamental trade-off between speed and accuracy. A slow, carefully controlled ramp rate is essential for achieving thermal equilibrium—the foundation of a correct reading—while a fast rate sacrifices this accuracy for the sake of speed.

The Physics of Melting: Why Equilibrium is Essential
To understand the impact of the ramp rate, you first need to understand the physical process of melting and the importance of thermal equilibrium.
What Happens During Melting?
Melting is a phase transition from a solid to a liquid. This process requires a specific amount of energy, known as the enthalpy of fusion.
Crucially, for a pure substance, this transition occurs at a constant temperature. The energy being added is used to break the crystal lattice structure, not to increase the kinetic energy (temperature) of the molecules.
The Concept of Thermal Equilibrium
For a melting point measurement to be accurate, the thermometer, the heating block, and the sample itself must all be at the exact same temperature at any given moment. This state is called thermal equilibrium.
If the system is not in equilibrium, the temperature you record from the thermometer will not be the actual temperature of the sample.
How a Fast Ramp Rate Breaks Equilibrium
When you heat the apparatus too quickly, the system cannot maintain thermal equilibrium. The thermometer, which measures the heating block, will report a rapidly rising temperature.
However, the sample takes time to absorb this heat. This creates a thermal lag, where the actual temperature of the sample is significantly lower than the temperature reported by the instrument.
Think of it like placing a frozen steak in a hot oven. The oven's thermostat might read 400°F, but the center of the steak remains frozen for a considerable time. The steak's temperature "lags" behind the oven's temperature.
The Practical Consequences of an Incorrect Ramp Rate
This thermal lag, caused by a fast ramp rate, leads directly to two major sources of error in your measurement.
The Error of "Overshooting"
By the time you visually observe the first drop of liquid (the onset of melting), the thermometer has already raced past the true melting point.
Because of the thermal lag, the sample is only just reaching its true melting temperature (e.g., 150 °C), but the rapidly heating thermometer might already read 154 °C. You therefore record an incorrectly high value.
An Artificially Broad Melting Range
This error continues throughout the melting process. The sample finishes melting at a temperature that is also higher than the true value.
This results in an observed melting range that is both elevated and broad (e.g., 154-158 °C) instead of sharp and accurate (e.g., 150-151 °C).
Impact on Purity Assessment
One of the primary uses of melting point is to assess the purity of a crystalline compound. Pure compounds have a sharp, narrow melting range (typically less than 2 °C). Impurities disrupt the crystal lattice, causing melting to begin at a lower temperature and occur over a wider range.
A fast ramp rate creates a broad range, mimicking the effect of an impurity. This can lead you to incorrectly conclude that a pure sample is impure, wasting time on unnecessary purification steps.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a ramp rate is a deliberate compromise between accuracy and efficiency.
The Problem with an Excessively Slow Ramp
While a very slow rate (e.g., 0.2 °C/min) yields high accuracy, it is often impractical for routine lab work.
Furthermore, some sensitive organic compounds can decompose or sublime if held at a high temperature for too long. This would also lead to an incorrect and unrepeatable reading.
The Professional Two-Stage Strategy
The most reliable method balances speed and accuracy. It involves two separate measurements:
- Rapid Scan: Use a fast ramp rate (5-10 °C/min) to get a quick, approximate melting range.
- Accurate Measurement: Cool the apparatus well below the approximate range. Then, perform a second measurement, programming a slow ramp rate of 1-2 °C/min through the expected range. This is the standard rate for accurate determination.
How to Set the Right Ramp Rate for Your Goal
Choosing the correct ramp rate depends entirely on the purpose of your measurement.
- If your primary focus is obtaining a definitive, publication-quality melting point: Always use a slow ramp rate of 1–2 °C/min through the expected melting range after a rapid pre-scan.
- If your primary focus is quickly assessing purity: A broad melting range observed even with a slow ramp rate (1–2 °C/min) is a strong indicator of an impure sample.
- If your primary focus is rapidly identifying an unknown compound: Use a fast initial ramp rate (5–10 °C/min) to find an approximate range, then repeat the measurement slowly for an accurate value to compare against known literature values.
Mastering the ramp rate transforms melting point analysis from a simple observation into a precise and reliable analytical technique.
Summary Table:
| Ramp Rate Goal | Recommended Rate (°C/min) | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Accurate Determination | 1 - 2 °C/min | Publication-quality, definitive measurement |
| Rapid Identification | 5 - 10 °C/min | Quick scan to find an approximate melting range |
| Purity Assessment | 1 - 2 °C/min | Detecting impurities by observing a broad melting range |
Achieve Unmatched Accuracy in Your Melting Point Analysis
Are inconsistent results and thermal lag errors affecting your research? The precision of your melting point measurements hinges on the performance of your equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing the reliable melting point apparatus you need for accurate, repeatable results.
Our instruments are designed to deliver the precise, controlled ramp rates essential for achieving thermal equilibrium and correct melting point determination. Stop compromising on data quality.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect melting point solution for your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why must hydrogen-charged 316L stainless steel samples be stored in liquid nitrogen? Ensure Accurate TDS Analysis
- What are the different types of sampling techniques used in IR spectroscopy? A Guide to KBr, Mull, and ATR Methods
- What copper alloy for brazing? Choose Between Phos-Copper & Silver for Strong Joints
- What frequency is used in RF sputtering? The Critical Role of 13.56 MHz
- Why you should avoid water contamination when performing FTIR measurements using NaCl or KBr plates? Protect Your Equipment & Data Integrity
- Does tensile strength increase with heat treatment? How to Engineer the Perfect Metal Properties
- Can a diamond tester tell the difference between lab grown and natural? The Truth About Diamond Identification
- Why is precise temperature and strain rate control essential in Beryllium deformation? Optimize High-Temp Characterization



















