The processes most similar to brazing are soldering and welding. While all three are used to join materials, they are fundamentally distinguished by the temperatures they use and whether or not the base materials being joined are melted. Other thermal treatments like annealing may use similar furnace equipment but serve an entirely different purpose.
The core distinction between soldering, brazing, and welding lies in a simple principle: welding melts the base materials to fuse them, while brazing and soldering use a lower-temperature filler metal to act as a glue without melting the base materials.
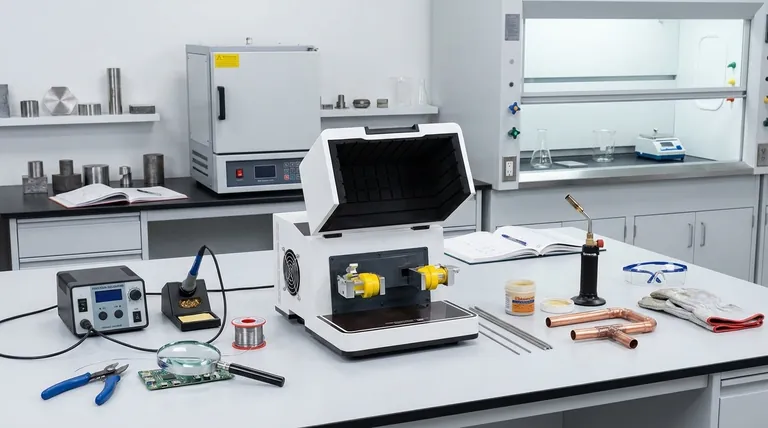

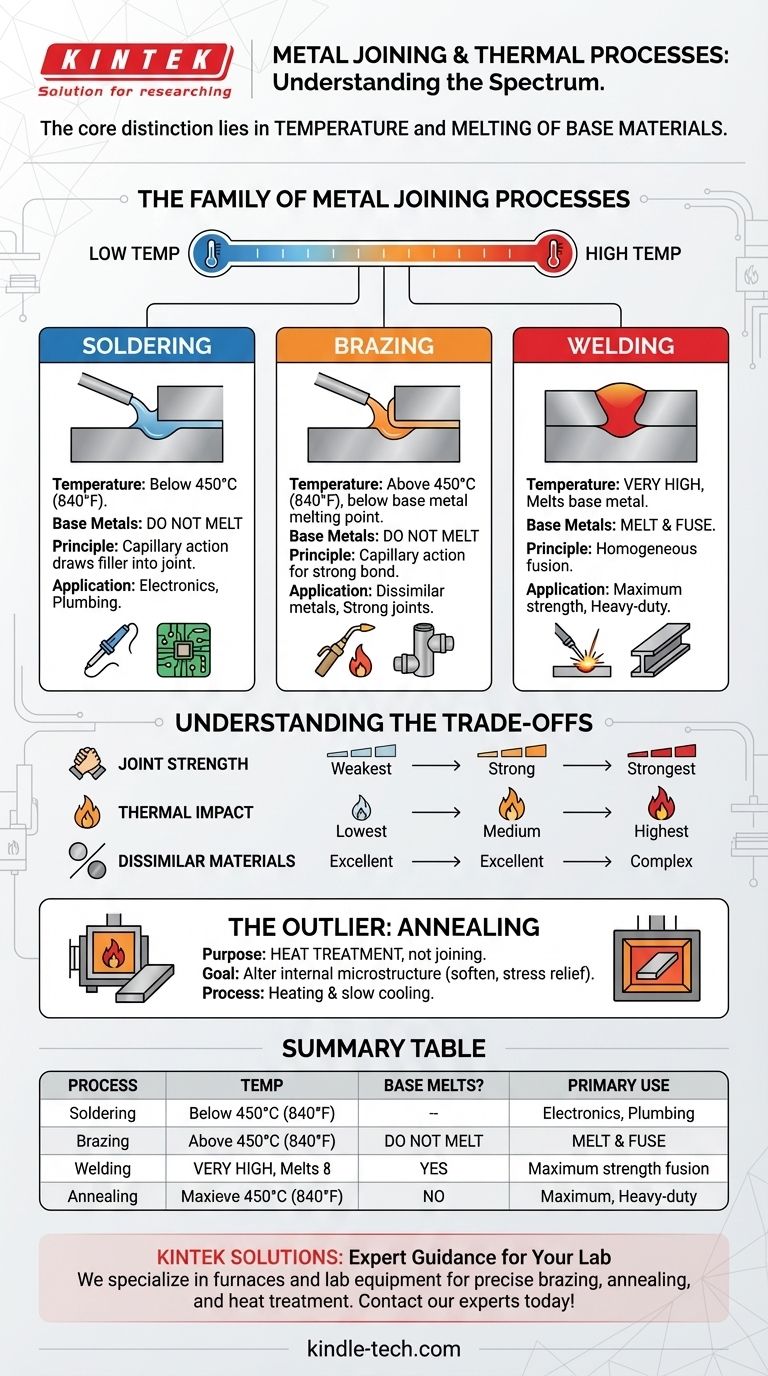
The Family of Metal Joining Processes
To understand brazing, you must see it as part of a spectrum of thermal joining techniques. The primary difference is heat. Each process occupies a distinct temperature range, which dictates its applications and outcomes.
Soldering: The Low-Temperature Bond
Soldering is the lowest-temperature process of the three. It involves melting a filler metal (solder) at a temperature below 450°C (840°F) to join two or more metal items.
The base metals are heated, but they never reach their melting point. The molten solder is drawn into the joint between the parts by capillary action, creating a solid bond once it cools. This is the common method for joining electronic components.
Brazing: The Mid-Temperature Bond
Brazing occupies the middle ground. It functions exactly like soldering but at higher temperatures, using a filler metal that melts above 450°C (840°F).
Crucially, this temperature is still below the melting point of the base materials. Like soldering, brazing relies on capillary action to draw the filler metal into a tight-fitting joint, resulting in a bond that is typically much stronger than a soldered one.
Welding: The High-Temperature Fusion
Welding is the hottest and most distinct process. Its goal is to melt the base metals themselves, causing them to fuse together directly, often with the addition of a filler material.
Because the base materials are melted and fused, welding creates a continuous, homogenous joint. This typically results in the strongest possible connection, essentially making the two pieces of metal one.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these methods involves clear trade-offs in strength, thermal impact, and material compatibility. Mistaking one for another can lead to project failure.
Joint Strength and Integrity
Welding produces the strongest joints, as the base metals are fused. Brazing creates a very strong bond that is often stronger than the filler metal itself, but weaker than a welded joint. Soldering produces the weakest joint of the three, suitable for lighter-duty applications.
Thermal Impact on Base Metals
The intense heat of welding can alter the mechanical properties of the base metals in the "heat-affected zone," sometimes requiring post-weld heat treatment. Brazing uses less heat, minimizing this distortion and impact. Soldering has the lowest thermal impact, making it ideal for delicate electronic components.
Joining Dissimilar Materials
Brazing and soldering excel at joining dissimilar materials (e.g., copper to steel). Because the base metals don't melt, compatibility issues are far less of a concern. Welding dissimilar metals is possible but is a much more complex metallurgical challenge.
Other Thermal Processes: The Case of Annealing
While processes like annealing may use the same controlled-atmosphere furnaces as brazing, their purpose is entirely different.
The Purpose of Annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment process, not a joining process. It involves heating a material to a specific temperature and then cooling it slowly. The goal is not to join parts, but to alter the material's internal microstructure—typically to make it softer, more ductile, and less brittle.
Joining vs. Treating
Think of it this way: brazing, soldering, and welding are like glue or cement, connecting separate components. Annealing is like tempering chocolate or steel, changing the properties of a single, existing component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's requirements should dictate the correct process.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and a single homogenous joint: Welding is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar or heat-sensitive metals without melting them: Brazing offers a strong, reliable bond with less thermal distortion.
- If your primary focus is joining delicate electronics or plumbing at low temperatures: Soldering provides a sufficient bond with minimal risk to the components.
- If your primary focus is to soften a metal or relieve internal stress: Annealing is the correct heat treatment process to modify the material's properties.
Ultimately, understanding the role of temperature and its effect on the base material is the key to selecting the right technique for the job.
Summary Table:
| Process | Temperature Range | Base Metal Melts? | Primary Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soldering | Below 450°C (840°F) | No | Electronics, plumbing, delicate joints |
| Brazing | Above 450°C (840°F) | No | Strong joints, dissimilar metals, minimal distortion |
| Welding | Very High (melts base metal) | Yes | Maximum strength, homogeneous fusion |
| Annealing | Varies by material | No | Softening metal, stress relief (heat treatment) |
Need expert guidance on thermal processing equipment for your lab? KINTEK specializes in furnaces and lab equipment for brazing, annealing, and other heat treatment processes. Our solutions ensure precise temperature control and reliable results for your metal joining and material science applications. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
People Also Ask
- Why is grinding important in sample preparation? Ensure Accurate & Reliable Analytical Results
- What are the different types of grinding mills? Match the Mechanism to Your Material for Optimal Size Reduction
- Why grinding is important in laboratory techniques? Ensure Accurate & Reproducible Results
- How much balls should be loaded in a ball mill for working? Optimize Grinding with the Correct Ball Charge
- What are the five methods of synthesis of nanoparticles? A Guide to Top-Down & Bottom-Up Approaches



















