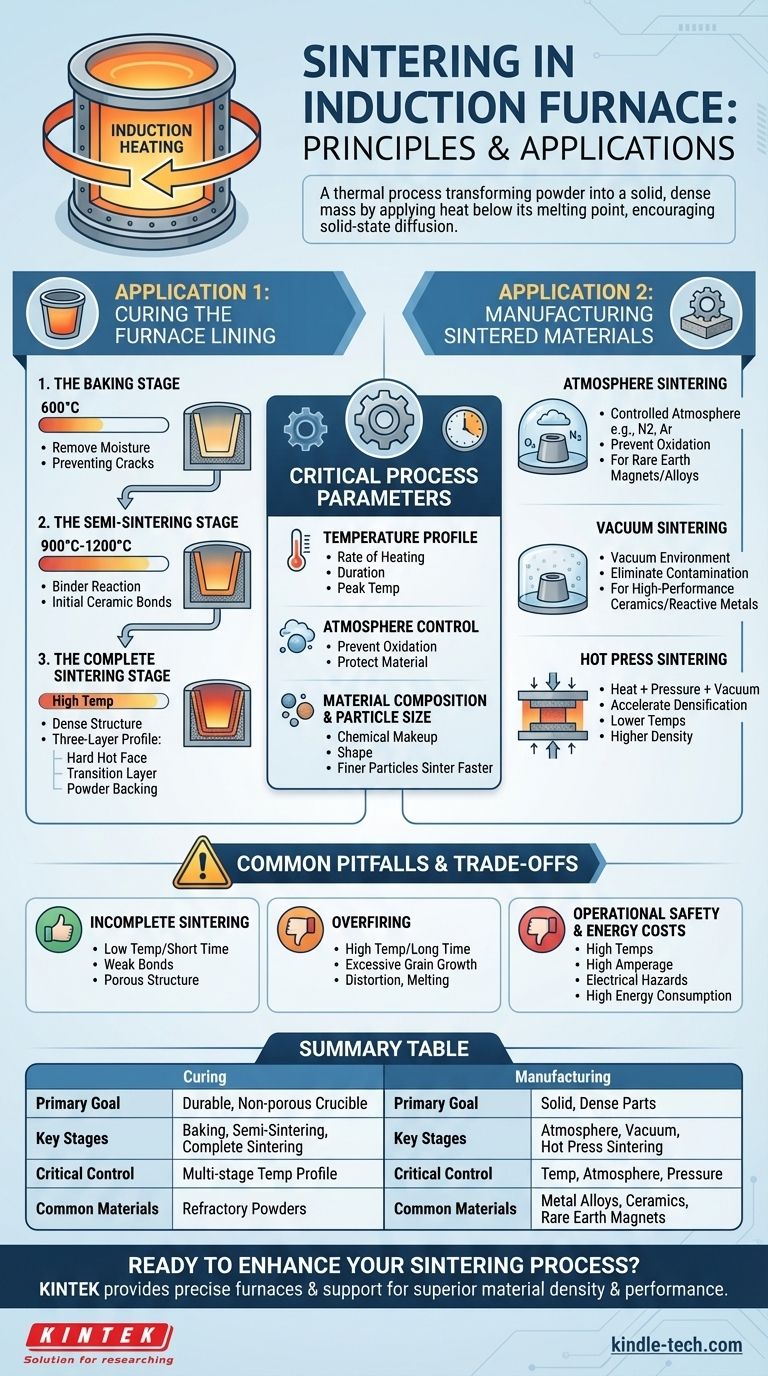
At its core, sintering is a thermal process used to transform a powder into a solid, dense mass by applying heat below its melting point. In the context of an induction furnace, this term refers to two distinct but related applications: first, the critical process of curing the furnace's own refractory lining, and second, using the furnace as a heat source to manufacture sintered parts from various powdered materials.
Sintering is not simply about high heat; it is a precisely controlled transformation. Success hinges on managing temperature, time, and atmosphere to encourage solid-state diffusion, which bonds individual particles together into a strong, unified structure without actually melting the material.

The Two Primary Applications of Sintering
The phrase "sintering in an induction furnace" can be ambiguous. It is crucial to distinguish whether you are preparing the furnace itself for operation or using a specialized induction furnace to create a product.
Application 1: Curing the Furnace Lining
This is the most common meaning when discussing the setup of a standard induction melting furnace. The lining, typically a dry refractory powder, must be sintered to form a solid, non-porous, and durable crucible.
A properly sintered lining is essential for the furnace's safety and service life. The process is methodical and follows distinct stages.
The Baking Stage The furnace is heated slowly to a low temperature, typically around 600°C. The primary goal is to gently drive off all residual moisture from the refractory material, which could otherwise turn to steam and cause cracks or spalling.
The Semi-Sintering Stage Temperature is increased further, often to a range of 900°C to 1200°C. At this point, the binder agents in the refractory mix begin to react, and the initial ceramic bonds start to form between particles, creating a semi-rigid structure.
The Complete Sintering Stage The furnace is brought to its final, high sintering temperature. This temperature is carefully chosen based on the refractory material's specifications. Holding at this temperature allows for the formation of a dense, strong ceramic structure with a desired three-layer profile: a hard, fully sintered "hot face" on the inside, a semi-sintered transition layer, and a loose powder backing for insulation.
Application 2: Manufacturing Sintered Materials
Induction heating is also a core technology in specialized furnaces designed specifically for sintering powdered materials into finished or near-finished parts. In this case, the induction coil heats a crucible or the material itself.
These furnaces offer precise control and are used for advanced materials.
Atmosphere Sintering The process is conducted under a controlled atmosphere (e.g., nitrogen, argon) to prevent oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions. This is vital for materials like rare earth magnets or certain metal alloys.
Vacuum Sintering By performing the process in a vacuum, any risk of contamination from atmospheric gases is eliminated. This improves the purity and performance of the final product and is common for high-performance ceramics and reactive metals.
Hot Press Sintering This advanced method combines heat (often from induction) with high mechanical pressure in a vacuum. The pressure physically forces the particles together, accelerating densification and allowing for sintering at lower temperatures or achieving higher final densities.
Understanding the Critical Process Parameters
Successful sintering is a science that depends on the careful management of several key variables, regardless of the application.
The Temperature Profile
Sintering is defined by its temperature profile—the rate of heating, the duration of holds (or "soaks"), and the final peak temperature. This profile is meticulously designed based on the material's composition and desired final properties. It must be hot enough to promote diffusion but remain safely below the melting point.
Atmosphere Control
The environment inside the furnace is critical. An uncontrolled atmosphere can lead to oxidation, which weakens the bonds between particles. Controlled atmospheres or vacuums are used to protect the material and ensure the integrity of the final product.
Material Composition and Particle Size
The chemical makeup and the size and shape of the initial powder particles heavily influence how the material will sinter. Finer particles generally sinter faster and at lower temperatures due to their higher surface area.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Achieving a perfect sinter requires balancing competing factors and avoiding common mistakes.
The Risk of Incomplete Sintering
If the temperature is too low or the hold time is too short, the bonds between particles will be weak. This results in a porous, low-density structure. For a furnace lining, this means a drastically reduced service life and a higher risk of metal penetration and catastrophic failure.
The Danger of Overfiring
Exceeding the optimal sintering temperature or holding it for too long can be just as damaging. This can cause excessive grain growth, part distortion, or even localized melting. The resulting material often has poor mechanical properties despite being dense.
Operational Safety and Energy Costs
Sintering furnaces operate at extremely high temperatures for extended periods, consuming significant energy and requiring robust safety protocols. The high amperage used in induction systems presents its own set of electrical hazards that must be professionally managed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to sintering should be dictated entirely by your end objective.
- If your primary focus is furnace installation and maintenance: Your goal is maximum lining durability. Follow the refractory manufacturer's recommended multi-stage heating schedule without deviation to ensure a fully cured, resilient crucible.
- If your primary focus is materials production: Your goal is achieving specific material properties. Invest in a system with precise control over temperature, atmosphere, and (if needed) pressure to create repeatable, high-quality components.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about using controlled thermal energy to transform loose powder into a high-performance, structurally sound component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Curing a Furnace Lining | Manufacturing Sintered Parts |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Create a durable, non-porous crucible for melting | Produce solid, dense parts from powdered materials |
| Key Stages | Baking, Semi-Sintering, Complete Sintering | Atmosphere Sintering, Vacuum Sintering, Hot Press Sintering |
| Critical Control | Multi-stage temperature profile | Temperature, atmosphere, and pressure |
| Common Materials | Refractory powders | Metal alloys, ceramics, rare earth magnets |
Ready to enhance your sintering process?
Whether you are setting up a new induction furnace or optimizing your materials production, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables is your key to success. We provide the precise, reliable furnaces and support you need to achieve superior material density and performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how our solutions can drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- Why is environmental control within a vacuum furnace important for diffusion bonding? Master Titanium Alloy Laminates
- What are the defects in sintered parts? Avoid Warping, Cracking, and Porosity Issues



















