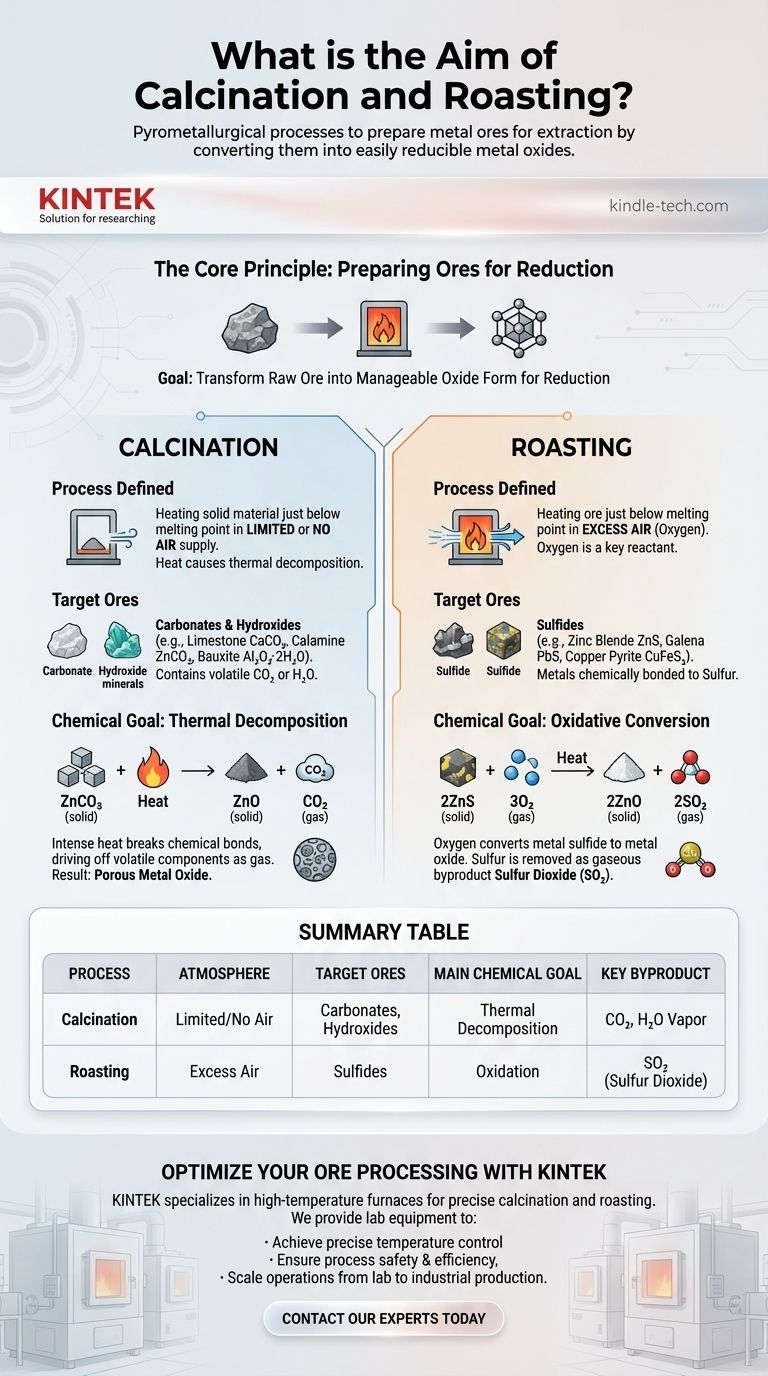
In short, calcination and roasting are pyrometallurgical processes designed to prepare metal ores for extraction. Both use high heat to convert ores into metal oxides, a chemical form that is much easier to reduce into a pure metal. Calcination achieves this by thermally decomposing the ore in limited or no air, while roasting uses an excess of air to oxidize the ore.
The core distinction lies in the type of ore being treated. Calcination is for ores that decompose with heat alone, like carbonates and hydroxides. Roasting is for ores that require oxygen to be converted, primarily sulfides.
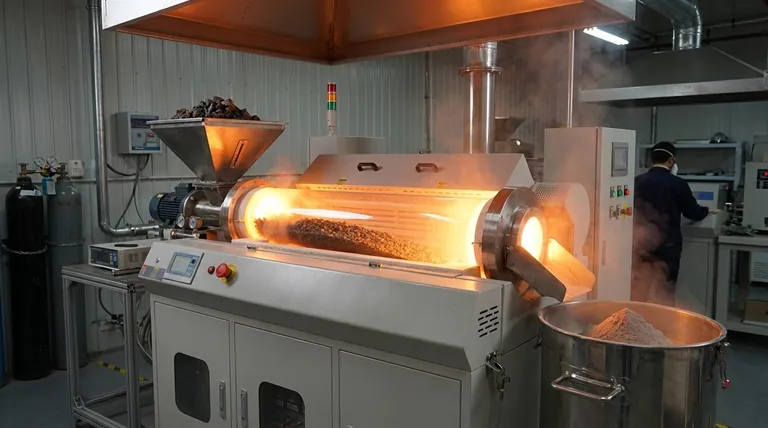

The Core Principle: Preparing Ores for Reduction
The ultimate goal of metallurgy is to extract a pure metal from its naturally occurring ore. Most ores, such as carbonates (like limestone) or sulfides (like zinc blende), are not easily converted directly into metal.
However, metal oxides are readily "reduced" to their metallic form, often by reacting them with carbon (coke) in a high-temperature furnace. Therefore, both calcination and roasting serve as a crucial pre-treatment step: to transform the raw ore into this more manageable oxide form.
Understanding Calcination
The Process Defined
Calcination involves heating a solid material to a high temperature, just below its melting point, in the complete absence or a very limited supply of air.
The heat itself is the primary agent of change, causing the material to break down without burning.
The Target Ores
This process is ideal for carbonate and hydroxide ores. These ores contain volatile components like carbon dioxide (CO₂) or water (H₂O) chemically bonded within their structure.
Common examples include limestone (CaCO₃), calamine (ZnCO₃), and bauxite (Al₂O₃·2H₂O).
The Chemical Goal: Thermal Decomposition
The aim of calcination is thermal decomposition. The intense heat breaks the chemical bonds in the ore, driving off volatile components as gas.
For a carbonate ore like zinc carbonate, the reaction is simple:
ZnCO₃ (solid) + Heat → ZnO (solid) + CO₂ (gas)
The result is a solid, porous metal oxide (zinc oxide) ready for the next stage of reduction.
Understanding Roasting
The Process Defined
Roasting involves heating an ore to a high temperature, also below its melting point, but in the presence of an excess supply of air (oxygen).
Unlike calcination, oxygen is a key reactant in the process.
The Target Ores
Roasting is the standard method for processing sulfide ores. These ores contain valuable metals chemically bonded to sulfur.
Famous examples include zinc blende (ZnS), galena (PbS), and copper pyrite (CuFeS₂).
The Chemical Goal: Oxidative Conversion
The aim of roasting is to use oxygen from the air to convert the metal sulfide into a metal oxide. Sulfur is removed as a gaseous byproduct, sulfur dioxide (SO₂).
For a sulfide ore like zinc blende, the reaction is:
2ZnS (solid) + 3O₂ (gas) + Heat → 2ZnO (solid) + 2SO₂ (gas)
This reaction replaces the sulfur with oxygen, again producing the desired metal oxide (zinc oxide).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Differences
Air Supply: The Defining Factor
The most critical difference is the atmosphere inside the furnace.
Calcination requires the exclusion of air to ensure the ore simply decomposes. Roasting requires an abundance of air to provide the oxygen needed for the oxidation reaction.
Byproduct Management
The byproducts of each process are fundamentally different and have distinct environmental and economic implications.
Calcination primarily produces carbon dioxide (CO₂) or water vapor, which are relatively benign. Roasting produces sulfur dioxide (SO₂) a major air pollutant responsible for acid rain. Modern smelters must capture this SO₂, which is often used to manufacture sulfuric acid, turning a harmful waste product into a valuable commodity.
Why Not Just Calcine a Sulfide Ore?
Heating a sulfide ore without air (calcination) would not effectively remove the sulfur or convert it to an oxide. The process relies on oxygen to break the metal-sulfur bond and form the more stable metal-oxygen bond.
Selecting the Correct Pre-treatment Process
Choosing between calcination and roasting is not a matter of preference but a chemical necessity dictated by the composition of the ore.
- If your primary focus is processing a carbonate or hydroxide ore: Use calcination to thermally decompose the ore and drive off carbon dioxide or water.
- If your primary focus is processing a sulfide ore: Use roasting to oxidize the ore with excess air, converting it to a metal oxide and removing sulfur as sulfur dioxide.
Matching the correct pyrometallurgical process to the specific ore chemistry is the foundational step for efficient and successful metal extraction.
Summary Table:
| Process | Atmosphere | Target Ores | Main Chemical Goal | Key Byproduct |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Limited/No Air | Carbonates, Hydroxides | Thermal Decomposition | CO₂, H₂O Vapor |
| Roasting | Excess Air | Sulfides | Oxidation | SO₂ (Sulfur Dioxide) |
Optimize Your Ore Processing with KINTEK
Understanding the correct pre-treatment process is the first step to efficient metal extraction. KINTEK specializes in supplying the robust, high-temperature furnaces required for precise calcination and roasting operations.
We provide the essential lab equipment and consumables to help you:
- Achieve precise temperature control for effective thermal decomposition or oxidation.
- Ensure process safety and efficiency, whether you're working with carbonates or sulfides.
- Scale your operations from laboratory research to industrial production.
Ready to enhance your pyrometallurgical processes? Contact our experts today to discuss the perfect furnace solution for your specific ore chemistry and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process



















