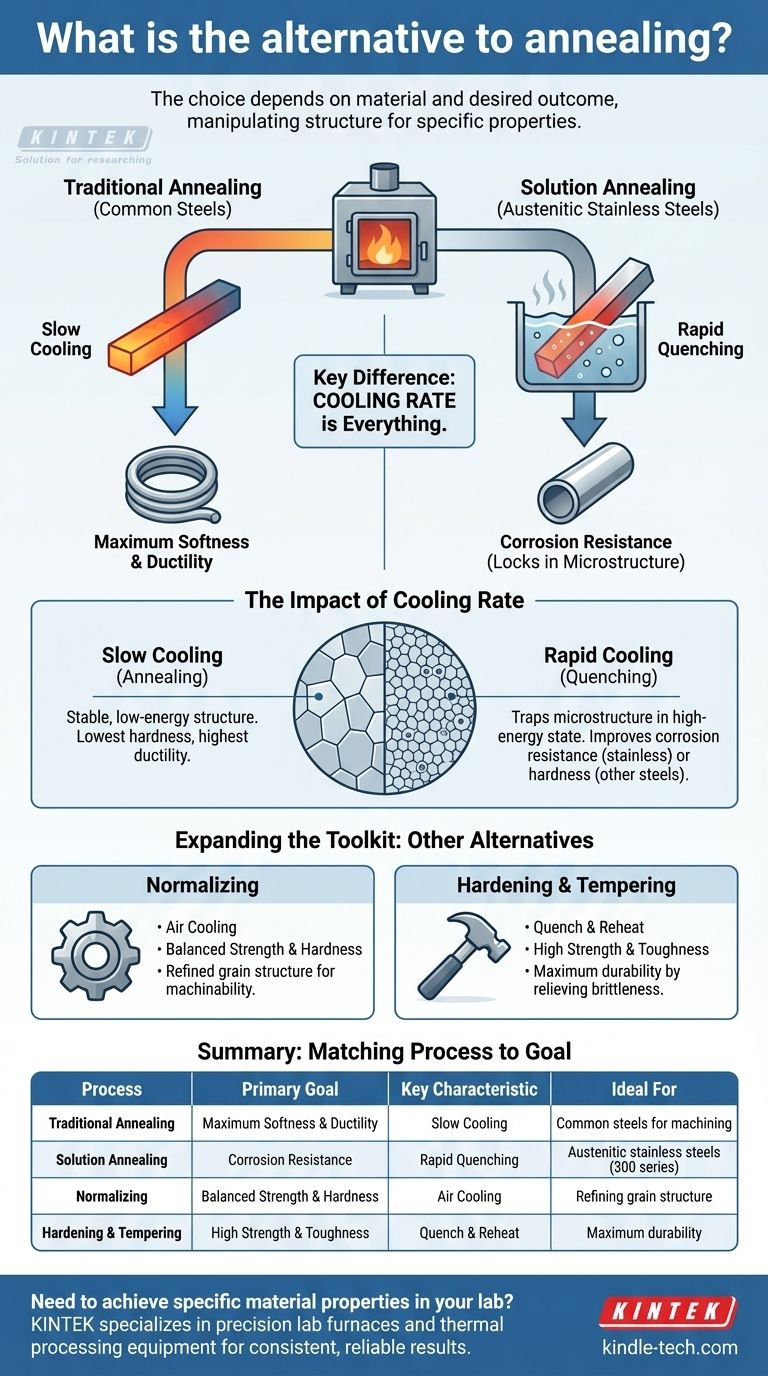
When seeking an alternative to traditional annealing, the correct process depends entirely on your material and your desired outcome. For austenitic stainless steels, the key alternative is solution annealing, a specific heat treatment designed to enhance corrosion resistance and ductility by dissolving harmful precipitates. While both involve heating, their critical difference lies in the cooling phase: traditional annealing uses slow cooling to maximize softness, whereas solution annealing uses rapid cooling to lock in a specific, corrosion-resistant microstructure.
The choice between annealing and its alternatives is not about finding a substitute, but about selecting the precise thermal process that will manipulate a metal's internal structure to achieve a specific set of properties, whether that be maximum softness, corrosion resistance, or strength.

The Goal of Heat Treatment: Manipulating Material Structure
Heat treatment is the controlled heating and cooling of metals to alter their physical and mechanical properties without changing their shape. It is a metallurgical tool used to change a material's microstructure—the arrangement of its crystalline phases.
By carefully managing temperature, time, and cooling rates, you can make a metal softer, harder, tougher, or more resistant to corrosion. The process you choose is a direct function of the result you need.
Differentiating Key Processes: Annealing vs. Solution Annealing
While both are heat treatments, their objectives and methods are distinct, particularly concerning the cooling rate. This distinction is critical for achieving the desired properties in different alloys.
Traditional Annealing: The Goal is Maximum Softness
The primary purpose of a full anneal is to return a metal to its softest, most ductile state. This is often done to make a material easier to machine or form.
The process involves heating the metal above its critical temperature, holding it there to ensure the structure is uniform, and then cooling it very slowly. This slow cooling allows the microstructure to re-form into its most stable, low-energy, and stress-free state.
Solution Annealing: The Goal is Corrosion Resistance
Solution annealing is a specialized process used almost exclusively for austenitic stainless steels (like the 300 series). Its main goal is to improve corrosion resistance, with a secondary benefit of softening the material.
It involves heating the steel to a high temperature (typically 900–1100 °C) to dissolve any chromium carbide precipitates back into the metal's matrix. This is followed by rapid cooling (quenching), which "freezes" the carbon and chromium in solution, preventing the harmful carbides from re-forming. These carbides, if present, reduce the steel's ability to resist corrosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cooling Rate is Everything
The single most important variable that separates annealing from its alternatives is the rate of cooling. This single factor dictates the final microstructure and, therefore, the material's properties.
The Impact of Slow Cooling
Slow cooling, the hallmark of traditional annealing, gives the metal's atoms ample time to arrange themselves into the most stable and orderly crystal structure possible.
This results in a material with the lowest hardness, lowest internal stress, and highest ductility. It is the ideal state for subsequent cold working or machining operations.
The Impact of Rapid Cooling (Quenching)
Rapid cooling, used in solution annealing, traps the microstructure in a less stable, higher-energy state. For stainless steel, this is beneficial because it keeps chromium dissolved, preventing the formation of carbides that lead to corrosion.
This same principle of rapid cooling is used in hardening other steels, where it traps carbon to create a very hard but brittle structure known as martensite. This demonstrates that the effect of quenching is highly dependent on the specific alloy being treated.
Expanding the Toolkit: Other Common Alternatives
Beyond solution annealing, other heat treatments serve as alternatives to traditional annealing when different properties are required.
Normalizing
Normalizing involves heating a steel above its critical temperature and then letting it cool in open air. This cooling rate is faster than annealing but slower than quenching.
The result is a material that is stronger and harder than an annealed steel but still possesses good ductility. It's often used to refine the grain structure and improve machinability for certain applications.
Hardening and Tempering
This is a two-step process used to achieve high strength combined with good toughness. The part is first heated and then rapidly quenched to make it extremely hard but also brittle.
It is then tempered—reheated to a lower temperature—to relieve some of the internal stress and reduce brittleness, resulting in a tough, durable, and hard final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal process requires a clear diagnosis of your material and your objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing softness and relieving stress in common steels: Traditional annealing, with its characteristic slow cooling cycle, is the correct and standard procedure.
- If your primary focus is improving corrosion resistance and ductility in austenitic stainless steel: Solution annealing, defined by its high heat and subsequent rapid quench, is the specific and necessary process.
- If your primary focus is achieving a balance of strength and hardness, rather than pure softness: You should investigate normalizing (for a stronger-than-annealed state) or a full hardening and tempering cycle (for maximum strength and toughness).
Ultimately, selecting the right thermal process is about matching the treatment's unique outcome to your specific engineering requirement.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Goal | Key Characteristic | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Annealing | Maximum Softness & Ductility | Slow Cooling | Common steels for machining/forming |
| Solution Annealing | Corrosion Resistance | Rapid Quenching | Austenitic stainless steels (300 series) |
| Normalizing | Balanced Strength & Hardness | Air Cooling | Refining grain structure |
| Hardening & Tempering | High Strength & Toughness | Quench & Reheat | Maximum durability |
Need to achieve specific material properties in your lab?
Choosing the correct heat treatment process is critical for your project's success. Whether you require maximum softness, superior corrosion resistance, or enhanced strength, the right equipment is essential.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment, helping laboratories like yours achieve consistent, reliable results. Our solutions are designed for the exacting demands of material science and metallurgy.
Let our experts help you select the ideal furnace for your heat treatment needs. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and discover how our equipment can enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What are the parts of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to the 5 Core Systems
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering



















