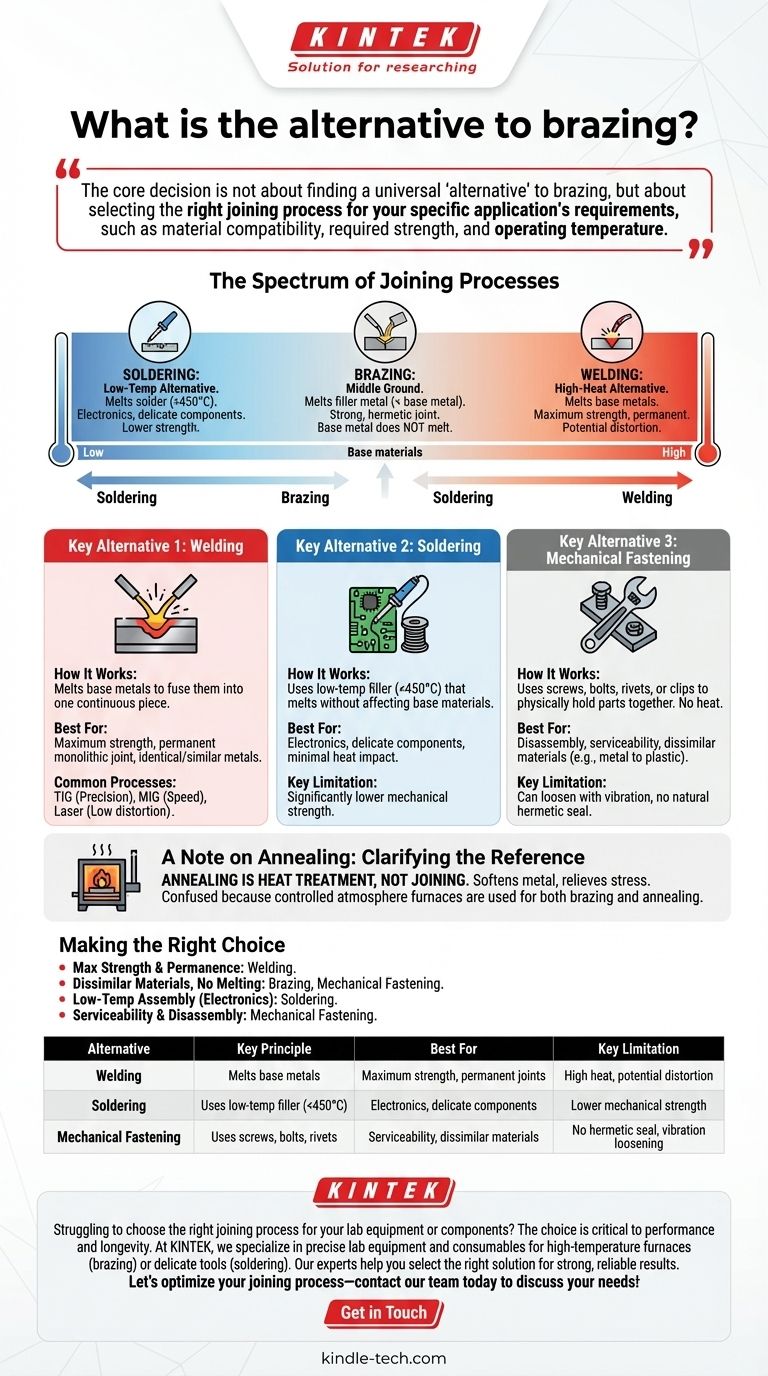
The primary alternatives to brazing are welding, soldering, and mechanical fastening. While processes like annealing may use similar furnace equipment, it is a heat treatment method for softening metal, not a process for joining components together. Each true alternative offers a distinct set of trade-offs in strength, cost, and applicability.
The core decision is not about finding a universal "alternative" to brazing, but about selecting the right joining process for your specific application's requirements, such as material compatibility, required strength, and operating temperature.
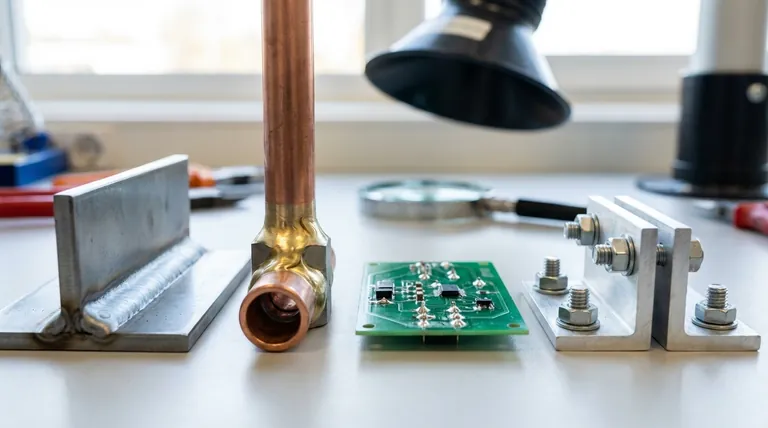

The Spectrum of Joining Processes
Before comparing alternatives, it's crucial to understand where brazing fits. Joining processes exist on a spectrum defined largely by heat and its effect on the base materials.
Brazing as the Middle Ground
Brazing involves melting a filler metal that flows between two base components via capillary action. The filler's melting point is lower than that of the base metals, so the components themselves never melt. This creates a strong, often hermetically sealed joint.
The Key Differentiators
The primary factors that separate brazing from its alternatives are temperature and whether the base metal is melted. This fundamental difference dictates the strength, distortion, and material compatibility of the final assembly.
Key Alternative 1: Welding
Welding represents the high-heat, high-strength end of the thermal joining spectrum.
How Welding Works
Unlike brazing, welding works by melting the base metals themselves, often along with a filler material, to fuse them into a single, continuous piece. Think of it as melting the edges of two ice cubes so they refreeze into one.
When to Choose Welding
Welding is the ideal choice when maximum strength and a permanent, monolithic joint are the absolute priorities. It is most effective when joining identical or very similar metals.
Common Welding Processes
Key processes include TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) for precision, MIG (Metal Inert Gas) for speed and automation, and Laser Welding for high-speed, low-distortion applications.
Key Alternative 2: Soldering
Soldering is the low-temperature counterpart to brazing.
How Soldering Works
Like brazing, soldering uses a filler metal (solder) that melts at a temperature lower than the base materials. The key distinction is that soldering occurs at a much lower temperature (typically below 450°C / 840°F).
When to Choose Soldering
Soldering is the standard for electronics and delicate components that cannot withstand high temperatures. Its low heat input prevents damage to sensitive parts.
The Strength Limitation
The lower-melting-point fillers used in soldering result in a joint with significantly lower mechanical strength compared to a brazed or welded joint.
Key Alternative 3: Mechanical Fastening
This category abandons thermal processes entirely in favor of mechanical force.
The Principle of Mechanical Joining
This involves using components like screws, bolts, rivets, or clips to physically hold parts together. No heating is involved, which eliminates any risk of thermal distortion or changes to the material's properties.
When to Choose Fasteners
Mechanical fastening is the only option when disassembly or serviceability is required. It also excels at joining highly dissimilar materials (e.g., metal to plastic) that cannot be joined thermally.
The Vibration and Sealing Challenge
Fastened joints can loosen under vibration and do not provide a natural hermetic seal, often requiring separate gaskets or sealants for fluid containment.
A Note on Annealing: Clarifying the Reference
It is critical to distinguish between joining and heat treatment processes, as they serve entirely different functions.
Annealing is Heat Treatment, Not Joining
Annealing is a thermal process used to soften a metal, making it more ductile and easier to form. It relieves internal stresses but does not join separate components.
Why They Are Often Confused
The confusion arises because controlled atmosphere furnaces are used for both high-quality brazing and annealing. The same equipment can perform both tasks, but they are fundamentally different operations with different goals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct process requires a clear understanding of your project's non-negotiable requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength and permanence: Welding is typically the superior choice, as it fuses the base materials into one.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials without melting them: Brazing remains a primary contender, with mechanical fastening as a non-thermal option.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature assembly, especially for electronics: Soldering is the industry standard due to its minimal thermal impact.
- If your primary focus is serviceability and the ability to disassemble: Mechanical fastening is the only viable option.
By understanding the fundamental principles of each joining method, you can select the process that ensures the integrity and performance of your design.
Summary Table:
| Alternative | Key Principle | Best For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Welding | Melts base metals to fuse them | Maximum strength, permanent joints | High heat, potential distortion |
| Soldering | Uses low-temp filler (<450°C) | Electronics, delicate components | Lower mechanical strength |
| Mechanical Fastening | Uses screws, bolts, rivets | Serviceability, dissimilar materials | No hermetic seal, can loosen with vibration |
Struggling to choose the right joining process for your lab equipment or components? The choice between brazing, welding, soldering, and mechanical fastening is critical to the performance and longevity of your assemblies. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for your specific application, whether you're working with high-temperature furnaces for brazing or delicate tools for soldering. Our experts can help you select the right solution to ensure strong, reliable, and efficient results. Let's optimize your joining process—contact our team today to discuss your needs! Get in Touch
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between hot mounting and cold mounting? Choose the Right Method for Your Sample
- What is the process of mounting in metallurgy? A Guide to Perfect Specimen Preparation
- What is the purpose of using epoxy resin and laboratory mounting equipment? Precision in U71Mn Weld Area Analysis
- What are the advantages of an electrolytic polishing device for EK-181 steel TEM samples? Ensure Peak Sample Integrity
- What is a hot mounting press machine? Precision Control for Metallurgy & Electronics Assembly



















