The primary application of heat treatment is to precisely manipulate the internal microstructure of a material, most commonly metal, to achieve specific, desirable properties. This controlled process of heating and cooling is used to enhance strength, improve machinability, increase wear resistance, or relieve internal stresses created during manufacturing processes like welding or forming.
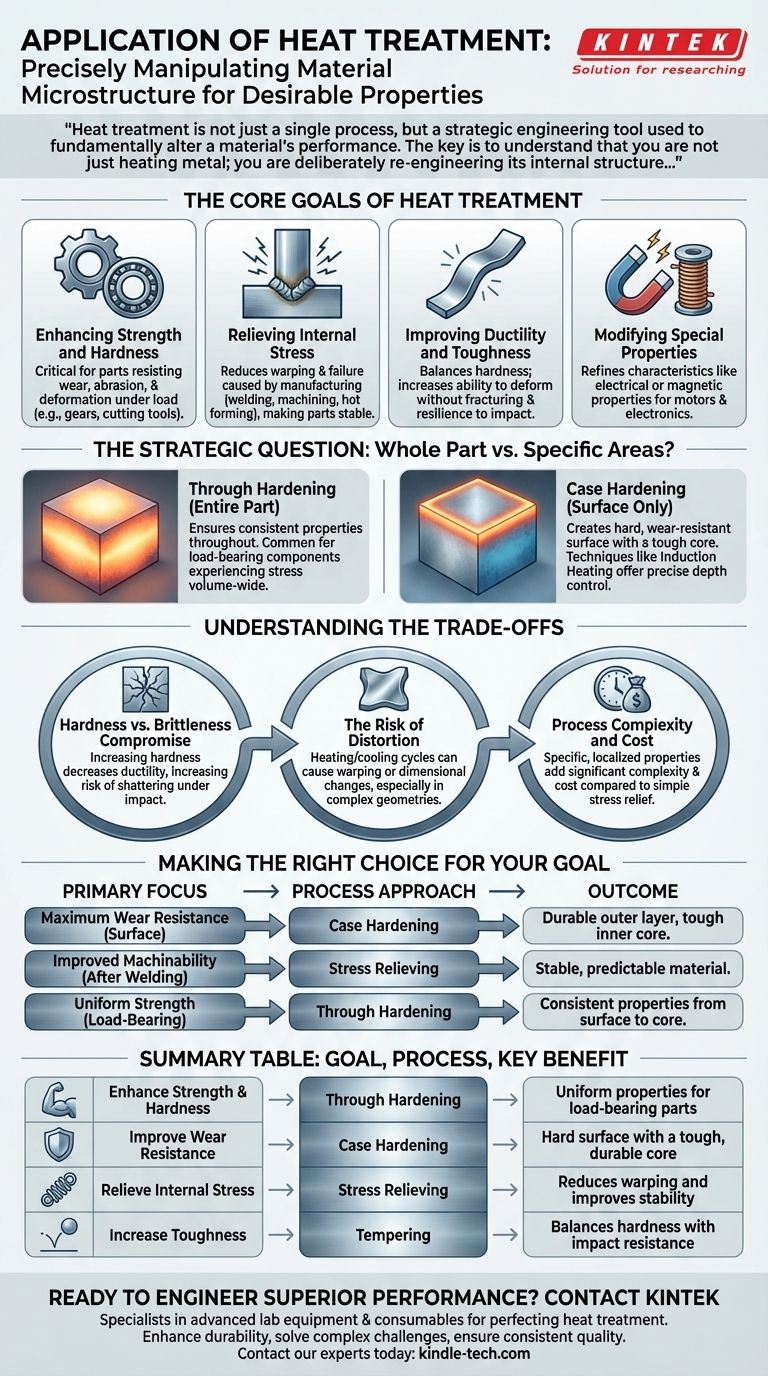
Heat treatment is not just a single process, but a strategic engineering tool used to fundamentally alter a material's performance. The key is to understand that you are not just heating metal; you are deliberately re-engineering its internal structure to match the precise demands of its final application.
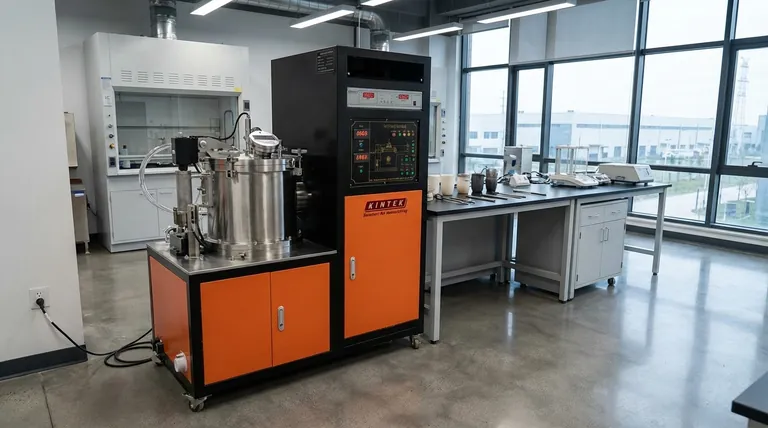

The Core Goals of Heat Treatment
Heat treatment is applied to solve specific engineering challenges. The choice of process is always driven by the desired outcome for the final component.
Enhancing Strength and Hardness
One of the most common goals is to make a material harder and stronger. This is critical for parts that must resist wear, abrasion, and deformation under load, such as gears, bearings, or cutting tools.
Relieving Internal Stress
Manufacturing processes like welding, machining, or hot forming create internal stresses within a material. These stresses can lead to warping or premature failure. Heat treatment can be used to relax these stresses, making the part more stable and easier to work with.
Improving Ductility and Toughness
While hardness is often desired, it can sometimes lead to brittleness. Certain heat treatments are designed to increase a material's ductility (its ability to deform without fracturing) and overall toughness, making it more resilient to impact.
Modifying Special Properties
Beyond purely mechanical traits, heat treatment can also refine a material's other characteristics. This includes enhancing specific electrical or magnetic properties, which is essential for components used in motors and electronics.
The Strategic Question: Whole Part vs. Specific Areas?
A critical decision in applying heat treatment is determining how much of the component needs to be altered. This choice is dictated entirely by the part's function.
Through Hardening: Treating the Entire Part
In some cases, the entire component requires uniform properties. Through hardening applies the heat treatment process to the whole part, ensuring its characteristics are consistent from the surface to the core. This is common for components that experience stress throughout their entire volume.
Case Hardening: Treating Only the Surface
For many applications, the ideal part has a very hard, wear-resistant surface while maintaining a softer, tougher core. Case hardening achieves this by treating only the outer layer. This creates a dual-property component that can withstand surface abrasion while resisting fracture from impacts.
Techniques like induction heating offer precise control over this process. By adjusting the frequency of the current, engineers can dictate the exact depth of the hardened layer, making it a highly versatile and targeted method.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Applying heat treatment is a balancing act. Improving one property often comes at the expense of another, and the process itself introduces risks that must be managed.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Compromise
The most fundamental trade-off is between hardness and brittleness. As you increase a metal's hardness, you almost always decrease its ductility, making it more susceptible to shattering under sudden impact. The goal is to find the optimal balance for the application.
The Risk of Distortion
The cycle of heating and cooling can cause parts to warp or change dimensions. This is a significant risk, especially for components with complex geometries or tight tolerances, and requires careful control of the process parameters.
Process Complexity and Cost
Simple stress-relieving processes can be relatively straightforward. However, achieving highly specific, localized properties through advanced methods adds significant complexity and cost to the manufacturing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct heat treatment strategy is always aligned with the component's end-use. Consider the primary performance requirement to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance on a surface: Case hardening is the most effective approach, creating a durable outer layer while preserving a tough inner core.
- If your primary focus is improved machinability after welding: A stress-relieving heat treatment will reduce internal stresses, making the material more stable and predictable to work with.
- If your primary focus is uniform strength through a load-bearing component: Through hardening ensures that the material properties are consistent from surface to core.
Ultimately, applying heat treatment correctly is about transforming a standard material into a high-performance component engineered for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Process | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Enhance Strength & Hardness | Through Hardening | Uniform properties for load-bearing parts |
| Improve Wear Resistance | Case Hardening | Hard surface with a tough, durable core |
| Relieve Internal Stress | Stress Relieving | Reduces warping and improves stability |
| Increase Toughness | Tempering | Balances hardness with impact resistance |
Ready to engineer superior performance into your components?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect your heat treatment processes. Whether you're developing new alloys or optimizing production, our solutions help you achieve precise control over material properties like hardness, strength, and wear resistance.
We serve manufacturers and R&D labs looking to:
- Enhance product durability and lifespan
- Solve complex material engineering challenges
- Ensure consistent, high-quality results
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application and material goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What are the five basic heat treatment processes of metals? Master Annealing, Hardening & More



















