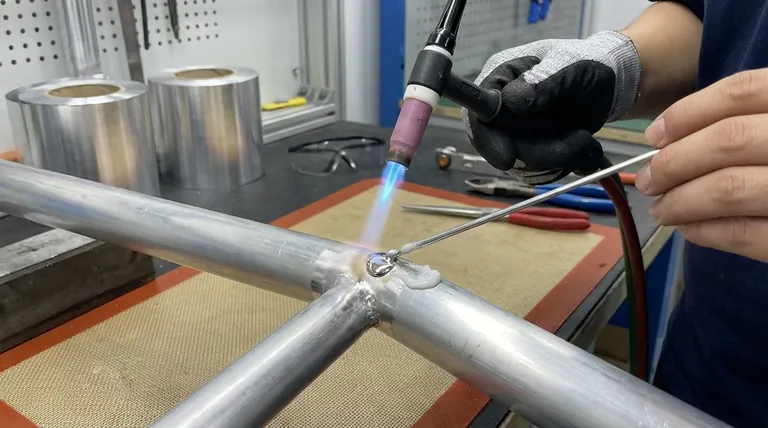
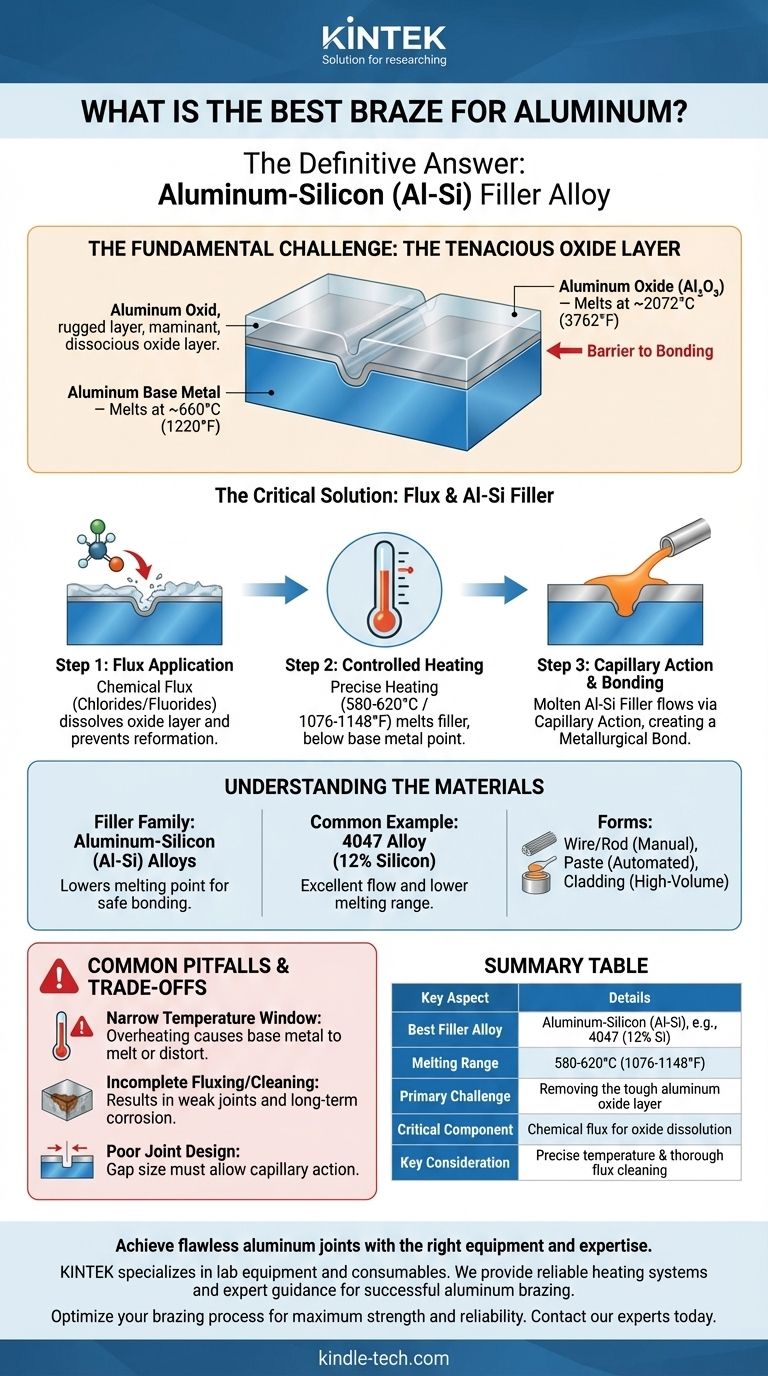
The best and most common braze for aluminum is an aluminum-silicon (Al-Si) filler alloy. These alloys are specifically designed with a melting point that is lower than the base aluminum parts you are joining, but high enough to create a strong, permanent bond. However, the true "best" choice is a system that combines the right filler metal with the correct flux and a precise heating method to overcome aluminum's unique chemical challenges.
The core challenge in brazing aluminum is not the joining itself, but defeating the tough, high-temperature layer of aluminum oxide that instantly forms on its surface. The best brazing approach is one that effectively removes this oxide layer, allowing the filler metal to form a direct, metallurgical bond with the clean aluminum underneath.

The Fundamental Challenge: Aluminum Oxide
Before selecting a filler metal, you must understand the primary obstacle in joining aluminum. It's a chemical barrier that dictates the entire process.
The Tenacious Oxide Layer
Aluminum is a highly reactive metal. The moment it is exposed to air, it forms a hard, transparent, and chemically inert layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃).
This oxide layer is self-healing, re-forming instantly if scratched or removed.
Why This Oxide is a Problem
The melting point of the aluminum oxide layer is approximately 2072°C (3762°F). This is vastly higher than the melting point of the aluminum base metal itself, which is around 660°C (1220°F).
You cannot braze through this oxide barrier. The filler metal will simply ball up on the surface, refusing to "wet" or bond with the underlying aluminum.
The Critical Role of Flux
To solve this, brazing requires a flux. Flux is an aggressive chemical compound, typically a mix of chlorides and fluorides, that performs two critical jobs.
First, it chemically attacks and dissolves the oxide layer as the part is heated. Second, it shields the cleaned joint area from oxygen, preventing the oxide from re-forming and allowing the molten filler to flow freely.
Understanding Aluminum Brazing Materials
The "braze" itself is a combination of a specific filler metal and a corresponding flux.
The Aluminum-Silicon (Al-Si) Filler Family
The industry standard for aluminum brazing is the family of aluminum-silicon alloys. Adding silicon to aluminum effectively lowers its melting point.
These filler metals are designed to melt in a precise window, typically between 580-620°C (1076-1148°F). This temperature is high enough for strong bonding but safely below the melting point of most common aluminum base alloys.
Common Alloy Example: 4047
A prime example is the 4047 alloy, which contains approximately 12% silicon. Its low melting point and excellent flow characteristics make it one of the most widely used filler metals for brazing alloys like 6061 and 3003.
Forms of Filler Material
Filler metal and flux can be applied in several ways, depending on the manufacturing process:
- Wire/Rod: For manual torch brazing, often coated with flux.
- Paste: A mixture of powdered filler metal and flux that can be precisely dispensed.
- Cladding: Brazing sheet where a thin layer of the filler alloy is metallurgically bonded to a core base alloy. This is common in high-volume production, like for automotive radiators.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
Success with aluminum brazing requires understanding its narrow process window and potential failure points.
The Narrow Temperature Window
The single greatest challenge is temperature control. The melting point of the Al-Si filler is only slightly below the melting point of the base material.
Overheating by even a small margin can cause the entire part to sag, distort, or melt completely. Precise, uniform heating is absolutely essential.
Incomplete Fluxing or Cleaning
The flux must be present everywhere the braze is intended to flow. Any area missed will retain its oxide layer, resulting in an incomplete or failed joint.
Furthermore, most effective fluxes are highly corrosive. After brazing, all residual flux must be thoroughly cleaned from the part, typically with hot water and brushing, to prevent long-term corrosion that can destroy the assembly.
Poor Joint Design
Brazing relies on capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into the gap between the two parts.
If the gap is too large, capillary action will be too weak to fill the joint. If the gap is too small, the flux and filler may not be able to penetrate it, leading to voids and a weak bond.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the "best" braze is about matching the materials and process to your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is joining common aluminum alloys (like 6061 or 3003): An Al-Si filler metal like 4047 is the industry standard and your best starting point, paired with an appropriate chemical flux.
- If you are producing complex assemblies like heat exchangers: Consider using clad brazing sheet, which provides the most uniform and reliable application of filler metal.
- If you are performing manual repairs or prototyping with a torch: Use a flux-coated or flux-cored brazing rod and prioritize practicing even heat application to avoid melting the base part.
- If long-term reliability is your highest priority: Your process must include a rigorous and validated post-braze cleaning step to completely remove all corrosive flux residue.
Ultimately, successful aluminum brazing depends less on a single "best" alloy and more on a controlled system of the right filler, flux, and heat.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Best Filler Alloy | Aluminum-Silicon (Al-Si), e.g., 4047 (12% Si) |
| Melting Range | 580-620°C (1076-1148°F) |
| Primary Challenge | Removing the tough aluminum oxide layer (melts at ~2072°C) |
| Critical Component | Chemical flux (chlorides/fluorides) to dissolve oxide and prevent reformation |
| Common Forms | Wire/rod, paste, or clad brazing sheet |
| Key Consideration | Precise temperature control and thorough post-braze flux cleaning are essential |
Achieve flawless aluminum joints with the right equipment and expertise.
Brazing aluminum requires precise temperature control and a deep understanding of material science to avoid common pitfalls like base metal melting or flux corrosion.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide the reliable heating systems and expert guidance necessary for successful aluminum brazing, whether you're in R&D, prototyping, or production.
Let us help you optimize your brazing process for maximum strength and reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Non-Standard Insulator Customization
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- 100L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath Water Bath Cooling
People Also Ask
- Why is carbon coating important? Boost Battery Performance and Longevity
- What is the difference between metallic and non-metallic coating? A Guide to Sacrificial vs. Barrier Protection
- What are two disadvantages of metal? Understanding Corrosion and Weight Limitations
- How to check the power of a lithium-ion battery? Master the difference between charge level and battery health.
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use



















