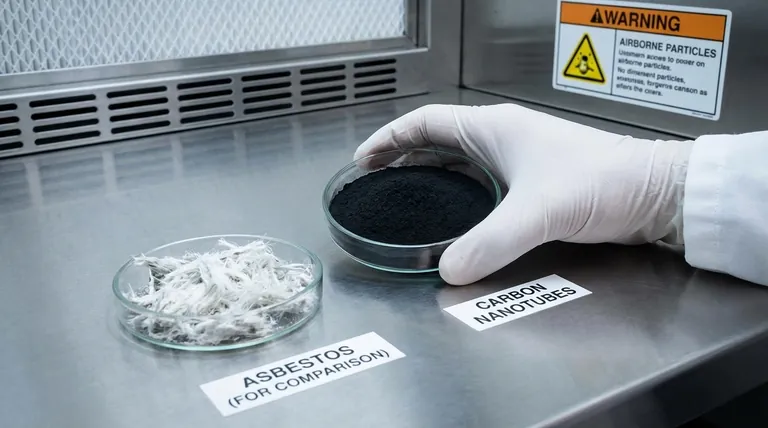
The primary controversy surrounding carbon nanotubes (CNTs) is not about their performance but their potential health and safety risks. Specifically, certain types of CNTs bear a striking physical resemblance to asbestos fibers, raising significant concerns about their potential to cause serious lung disease if inhaled by workers during manufacturing and processing.
While carbon nanotubes offer revolutionary potential across industries like batteries and composites, their needle-like structure creates a critical health controversy. The central issue is that certain CNTs, if inhaled, can mimic the behavior of asbestos, leading to lung inflammation and long-term disease, which necessitates strict safety protocols.

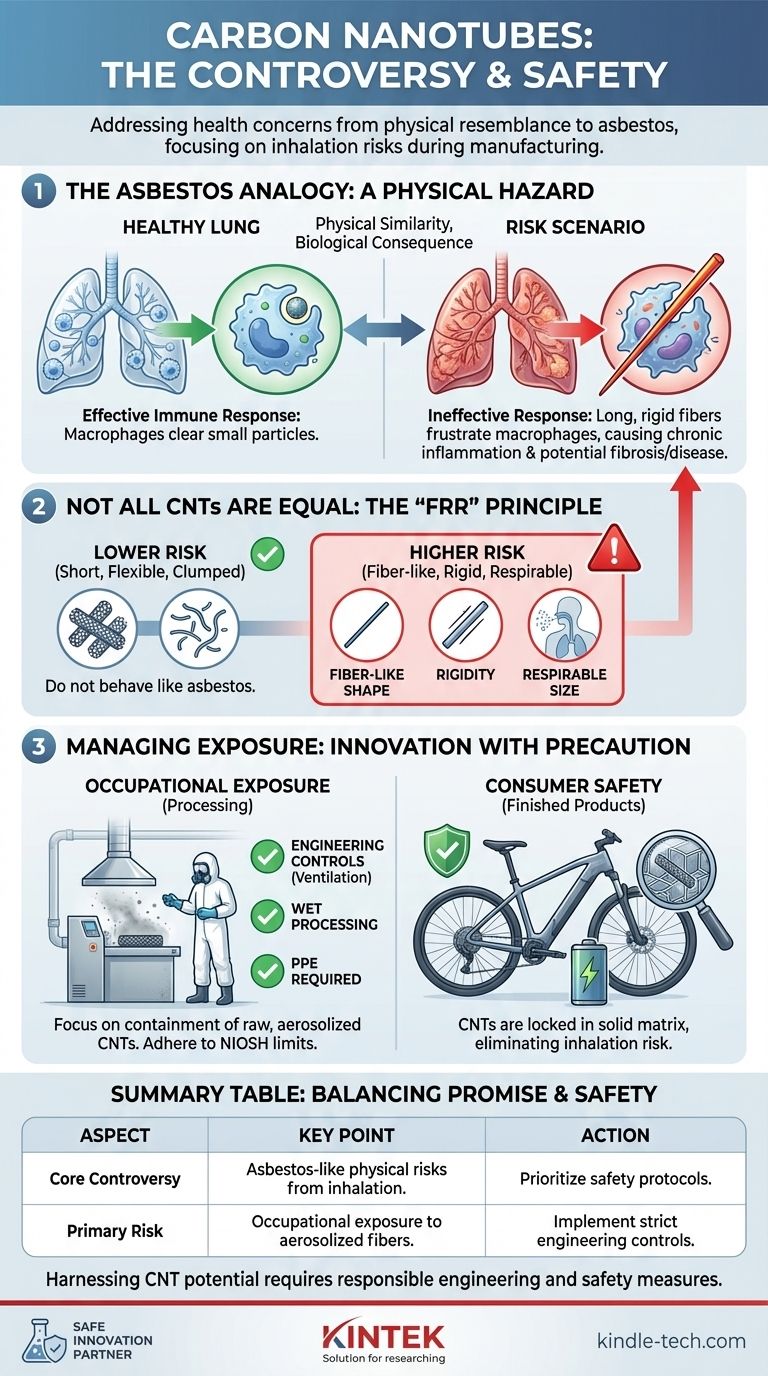
The Root of the Concern: The Asbestos Analogy
The entire controversy stems from a simple but powerful observation: some carbon nanotubes look and act like asbestos fibers at the microscopic level. This isn't a chemical similarity, but a physical one with serious biological implications.
A Matter of Shape and Size
The most hazardous fibers, whether asbestos or CNTs, are long, thin, and rigid. This specific morphology is often referred to as a high-aspect-ratio nanoparticle.
This needle-like shape prevents the body's immune cells, known as macrophages, from fully engulfing and clearing the fibers from the deep lung tissue where they can become lodged.
The Body's Ineffective Response
When macrophages fail to clear these foreign fibers, they can trigger a state of chronic inflammation. The persistent immune response in the lung lining (the pleura) is the same mechanism that makes asbestos so dangerous.
This sustained inflammation can lead to the formation of scar tissue (fibrosis) and other cellular damage over long periods.
Potential Long-Term Health Outcomes
Animal studies have shown that introducing certain types of long, rigid CNTs into the pleural space can cause inflammation, granulomas, and fibrosis. These are the same precursors to diseases like asbestosis and mesothelioma, a rare and aggressive cancer strongly linked to asbestos exposure.
It is this potential for long-term, severe lung disease that forms the core of the controversy and drives regulatory caution.
Deconstructing the Risk: Not All CNTs Are Equal
It is a critical mistake to view all carbon nanotubes as a single entity. The term covers a wide range of materials, and their potential hazard is highly dependent on their specific physical characteristics.
The "FRR" Principle: Fiber, Rigidity, and Respirability
The risk is highest for CNTs that meet three criteria: they have a fiber-like shape, they are rigid enough to pierce cell membranes, and they are respirable (small enough to be inhaled deep into the lungs).
CNTs that are short, flexible, or clumped together in large aggregates are generally considered to pose a much lower risk because they do not behave like asbestos in the body.
Tangled Aggregates vs. Free Fibers
In many applications, CNTs are produced or supplied as tangled, messy clumps. These aggregates are typically too large to travel into the deep lung, significantly reducing the inhalation hazard.
The primary risk emerges when these clumps are broken apart during processing, potentially releasing individual, high-aspect-ratio fibers into the air.
The Critical Role of Exposure
The controversy is almost exclusively focused on occupational exposure for workers in CNT production and processing facilities. The risk comes from breathing in raw, aerosolized CNTs.
For consumers, the risk is virtually nonexistent. In finished products like composites, batteries, or polymers, the CNTs are locked within a solid matrix and cannot become airborne.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Innovation vs. Precaution
The immense technological promise of CNTs places their potential risks in sharp relief. Their applications in next-generation batteries, ultra-strong composites, and advanced electronics are transformative.
The Precautionary Principle in Action
Given the parallels with asbestos, regulatory bodies like the U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) have adopted a cautious approach.
NIOSH has established a Recommended Exposure Limit (REL) for airborne CNTs to protect workers, treating them as a potential occupational carcinogen until more data proves otherwise.
Engineering Safety into the Process
The industry mitigates risk not by abandoning the technology, but by implementing strict engineering controls. These include advanced ventilation systems, wet processing methods to prevent dust, and requiring personal protective equipment (PPE) for workers.
By containing the raw material, manufacturers can leverage the benefits of CNTs while protecting their workforce from exposure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Navigating the carbon nanotube controversy requires a nuanced understanding of the specific material and its application.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing or research: Prioritize implementing strict engineering controls and workplace safety protocols recommended by agencies like NIOSH to manage inhalation risks.
- If your primary focus is product development: Concentrate on applications where CNTs are firmly embedded within a solid matrix, as this effectively eliminates the exposure pathway and risk for end-users.
- If your primary focus is investment or strategic planning: Differentiate between the types of CNTs and their handling; the risk profile for a liquid dispersion of tangled nanotubes is vastly different from that of a dry, aerosolized powder.
Ultimately, harnessing the power of carbon nanotubes safely is a solvable engineering challenge, allowing us to pursue innovation with responsibility.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Point |
|---|---|
| Core Controversy | Physical resemblance to asbestos fibers, posing inhalation risks. |
| Primary Risk | Occupational exposure during manufacturing/processing. |
| Risk Factors | Long, rigid, respirable fibers (high-aspect-ratio). |
| Consumer Risk | Virtually nonexistent when CNTs are embedded in products. |
| Mitigation | Strict engineering controls, NIOSH exposure limits, and PPE. |
Safely Integrate Advanced Materials into Your Laboratory Workflow
Navigating the complexities of materials like carbon nanotubes requires not only innovation but also a commitment to safety. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment and consumables designed to help you manage advanced materials responsibly. Whether you are involved in materials research, product development, or manufacturing, our solutions support stringent safety protocols and efficient processes.
Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation and safety. We provide the reliable equipment you need to handle nanomaterials with confidence, ensuring your team is protected while pushing the boundaries of technology.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities safely? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your groundbreaking work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Tube
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Centrifuge Tubes
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven assist in processing raw COF products? Master Material Activation
- What is the difference between burning and pyrolysis? Unlock Value from Waste Materials
- What is the heat treatment process for castings? Transform Your Components for Peak Performance
- Have other labs successfully stored samples at -70°C? Proven Long-Term Preservation for Biological Materials
- What is electron coating? A Guide to High-Performance E-Coating and Finishing Processes
- How are incubators heated? Master Temperature Control for Your Lab's Success
- What are the benefits of converting plastic waste into fuel? Turning Waste into a Valuable Energy Resource
- What are some of the applications of FTIR? Identify Materials from Pharma to Forensics



















