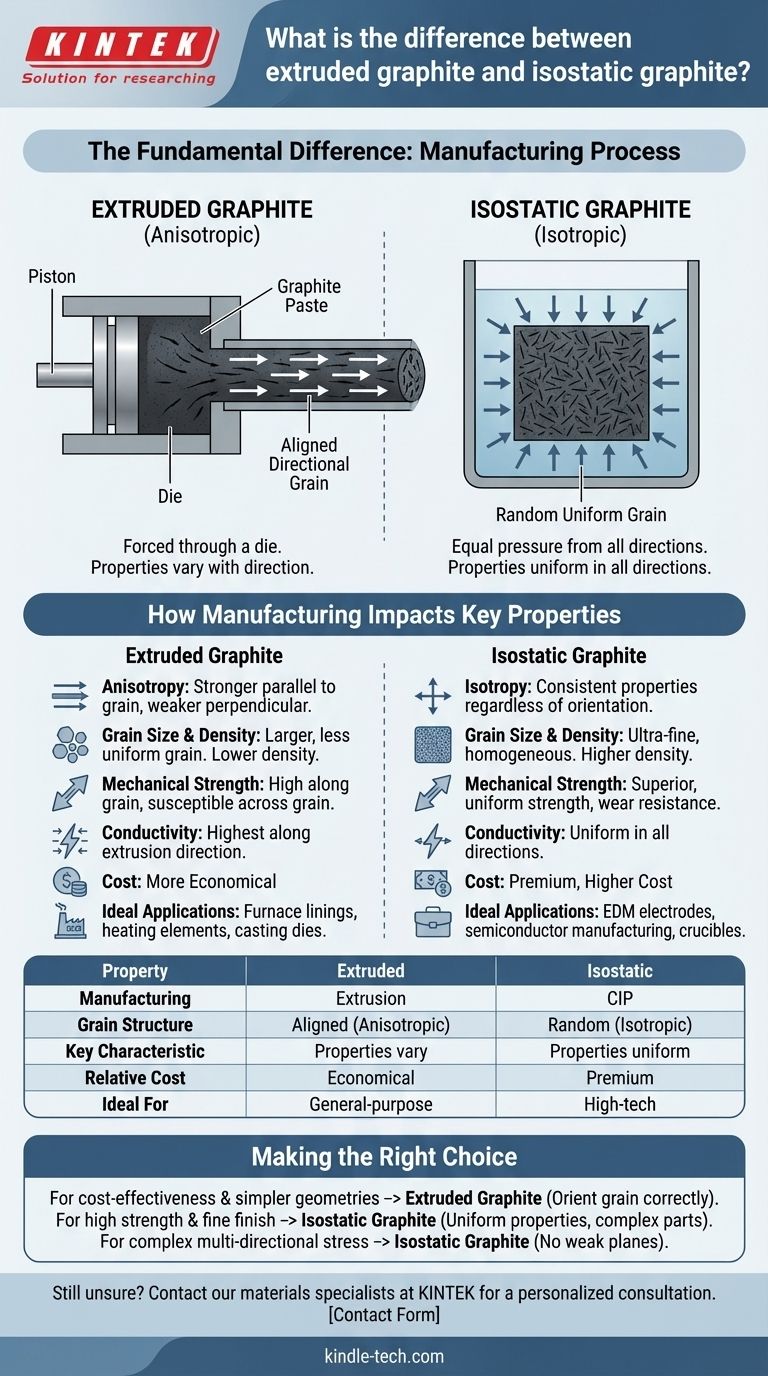
The fundamental difference between extruded and isostatic graphite lies in their manufacturing process. Extrusion forces graphite material through a die, creating an aligned, directional grain structure, while isostatic pressing uses equal pressure from all directions to form a block with a random, uniform grain structure. This core distinction dictates the material's physical properties, performance, and ideal applications.
The choice between extruded and isostatic graphite is not about which is superior overall, but which is correct for your specific need. Extruded graphite offers a cost-effective solution where properties can be oriented to the load, while isostatic graphite provides uniform, high performance in all directions for more demanding applications.

The Manufacturing Process: The Root of the Difference
The properties of a finished graphite component are a direct result of how it was formed. The two methods create materials with fundamentally different internal structures.
Extrusion: Directional Force, Directional Properties
Extrusion involves mixing graphite powder with a binder to create a paste-like mass. This mass is then forced (extruded) through a die to form rods, blocks, or tubes.
This process forces the needle-like graphite particles to align with the direction of extrusion. The resulting material is anisotropic, meaning its properties are not the same in all directions.
Isostatic Pressing: Uniform Pressure, Uniform Properties
Isostatic graphite is made by placing an ultra-fine graphite powder into a flexible mold, which is then submerged in a fluid within a high-pressure vessel. This process, known as Cold Isostatic Pressing (CIP), applies immense, equal pressure from all directions.
This uniform pressure compacts the powder without creating any preferential alignment of particles. The result is a fully dense block of graphite that is isotropic, meaning its properties are identical regardless of orientation.
How Manufacturing Impacts Key Properties
The distinction between an anisotropic and isotropic structure has significant consequences for how the material behaves under stress, heat, and electrical load.
Anisotropy vs. Isotropy
This is the most critical concept. In extruded (anisotropic) graphite, properties like mechanical strength and electrical conductivity are higher when measured parallel to the grain (the direction of extrusion) and lower when measured perpendicular to it.
In isostatic (isotropic) graphite, these properties are consistent and uniform no matter which direction you measure. There is no "grain" direction to consider.
Grain Size and Density
Isostatic pressing produces a material with an ultra-fine, homogeneous grain structure. This leads to a higher and more uniform density throughout the block.
Extruded graphite typically has a larger and less uniform grain size. This can impact the machinability and the quality of the final surface finish.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
The fine grain and isotropic nature of isostatic graphite give it superior mechanical strength, flexural strength, and resistance to wear. It is ideal for applications with complex, multi-directional stresses because there are no weak planes.
Extruded graphite is strong along its grain but weaker across it, making it more susceptible to failure if stressed incorrectly.
Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
In extruded graphite, conductivity is highest along the direction of extrusion. This can be an advantage if you need to direct heat or electricity in a specific path.
Isostatic graphite provides consistent, predictable thermal and electrical conductivity in all directions, which is crucial for uniform heating or consistent performance in applications like EDM electrodes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material requires balancing performance requirements with practical constraints.
Performance vs. Cost
Isostatic graphite is a premium, high-performance material. The complex CIP process and higher-quality raw materials make it significantly more expensive than extruded graphite.
Extruded graphite is a more economical choice. Its manufacturing process is simpler and less costly, making it suitable for a wide range of general-purpose applications where peak performance is not the primary driver.
Suitable Applications
The uniform strength and fine finish of isostatic graphite make it the standard for high-tech applications. This includes semiconductor manufacturing (crucibles, heaters), nuclear reactors, and precision Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) electrodes.
Extruded graphite is often used for applications like furnace linings, heating elements, casting dies, and crucibles where its directional properties can be accommodated by the design and cost is a major factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for simpler geometries: Choose extruded graphite and ensure your design orients the material's grain in the direction of the primary stress or conductive path.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical strength and a fine surface finish: Choose isostatic graphite for its superior, uniform properties, especially for parts that require intricate machining.
- If your application involves complex thermal or mechanical stress from multiple directions: Choose isostatic graphite to eliminate the risk of failure along a weak grain axis.
Understanding this fundamental difference in manufacturing empowers you to select the precise material engineered for your specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Property | Extruded Graphite | Isostatic Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Forced through a die (Extrusion) | Equal pressure from all directions (CIP) |
| Grain Structure | Aligned, Directional (Anisotropic) | Random, Uniform (Isotropic) |
| Key Characteristic | Properties vary with direction | Properties are uniform in all directions |
| Relative Cost | More Economical | Premium, Higher Cost |
| Ideal For | Furnace linings, heating elements | EDM electrodes, semiconductor manufacturing |
Still unsure which graphite material is right for your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including precision graphite components. Our experts can help you analyze your specific requirements for thermal management, mechanical stress, and surface finish to recommend the optimal material—whether cost-effective extruded graphite or high-performance isostatic graphite—ensuring your application's success.
Contact our materials specialists today for a personalized consultation and discover how the right graphite solution can enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- Carbon Graphite Boat -Laboratory Tube Furnace with Cover
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of activated carbon regeneration? Unlock the 1000°F Process for Reuse
- What are the properties of refrigerant fluids used in Ultra Freezers? Achieving Reliable -86°C Performance
- What is the magnetic field sputtering of DC magnetron? Boost Deposition Rates & Film Quality
- When selecting a flux for brazing or braze welding what criteria must be considered? Ensure Strong, Reliable Joints
- Can you harden non-ferrous metals? Yes, with the right methods for aluminum, copper, and titanium
- What is the target substrate distance for sputtering? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- How is a sample analysis done in FTIR? A Step-by-Step Guide to Reliable Results
- Can people tell the difference between real and fake diamonds? The Truth About Lab-Grown vs. Natural



















