In materials science, smelting is a chemical process used to extract a pure metal from its raw, impure ore, while sintering is a physical process used to bond particles together into a solid mass without melting them. Smelting fundamentally changes the chemical nature of a substance through reduction reactions at high temperatures. Sintering, in contrast, changes a material's physical structure, increasing its density and strength by fusing its particles together.
The critical difference is one of purpose and transformation. Smelting's goal is chemical purification to produce a new material (pure metal) from an old one (ore). Sintering's goal is physical consolidation to form a solid object from a powder, without changing its core chemical identity.

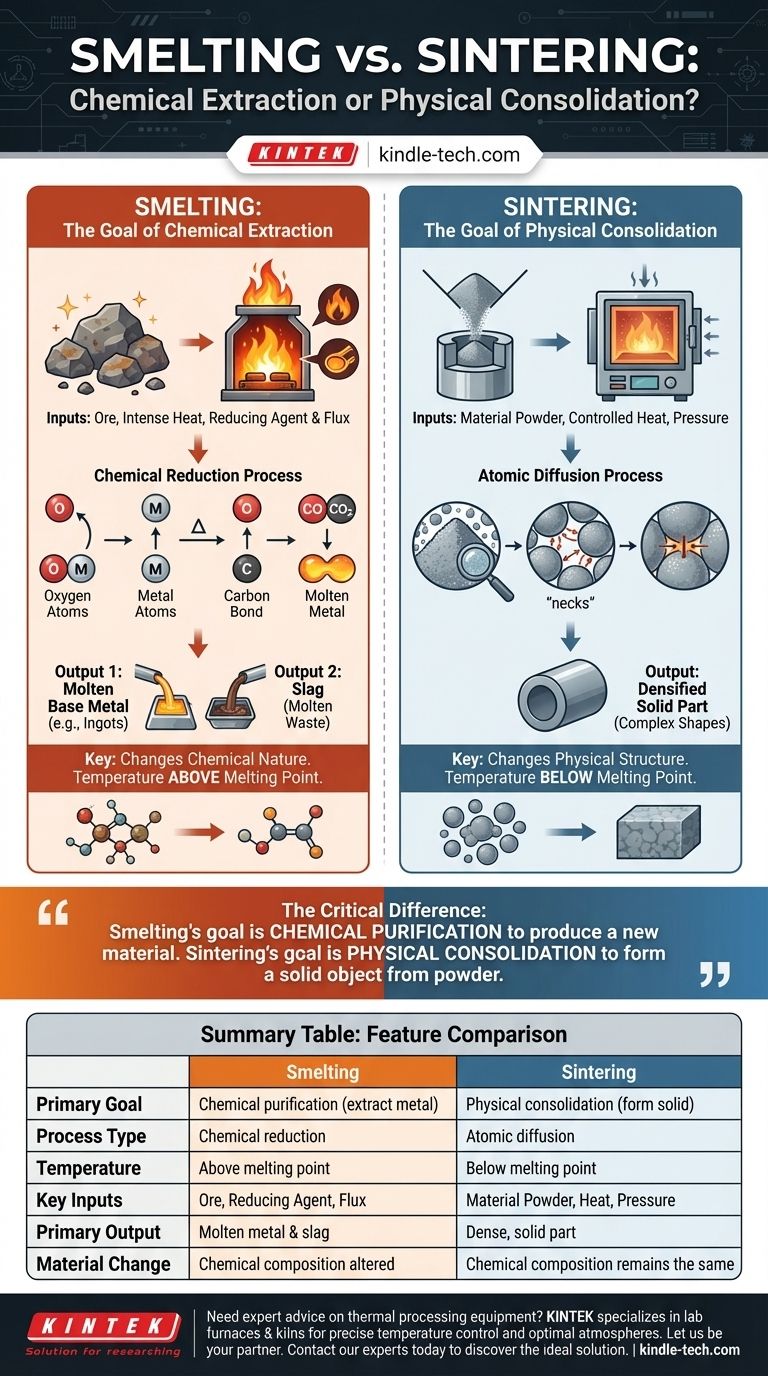
What is Smelting? The Goal of Chemical Extraction
Smelting is one of humanity's oldest metallurgical techniques, used to produce foundational metals like iron, copper, and tin from their naturally occurring ores. The process is defined by chemical change.
A Process of Chemical Reduction
The primary purpose of smelting is to "reduce" an ore. In chemistry, reduction is the process of removing oxygen or other non-metal elements to isolate the pure metal.
This is achieved by heating the ore to an extreme temperature in the presence of a reducing agent, such as carbon (in the form of coke) or carbon monoxide. The reducing agent chemically bonds with the unwanted elements, freeing the metal.
The Key Inputs: Ore, Heat, and a Flux
A smelting operation requires three things:
- Metal Ore: The raw, impure mineral compound (e.g., iron oxide).
- Intense Heat: Temperatures high enough to melt the metal and drive the chemical reaction.
- A Reducing Agent & Flux: A chemical like coke to strip oxygen from the ore, and a flux (like limestone) to bind with other impurities.
The Output: Molten Metal and Slag
The result of smelting is twofold. First, you get the desired molten base metal, which can be cast into forms like ingots. Second, the flux and other non-metallic impurities combine to form a molten waste product called slag, which is lighter and floats on top of the metal for easy removal.
What is Sintering? The Goal of Physical Consolidation
Sintering is a more modern and precise thermal process used in powder metallurgy, ceramics manufacturing, and even 3D printing. Its goal is to create dense, solid parts from powders.
A Process of Atomic Diffusion
In sintering, a compacted powder is heated to a high temperature that is below its melting point.
Instead of liquefying, the heat gives the atoms at the contact points between particles enough energy to migrate, or diffuse, across the particle boundaries. This atomic movement fills in the gaps and creates strong, solid bonds, fusing the individual particles into a single, dense piece.
The Key Inputs: Powder, Heat, and Pressure
Sintering relies on a different set of inputs:
- Material Powder: A fine powder of a metal, alloy, or ceramic.
- Controlled Heat: A specific temperature held for a set time, always below the melting point.
- Pressure: Often, pressure is applied before or during heating to force the particles into close contact, which accelerates diffusion.
The Output: A Densified Solid Part
The final product of sintering is a solid object that retains the chemical composition of the starting powder but has become a dense, strong, and coherent mass. The process is essential for creating components from materials with extremely high melting points, like tungsten or advanced ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these processes is not a matter of preference; they solve entirely different engineering problems.
Smelting: Purity from Raw Materials
Smelting is the essential first step in the metals supply chain. It is the only practical way to produce vast quantities of a base metal like iron or aluminum from the earth's crust. Its purpose is exclusively extraction and purification.
Sintering: Complex Shapes from Purified Powders
Sintering is a manufacturing or finishing step used after a pure material has already been created. It excels at forming intricate shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through casting or machining. Its purpose is forming and densification.
The Role of Atmosphere
The environment for each process is also critical. Smelting often produces its own reactive gases. Sintering, however, often requires a carefully controlled atmosphere (like hydrogen or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation and ensure the final part achieves full density and desired properties, especially for reactive metals, nitrides, and carbides.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To distinguish the two, always ask what the primary objective of the process is.
- If the primary focus is extracting a base metal from its raw ore: You are dealing with smelting, a process of chemical purification.
- If the primary focus is creating a solid part from a purified powder: You are dealing with sintering, a process of physical bonding.
- If the process involves melting and creating a waste product (slag): It is almost certainly smelting.
- If the process intentionally avoids melting to fuse particles together: It is definitively sintering.
Ultimately, smelting changes a material's fundamental chemistry, while sintering only changes its physical form.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Smelting | Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Chemical purification (extract metal from ore) | Physical consolidation (form solid from powder) |
| Process Type | Chemical reduction | Atomic diffusion |
| Temperature | Above melting point of the metal | Below melting point of the material |
| Key Inputs | Ore, Reducing Agent (e.g., coke), Flux | Material Powder, Controlled Heat, Pressure |
| Primary Output | Molten base metal and slag (waste) | Dense, solid part |
| Material Change | Chemical composition is altered | Chemical composition remains the same |
Need expert advice on thermal processing equipment?
Whether your project involves high-temperature chemical reactions like smelting or precise powder consolidation through sintering, having the right equipment is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in providing robust and reliable lab furnaces, kilns, and consumables designed for demanding thermal processes. Our expertise helps laboratories and manufacturers achieve precise temperature control, optimal atmospheres, and consistent results.
Let KINTEK be your partner in thermal processing. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover the ideal solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What are the different sintering methods? Choose the Right Technique for Your Material & Application
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts



















