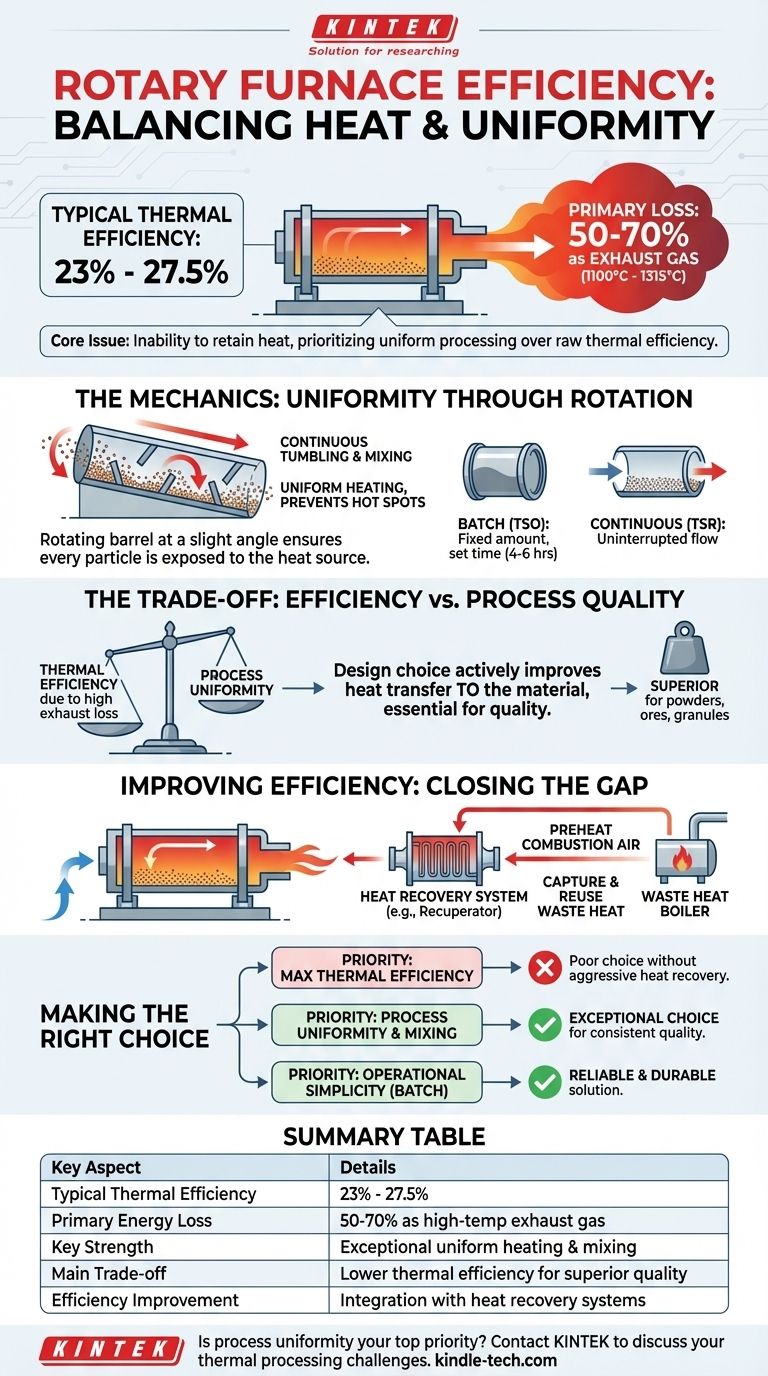
For industrial melting applications, a rotary furnace typically has a thermal efficiency in the range of 23% to 27.5%. This relatively low figure is primarily because the majority of the energy input—often between 50% and 70%—is lost as waste heat in the high-temperature exhaust gas.
The core issue with rotary furnace efficiency is not the furnace's ability to heat material, but its inability to retain that heat within the system. Its design prioritizes uniform material processing over raw thermal efficiency, a trade-off that defines its use cases.

The Mechanics of a Rotary Furnace
To understand its efficiency, you must first understand its fundamental design. A rotary furnace is built around a central, rotating barrel or tube, which is lined with refractory material to withstand high temperatures.
Core Design and Operation
The furnace is installed at a slight angle. As the barrel slowly rotates around its axis, the material inside—whether a mineral, metal, or chemical compound—tumbles and gradually moves from the higher entry point to the lower exit point.
This continuous tumbling action is the furnace's key feature. It constantly mixes the material, ensuring every particle is exposed to the heat source. This results in exceptionally uniform heating and prevents hot spots, which is critical for many sensitive processes.
Types and Scales
Rotary furnaces are not one-size-fits-all. They range from small laboratory models with capacities measured in milliliters to massive industrial units for continuous processing.
- Batch Furnaces (TSO): A fixed amount of material is charged, processed for a set time (e.g., 4-6 hours), and then tapped. These are often valued for their operational simplicity.
- Continuous Furnaces (TSR): Material is fed continuously into one end and processed product is discharged from the other, allowing for uninterrupted production.
Deconstructing Furnace Efficiency
The efficiency number only tells part of the story. The real question is why the efficiency is what it is and what factors control it.
The Primary Source of Inefficiency: Exhaust Heat
The most significant factor driving down efficiency is heat loss through exhaust gas. In high-temperature melting applications, this gas can exit the furnace at temperatures between 1100°C and 1315°C.
This isn't wasted energy in the sense that it did no work; it was required to bring the furnace and its contents to the target temperature. However, it represents a massive amount of thermal energy that is not transferred to the final product and is simply vented from the system.
The Role of Material Agitation
The rotation of the furnace is a design choice that actively improves heat transfer to the material. By constantly turning over the load, it ensures that heat from the internal source or hot gases is absorbed effectively and evenly.
Without this agitation, the material on top would shield the material below, leading to an inconsistent product. Therefore, the mechanical action is essential for process quality, even if the overall system is thermally inefficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a rotary furnace is an exercise in weighing its unique advantages against its inherent limitations. Its lower thermal efficiency is a direct trade-off for other significant process benefits.
Efficiency vs. Process Uniformity
The primary reason to select a rotary furnace is for its superior material mixing and uniform heating. For processes involving powders, ores, or granulated materials, this consistency is non-negotiable and often outweighs the concern of lower energy efficiency.
Operational Simplicity vs. Complexity
Many batch-style rotary furnaces are mechanically robust and straightforward to operate. They can often be run by less specialized staff, reducing operational complexity and labor costs compared to more sophisticated furnace systems.
The Heat Recovery Gap
The high-temperature exhaust gas that causes poor efficiency is also a major opportunity. While a basic rotary furnace is inefficient, one paired with a heat recovery system (like a recuperator to preheat combustion air or a waste heat boiler) can become significantly more efficient. The "waste" heat can be captured and reused, dramatically improving the energy balance of the entire operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The suitability of a rotary furnace depends entirely on your primary technical and operational goals.
- If your primary focus is maximizing thermal efficiency for simple melting: A standard rotary furnace is likely a poor choice unless it is integrated with an aggressive heat recovery system.
- If your primary focus is process uniformity and material mixing: The rotary furnace is an exceptional choice, especially for treating granular materials, powders, or ores where consistent quality is the main driver.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity and robustness in a batch process: The straightforward design and operation of many rotary furnaces make them a reliable and durable solution.
Ultimately, a rotary furnace's value is found not in its raw thermal efficiency, but in its unique ability to deliver exceptionally uniform heat treatment to a moving material load.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Typical Thermal Efficiency | 23% - 27.5% |
| Primary Energy Loss | 50-70% as high-temperature exhaust gas (1100°C - 1315°C) |
| Key Strength | Exceptional uniform heating and material mixing |
| Main Trade-off | Lower thermal efficiency for superior process quality |
| Efficiency Improvement | Integration with heat recovery systems (e.g., recuperators) |
Is process uniformity your top priority? While rotary furnaces have lower thermal efficiency, their ability to deliver exceptionally uniform heat treatment is unmatched for powders, ores, and granular materials. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing robust laboratory and industrial equipment tailored to your specific needs. Let our experts help you determine if a rotary furnace is the right solution for your application or guide you to a more efficient alternative.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your lab's thermal processing challenges and discover the optimal equipment for superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- How does a rotary extractor work? Master Continuous High-Volume Solid Processing
- What is a rotary kiln reactor? A Guide to Industrial Thermal Processing
- How is the operational mode of bed motion selected for a rotary kiln? Optimize Heat Transfer and Material Homogeneity
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding



















