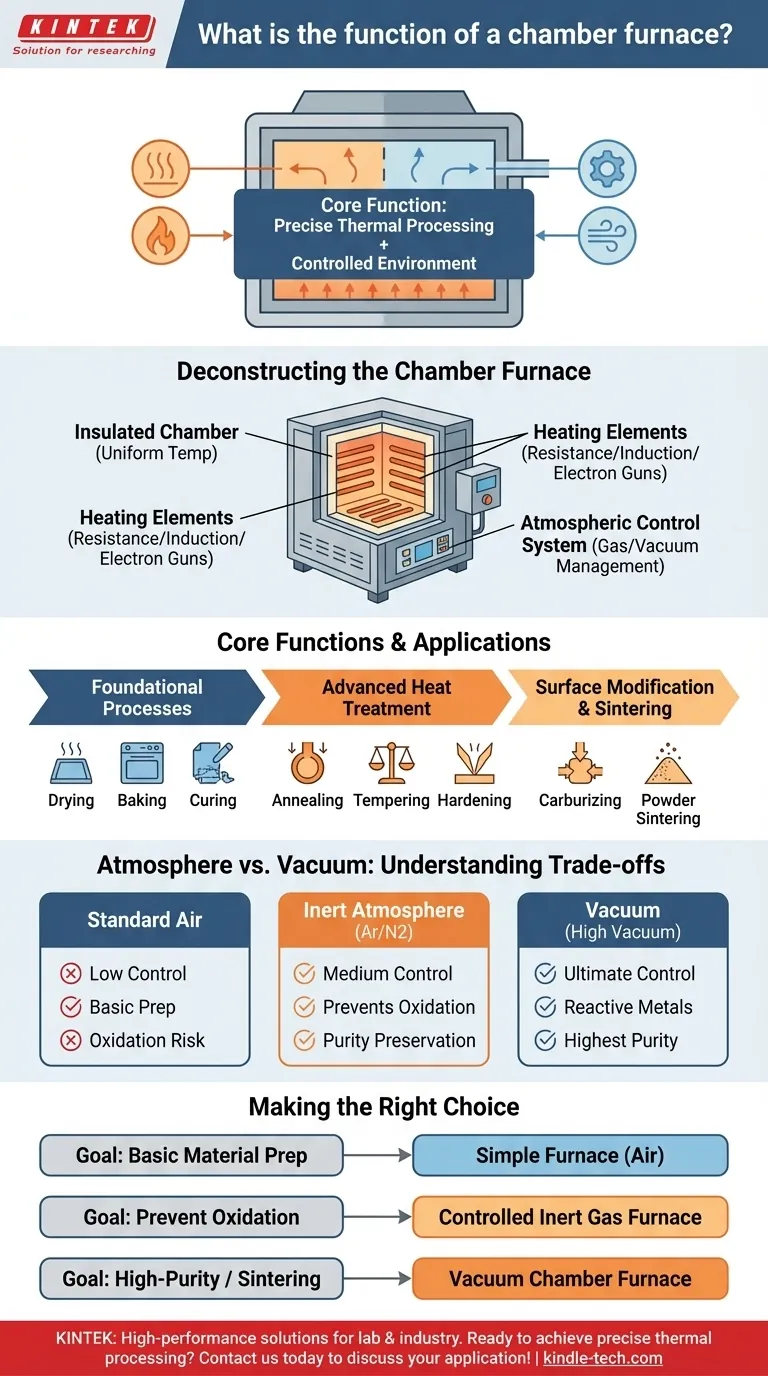
At its core, a chamber furnace is a high-temperature oven designed for precise thermal processing in a controlled environment. Its fundamental functions include drying to remove moisture, baking to heat samples without dehumidification, and curing to induce physical or chemical changes in a material. However, its capabilities extend far beyond simple heating.
The true function of a chamber furnace is not just to heat a material, but to do so with extreme precision while meticulously controlling the atmospheric environment around it. This control is what allows for the intentional modification of a material's properties.
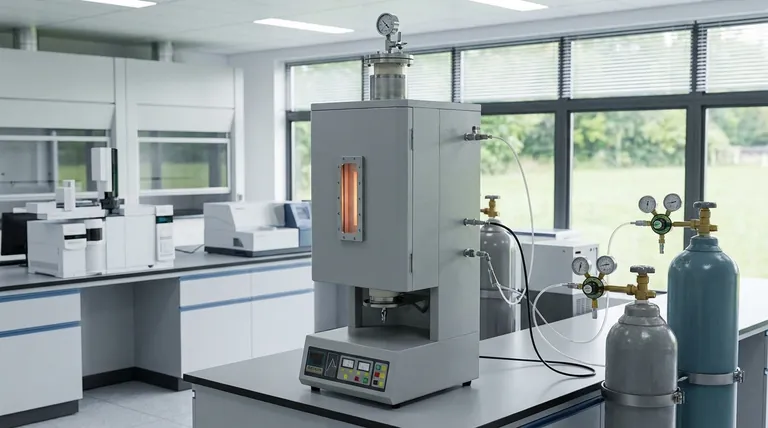

Deconstructing the Chamber Furnace
To understand its function, you must first understand its key components. A chamber furnace is more than just a hot box; it is an integrated system for thermal and atmospheric control.
The Insulated Chamber
The heart of the furnace is the chamber itself, located within a sealed outer shell. This space is heavily insulated to maintain extremely high and uniform temperatures efficiently.
The Heating Elements
The method of heating is determined by the furnace's intended purpose. Heating elements can include simple resistance coils for general use, induction coils, or even specialized systems like electron guns for advanced applications.
The Atmospheric Control System
This is arguably the most critical component. The atmosphere inside the chamber can be precisely managed to protect the material from unwanted reactions, like oxidation, or to encourage desired ones.
Core Functions and Applications
The combination of precise temperature and atmospheric control enables a wide range of applications, from basic laboratory work to advanced industrial manufacturing.
Foundational Processes: Drying, Baking, & Curing
These are the most basic functions.
- Drying involves heating at relatively low temperatures to remove moisture.
- Baking is the general application of heat to a sample.
- Curing uses heat to trigger a chemical or physical transformation, such as hardening a polymer.
Advanced Heat Treatment
Chamber furnaces are essential for metallurgical processes that alter a material's microstructure and mechanical properties. This includes annealing, tempering, and hardening, which require precise temperature ramps and soak times.
Surface Modification and Sintering
By using a reactive atmosphere, a furnace can intentionally alter the surface of a material. For example, introducing a carbon-rich gas can achieve carburizing, which hardens the surface of steel.
In other cases, an inert atmosphere (like Argon or Nitrogen) or a vacuum is used to prevent any surface reactions, which is critical for processes like sintering metal powders into a solid mass.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Atmosphere vs. Vacuum
The choice of atmospheric control is the primary differentiator between chamber furnaces and dictates their ideal use case.
Standard Air Atmosphere
A basic furnace that heats in ambient air is suitable for processes where surface oxidation is not a concern, such as in ceramics or for some curing applications. They are the simplest and most cost-effective option.
Controlled Inert Atmosphere
For materials sensitive to oxygen at high temperatures, a controlled atmosphere furnace is required. It purges air from the chamber and replaces it with an inert gas like Argon or Nitrogen. This prevents oxidation and contamination, preserving the material's purity.
Vacuum: The Ultimate Control
A vacuum chamber furnace represents the highest level of environmental control. By removing nearly all atmospheric gases (achieving a vacuum degree as low as 5 Pa), it provides the cleanest possible environment. This is essential for processing highly reactive metals, advanced research, and high-purity sintering where any contamination is unacceptable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right type of chamber furnace depends entirely on the material you are processing and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is basic material preparation: A simple furnace for drying, baking, or curing in air is often sufficient.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation on common metals: A furnace with controlled inert gas (Argon or Nitrogen) capabilities is the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing, sintering, or working with reactive materials: A vacuum chamber furnace is the necessary and non-negotiable choice.
Ultimately, understanding the interplay between temperature and atmosphere is the key to leveraging a chamber furnace for your specific material engineering goals.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Feature | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Drying, Baking, Curing | Basic heating in air | Material preparation, polymer hardening |
| Heat Treatment | Precise temperature ramps | Annealing, tempering, hardening metals |
| Surface Modification | Reactive atmosphere (e.g., carburizing) | Hardening steel surfaces |
| High-Purity Sintering | Inert gas or vacuum atmosphere | Processing reactive metals, advanced ceramics |
Ready to achieve precise thermal processing for your materials?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance chamber furnaces for laboratories and industrial settings. Whether you need basic heating, advanced heat treatment, or high-purity sintering under controlled atmospheres, our equipment ensures accuracy, reliability, and superior results.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and discover the perfect chamber furnace solution for your lab's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results



















