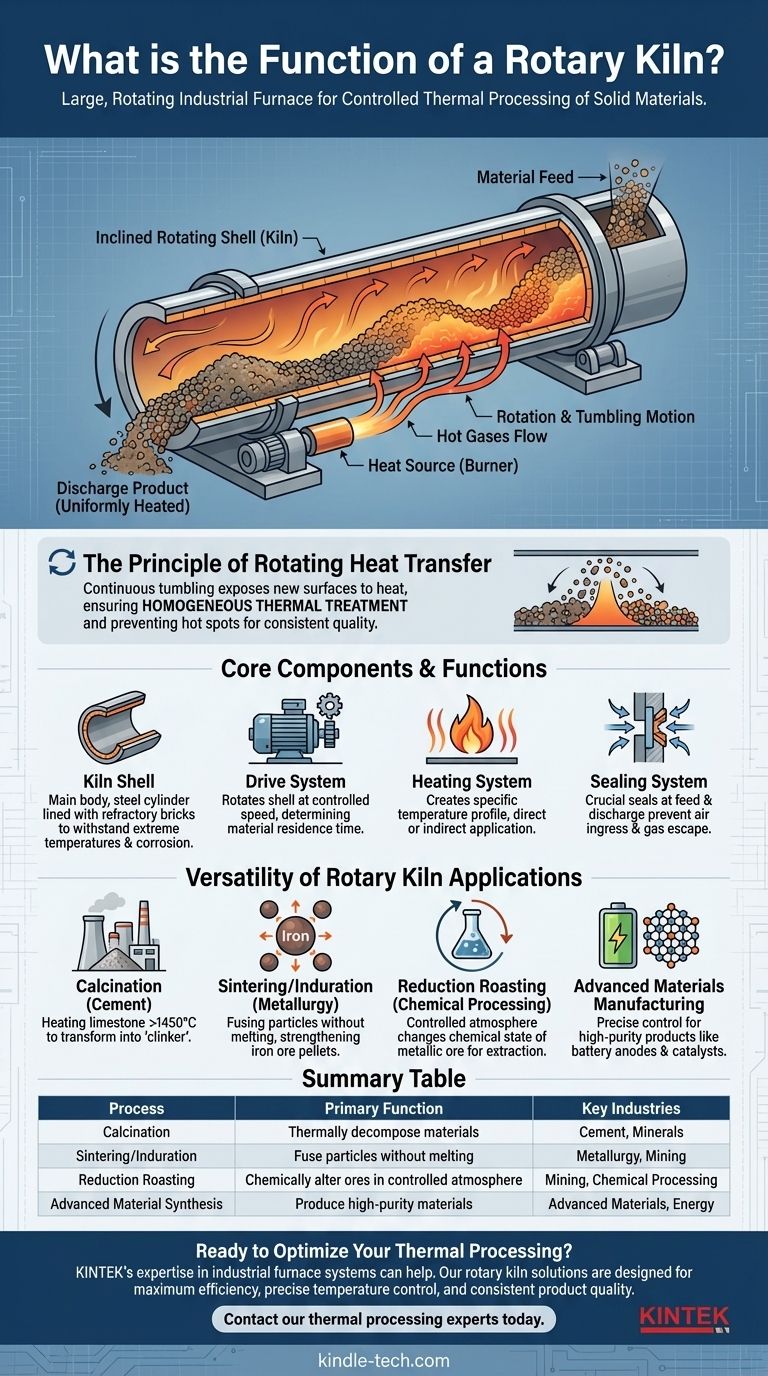
At its core, a rotary kiln is a large, rotating industrial furnace used to heat solid materials to extremely high temperatures. It functions as a powerful tool for inducing a specific chemical reaction or physical change, transforming raw materials into a new, desired product through a carefully controlled thermal process.
The fundamental advantage of a rotary kiln is its rotation. This continuous tumbling motion ensures every particle of the material is heated uniformly, leading to a highly consistent and predictable final product, which is critical for large-scale industrial applications.

How a Rotary Kiln Achieves Material Transformation
A rotary kiln is more than just a furnace; it is a dynamic processing system. Its design is engineered to combine heat, motion, and controlled residence time to achieve a specific outcome.
The Principle of Rotating Heat Transfer
The kiln is a long, cylindrical shell mounted at a slight incline. As the shell rotates, the solid material inside is continuously lifted and cascaded down through the hot gases.
This tumbling action is the key. It constantly exposes new surfaces of the material to the heat source, preventing hot spots and ensuring a homogenous thermal treatment that is impossible to achieve in a static furnace.
Core Components and Their Functions
A rotary kiln system is composed of several critical parts working in concert.
- The Kiln Shell: This is the main body, a large steel cylinder lined with refractory bricks. The bricks protect the steel from the extreme internal temperatures and any corrosive materials.
- The Drive System: A motor and gear system rotates the shell at a slow, controlled speed. The speed of rotation, along with the kiln's tilt, determines how long the material spends inside, known as its residence time.
- The Heating System: Heat can be applied directly, by a flame inside the kiln, or indirectly, where the shell is heated from the outside. The goal is to create a specific temperature profile along the length of the kiln to match the process requirements.
- The Sealing System: Seals at both the feed and discharge ends are crucial. They prevent cold air from entering the kiln, which would disrupt temperature control, and stop process gases or material dust from escaping.
The Versatility of Rotary Kiln Applications
The ability to control temperature, atmosphere, and residence time makes the rotary kiln exceptionally versatile. It is used across numerous industries for a wide range of thermal processes.
Calcination: Creating Cement
Perhaps the most common use of a rotary kiln is in cement manufacturing. Raw materials like limestone are heated to over 1450°C (2640°F) in a process called calcination, which transforms them into "clinker," the primary component of modern cement.
Sintering and Induration: Strengthening Materials
In metallurgy, kilns are used to sinter or indurate materials like iron ore pellets. This process heats the particles to just below their melting point, causing them to fuse together and gain significant strength and stability for further processing in a blast furnace.
Reduction Roasting: Chemical Processing
Kilns can facilitate chemical reactions by controlling the internal atmosphere. For example, reduction roasting is used in mining to change the chemical state of a metallic ore, making the desired metal easier to extract in subsequent steps.
Advanced Materials Manufacturing
The precise control offered by rotary kilns makes them essential for producing high-performance materials. This includes creating tungsten carbide (WC) for cutting tools, carbon materials, and silicon-based anode materials used in modern batteries.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Considerations
While powerful, operating a rotary kiln involves managing specific engineering challenges. Understanding these is key to its successful implementation.
The Challenge of Structural Integrity
The combination of extreme heat and the immense weight of the rotating shell and its contents puts enormous stress on the structure. Over time, the steel shell can deform slightly, which can reduce the lifespan of the internal refractory brick lining.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Many processes require a specific atmosphere, such as one rich in oxygen (oxidizing) or one lacking it (reducing). The effectiveness of the kiln's seals is paramount to maintaining this atmosphere, ensuring product quality and process efficiency.
High Energy Consumption
Bringing tons of material up to thousands of degrees is an energy-intensive process. Modern kilns incorporate sophisticated heat recovery systems, but energy remains a significant operational cost and a key factor in plant design.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary kiln is driven by the material you need to process and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-volume bulk material processing like cement or minerals: The rotary kiln's continuous, high-throughput nature makes it the industry standard for achieving consistent quality at scale.
- If your primary focus is specialty chemical or advanced material synthesis: The kiln's precise control over temperature profiles and internal atmosphere is crucial for producing high-purity products like battery components or industrial catalysts.
- If your primary focus is environmental remediation or waste processing: The kiln's ability to achieve thermal desorption or incineration is used to remove hazardous organic compounds from contaminated soil or to process industrial waste.
By combining intense heat with constant motion, the rotary kiln provides a uniquely powerful and adaptable solution for transforming solid materials on an industrial scale.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Function | Key Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Calcination | Thermally decompose materials (e.g., limestone to cement) | Cement, Minerals |
| Sintering/Induration | Fuse particles without melting (e.g., iron ore pellets) | Metallurgy, Mining |
| Reduction Roasting | Chemically alter ores in a controlled atmosphere | Mining, Chemical Processing |
| Advanced Material Synthesis | Produce high-purity materials (e.g., battery anodes, catalysts) | Advanced Materials, Energy |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Processing?
Whether your goal is high-volume production of cement or minerals, or the precise synthesis of specialty chemicals and advanced materials, KINTEK's expertise in industrial furnace systems can help. Our rotary kiln solutions are designed for maximum efficiency, precise temperature control, and consistent product quality.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory or industrial project with reliable, high-performance equipment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What is the primary function of an industrial rotary tube furnace? Master Tungsten Powder Hydrogen Reduction
- What are the advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for MoVOx catalysts? Elevate Uniformity and Crystallinity
- What is the purpose of pre-treating coal samples? Ensure Accurate Pyrolysis with Nitrogen Drying
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of rotary furnace? Maximize Uniformity & Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















