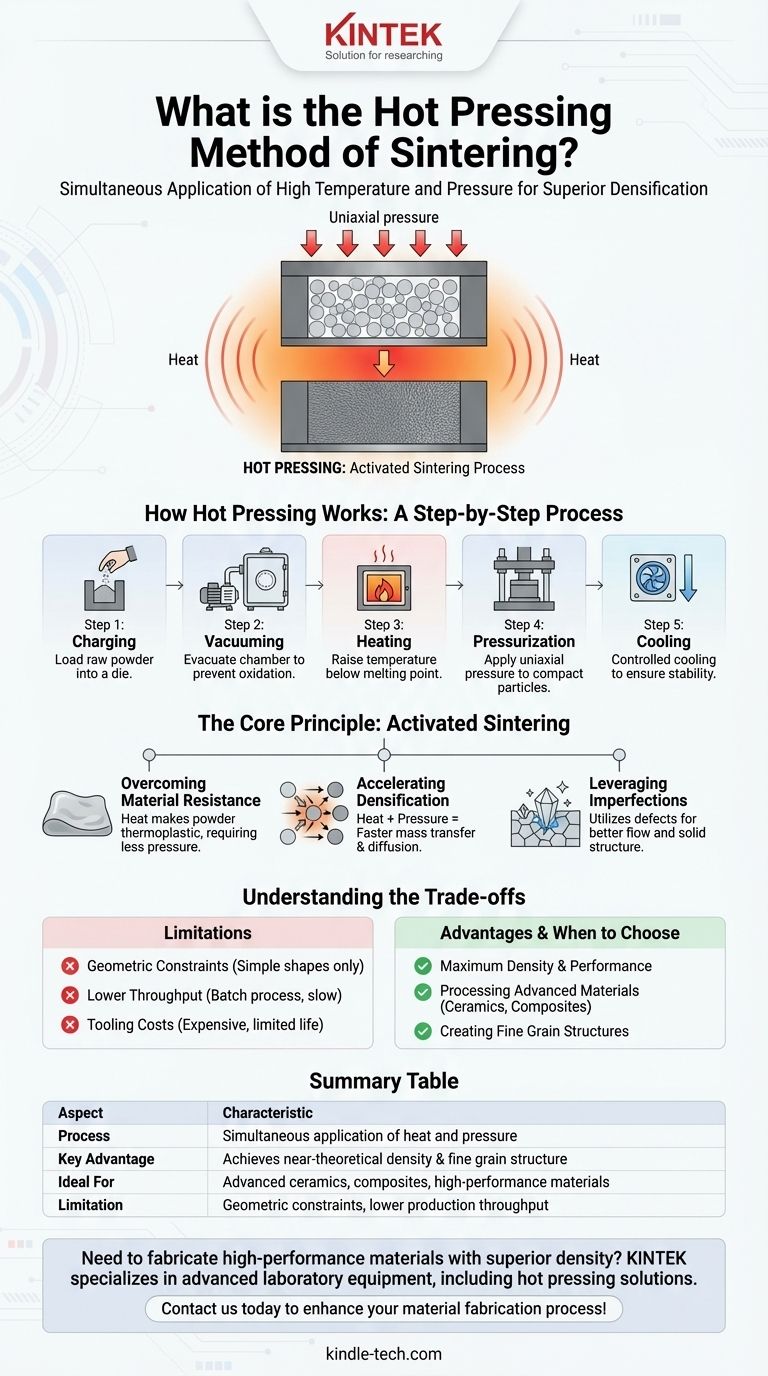
In essence, hot pressing is a powder metallurgy process that simultaneously applies high temperature and pressure to a loose powder to compact it into a dense, solid component. Unlike traditional methods that separate pressing and heating, this combined approach activates the sintering process, allowing for superior results at lower temperatures and in less time. It operates below the material’s melting point, using pressure to fuse the particles together and eliminate porosity.
The critical distinction of hot pressing is its efficiency. By applying heat and pressure at the same time, it enhances the atomic diffusion between particles, producing components with near-perfect density and a fine-grained internal structure that is often impossible to achieve with other methods.

How Hot Pressing Works: A Step-by-Step Process
The hot pressing process is methodical and precise, often taking place in a vacuum to prevent oxidation and remove impurities. The typical operational sequence follows five distinct stages.
Step 1: Charging
First, the raw material, typically a fine ceramic or metal powder, is loaded into a die or mold. This die is engineered to withstand the extreme temperatures and pressures of the process.
Step 2: Vacuuming
The entire furnace chamber containing the loaded die is evacuated. Creating a vacuum is critical for removing trapped gases and preventing unwanted chemical reactions with atmospheric elements at high temperatures.
Step 3: Heating
The furnace temperature is raised to the predetermined sintering temperature. This heat makes the powder particles more plastic and receptive to bonding, but it remains below the material's actual melting point.
Step 4: Pressurization
Once at the target temperature, uniaxial pressure is applied to the powder through a press or ram. This force squeezes the particles together, breaking down surface oxide layers and drastically reducing the empty space between them.
Step 5: Cooling
After holding at temperature and pressure for a sufficient duration, the component is cooled in a controlled manner. This gradual cooling prevents thermal shock and ensures the final part is stable and free of internal stresses.
The Core Principle: An Activated Sintering Process
Hot pressing is fundamentally different from simply pressing a powder cold and then heating it in a separate step. The simultaneous application of heat and pressure creates a highly efficient environment for densification.
Overcoming Material Resistance
Under heat, the powder enters a thermoplastic state, making it much softer and easier to deform. As a result, hot pressing often requires only 1/10th of the pressure needed for cold pressing the same material.
Accelerating Densification
The combination of heat and pressure significantly accelerates mass transfer and atomic diffusion between particles. This "activates" the sintering process, reducing the required temperature and time while inhibiting the growth of large, undesirable grains.
Leveraging Imperfections
The process is so effective that even powders with crystal defects can be densified to a high degree. The pressure helps utilize these defects as pathways for material flow, turning a potential weakness into an advantage for achieving a solid structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, hot pressing is not a universal solution. Its unique nature introduces specific limitations that must be considered.
Geometric Constraints
The process relies on a rigid die and uniaxial pressure, which inherently limits the complexity of shapes that can be produced. It is best suited for parts with relatively simple geometries, such as discs, blocks, or cylinders.
Lower Production Throughput
Hot pressing is a batch process. The cycle of loading, heating, pressing, and cooling a single component or a small batch of components is significantly slower than continuous processes like cold pressing followed by furnace sintering.
Tooling Costs and Durability
The dies and punches used must be made from materials that can withstand extreme heat and pressure simultaneously, such as graphite or advanced ceramics. This tooling is expensive to fabricate and has a limited operational life, adding to the overall cost per part.
When to Choose Hot Pressing
Your choice of manufacturing process should always align with your end goal. Hot pressing excels in specific scenarios where material performance is the highest priority.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and performance: Hot pressing is the ideal choice for creating components with near-theoretical density, fine grain structure, and superior mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is processing advanced materials: It is exceptionally effective for densifying non-oxide ceramics, composites, and other high-performance materials that are difficult to sinter using conventional methods.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: A traditional cold press and furnace sintering workflow will likely offer a more cost-effective and faster solution for less demanding applications.
Ultimately, hot pressing empowers you to create materials that are not just formed, but fundamentally optimized at a microscopic level.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hot Pressing Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Process | Simultaneous application of heat and pressure |
| Key Advantage | Achieves near-theoretical density and fine grain structure |
| Ideal For | Advanced ceramics, composites, and high-performance materials |
| Limitation | Geometric constraints and lower production throughput |
Need to fabricate high-performance materials with superior density?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment, including hot pressing solutions, to help you achieve optimal material properties for your research and production needs. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you have the right tools for densifying advanced ceramics, composites, and other challenging materials.
Contact us today to discuss how our hot pressing technology can enhance your material fabrication process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 99.1% Density in CuW30 Composites
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics



















