At its core, induction melting is a metallurgical process that uses powerful, fluctuating magnetic fields to turn solid metal into liquid. Instead of applying an external flame or electric arc, this method generates heat directly inside the metal itself, making it an exceptionally clean and efficient way to melt conductive materials.
The central principle of induction melting is turning the metal itself into the heat source. By inducing strong electrical currents within the charge, the process avoids direct contact and contamination, offering unparalleled control over the melting environment.
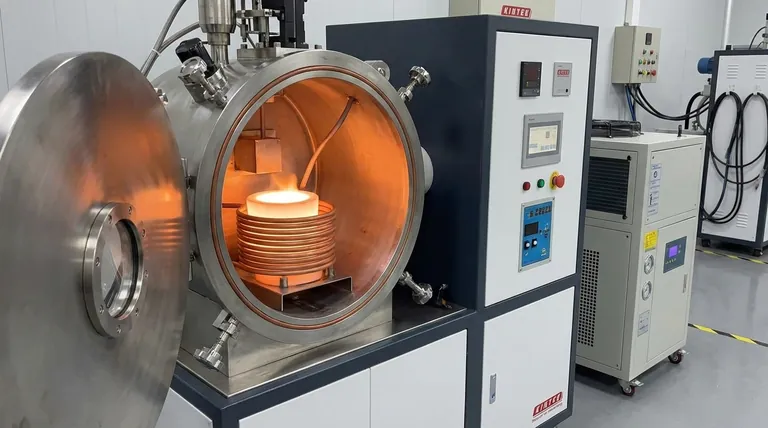

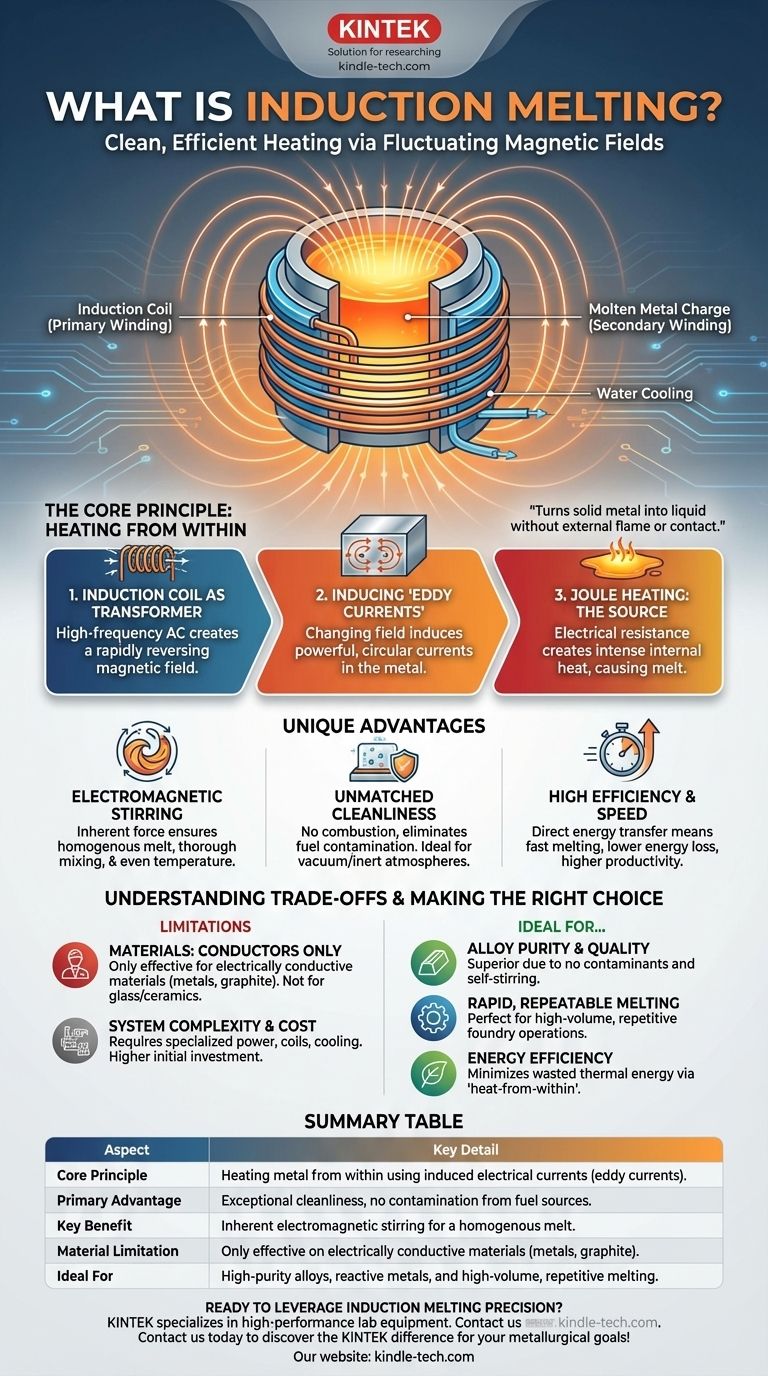
The Core Principle: Heating from Within
Induction melting operates on the fundamental laws of electromagnetism discovered by Michael Faraday. The entire process is a contactless form of energy transfer.
The Induction Coil as a Transformer
The system's primary component is a water-cooled copper coil. When a high-frequency alternating current (AC) from a power supply is passed through this coil, it generates a strong and rapidly reversing magnetic field in the space within the coil.
This setup functions like a transformer. The copper coil acts as the primary winding, and the metal placed inside it to be melted becomes the secondary winding.
Inducing "Eddy Currents" in the Metal
As the magnetic field rapidly changes direction, it induces powerful, circular electrical currents within the conductive metal. These are known as eddy currents.
This is the same principle used in many common technologies, but massively scaled up. The metal charge doesn't need to touch the coil; it only needs to be within its magnetic field.
Joule Heating: The Source of the Melt
The induced eddy currents flow against the metal's natural electrical resistance. This resistance creates intense heat, a phenomenon known as Joule heating.
This internally generated heat quickly raises the metal's temperature to its melting point and beyond, turning it into a liquid state without any external flame or element making contact.
The Unique Advantages of the Induction Method
The physics behind induction melting provides several distinct operational advantages over other methods, such as arc or gas furnaces.
Inherent Electromagnetic Stirring
The same forces that induce the eddy currents also exert a powerful stirring action on the molten metal. This electromagnetic stirring is a critical benefit.
It ensures that the entire batch of molten metal is homogenous, with alloying elements mixed thoroughly and the temperature distributed evenly. This leads to a higher quality and more consistent final product.
Unmatched Cleanliness and Purity
Because the heat is generated within the metal, there is no need for combustion. This completely eliminates contamination from fuel byproducts like gas and soot.
The process is so clean it can be performed in a vacuum or inert atmosphere, which is essential for melting reactive metals or producing alloys with extremely high purity.
High Efficiency and Speed
Induction heating is remarkably fast and efficient because energy is transferred directly to the material. Very little heat is lost to the surrounding environment compared to traditional furnaces where heat must radiate from an external source.
This speed and efficiency translate directly into lower energy consumption per ton of metal melted and higher productivity.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the induction method is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is tied directly to the physical properties of the material being melted.
Material Limitation: Conductors Only
The entire process relies on inducing electrical currents within the target material. Therefore, induction melting is only effective for electrically conductive materials, namely metals and certain conductive compounds like graphite.
It cannot be used to directly melt non-conductive materials such as glass, ceramics, or polymers, as the magnetic field will pass through them without inducing heat.
System Complexity and Cost
An induction furnace is a sophisticated piece of equipment. It requires a specialized high-frequency power supply, precisely engineered coils, and robust cooling systems.
This can result in a higher initial capital investment compared to simpler furnace designs. The frequency of the power supply must also be carefully matched to the size, shape, and type of metal being melted for optimal efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a melting process depends entirely on the requirements of your final product. Induction melting excels where control and purity are paramount.
- If your primary focus is alloy purity and quality: Induction is the superior choice due to the absence of contaminants and the self-stirring action that guarantees a homogenous mix.
- If your primary focus is rapid, repeatable melting: The speed and precise temperature control of induction systems make them ideal for high-volume, repetitive foundry operations.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: The "heat-from-within" principle makes induction one of the most energy-efficient melting technologies available, minimizing wasted thermal energy.
By understanding these core principles, you can determine if the precision and cleanliness of induction melting align with your specific metallurgical goals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Heating metal from within using induced electrical currents (eddy currents). |
| Primary Advantage | Exceptional cleanliness, no contamination from fuel sources. |
| Key Benefit | Inherent electromagnetic stirring for a homogenous melt. |
| Material Limitation | Only effective on electrically conductive materials (metals, graphite). |
| Ideal For | High-purity alloys, reactive metals, and high-volume, repetitive melting. |
Ready to leverage the precision of induction melting in your lab or foundry? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the ideal induction melting system to achieve superior metal purity, efficiency, and consistency for your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys



















