At its core, a furnace is an enclosed structure designed to generate and contain extremely high temperatures. While most commonly known for heating air in homes, the fundamental purpose of a furnace is to use controlled heat to either warm a space or, more broadly, to physically or chemically transform materials for industrial and scientific applications.
The term "furnace" is context-dependent. Its main purpose is always to generate controlled high heat, but whether that heat is used for personal comfort (like home heating) or for material processing (like melting metal or creating ceramics) depends entirely on its specific design and application.
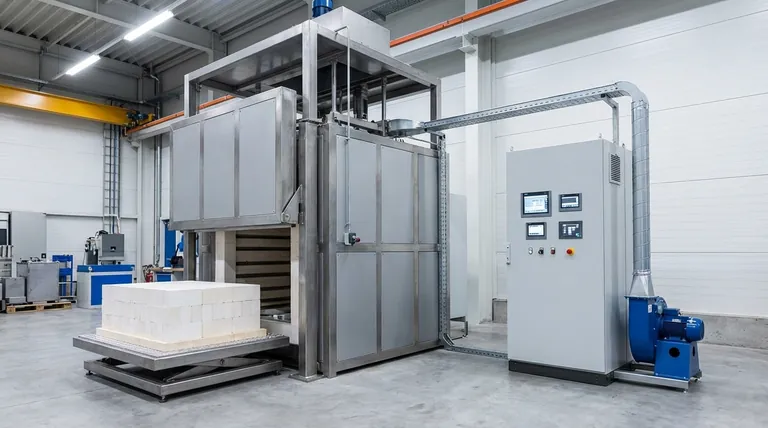

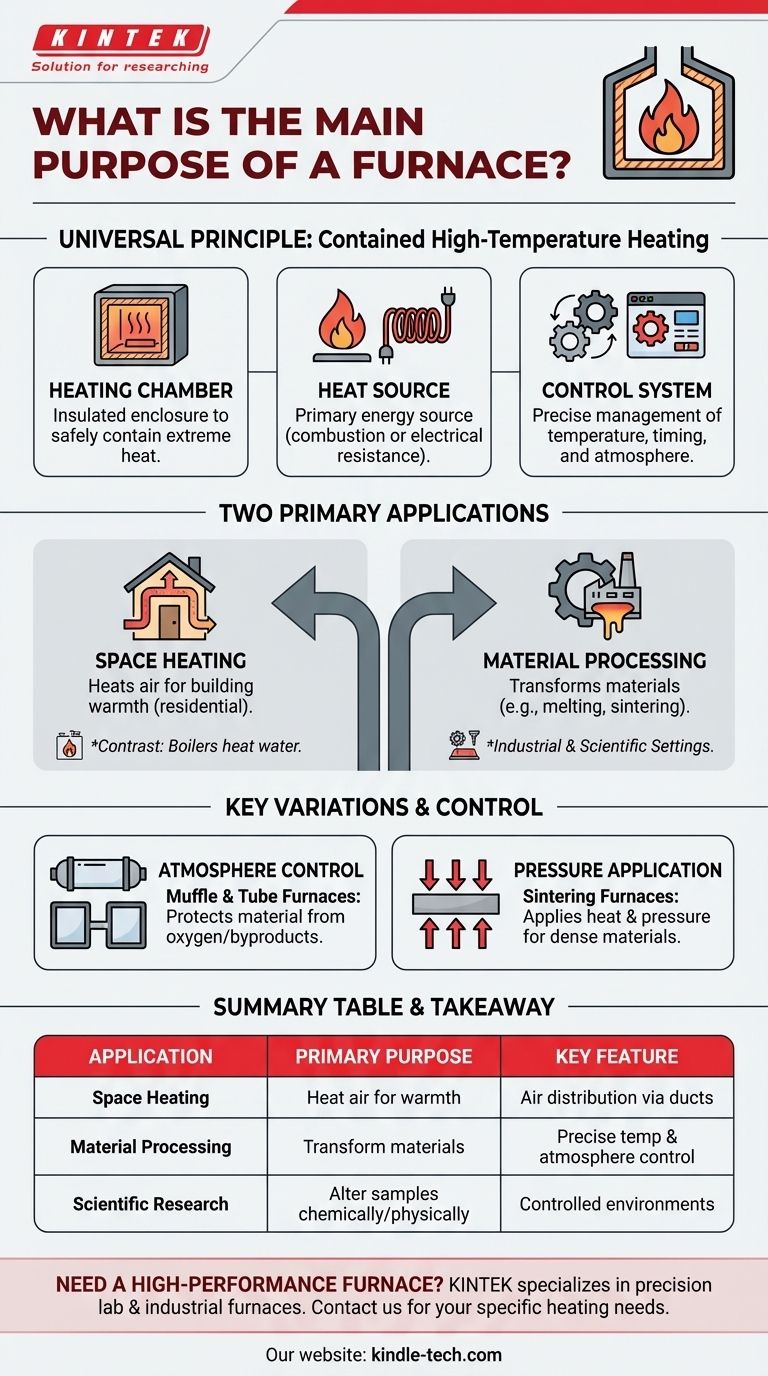
The Universal Principle: Contained High-Temperature Heating
Every device called a furnace, regardless of its end use, operates on the same foundational principles. Understanding these components clarifies its function.
The Heating Chamber
The heart of any furnace is an insulated enclosure. This chamber is designed to safely contain extreme heat, focus it on the target (air, water, or a material), and operate efficiently.
The Heat Source
To generate high temperatures, a furnace uses a primary energy source. This is most often the combustion of fuel like natural gas, but it can also be electrical resistance heating, as seen in many scientific and industrial models.
The Control System
Modern furnaces are not simple ovens. They rely on control systems, often a combination of a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) for safety and sequencing and a PC for the operator interface, to precisely manage temperature, timing, and atmospheric conditions.
The Two Primary Applications of a Furnace
The confusion around the word "furnace" stems from its two distinct and very different applications: providing comfort and processing materials.
Application 1: Space Heating (Comfort)
This is the furnace most people know. Its sole purpose is to heat air and distribute it throughout a building via a system of ducts to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
These systems are often contrasted with boilers, which serve the same purpose of heating a building but do so by heating water instead of air.
Application 2: Material Processing (Industrial & Scientific)
In industrial and scientific settings, a furnace is a tool for transformation. The high heat is used to alter the physical or chemical properties of a material.
Examples include melting furnaces for metal recycling, sintering furnaces for bonding materials like ceramics or diamond tool tips, and furnaces for the heat treatment of steel to change its hardness.
Understanding Key Furnace Variations
Specialized furnaces are defined by their ability to control the heating environment, which is critical for advanced manufacturing and research.
Controlling the Atmosphere: Muffle & Tube Furnaces
For many processes, the material being heated must be protected from the byproducts of combustion or even from oxygen in the air.
A muffle furnace achieves this with separate combustion and heating chambers. A tube furnace places the material inside a sealed tube that can hold a vacuum or be filled with a specific, non-reactive gas.
Applying Pressure: Sintering Furnaces
Some processes require more than just heat. A gas pressure sintering furnace, for example, is used to create dense, high-strength ceramic parts by applying intense heat and pressure simultaneously.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Misconceptions
Clarity on this topic requires acknowledging its common points of confusion.
Furnace vs. Boiler
This is the most common mix-up in a residential context. Remember the medium being heated: a furnace heats air, while a boiler heats water.
The Term is Context-Dependent
The purpose of a "furnace" to a homeowner is completely different from its purpose to a metallurgist or a research scientist. The application defines the specific function.
More Than Just Raw Heat
For industrial and scientific work, the most important feature is not just the maximum temperature but the degree of control. The ability to regulate the atmosphere (vacuum, specific gases) and apply pressure is what makes these furnaces such powerful tools.
Making the Right Interpretation
To understand what a furnace does, you must first understand its context.
- If you are discussing home systems: The furnace's purpose is to heat air and distribute it through ducts to warm a living space.
- If your context is industrial or scientific: A furnace is a specialized tool used to apply high heat—and often pressure or a controlled atmosphere—to physically or chemically transform a material.
- If you are simply defining the term: A furnace is any device that generates and contains high heat in a controlled environment for a specific outcome.
Ultimately, knowing the application is the key to understanding the furnace's purpose.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Purpose | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Space Heating (Comfort) | Heat air for building warmth | Distributes heated air via ducts |
| Material Processing (Industrial) | Transform materials (e.g., melting, sintering) | Precise temperature & atmosphere control |
| Scientific Research | Chemically or physically alter samples | Controlled environments (vacuum, specific gases) |
Need a high-performance furnace for your lab or industrial process? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including advanced furnaces for sintering, heat treatment, and material research. Our experts can help you select the right furnace with the exact temperature control and atmospheric conditions your application requires. Contact us today to discuss your specific heating needs and enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering process of powder metallurgy? Transform Powder into Durable Metal Parts
- What furnace is used for heat treatment? Match Your Process to the Perfect Equipment
- What properties can change during heat treatment process? Control Hardness, Strength, and More
- What is the source of electron beam welding? The High-Voltage Power Supply Explained
- Why is a vacuum oven used at 80°C to dry MOF precursors? Preserving Structural Integrity in Al-Based Materials
- How is heat transferred through a gas or vacuum? Master the 3 Key Mechanisms
- What are arc furnaces mainly used for? Efficiently Recycling Scrap into High-Quality Steel
- How does heat transmit in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Radiation for Purity & Precision



















