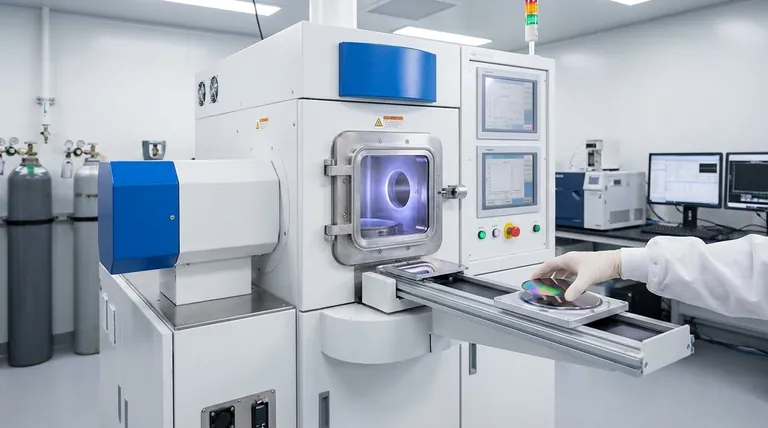
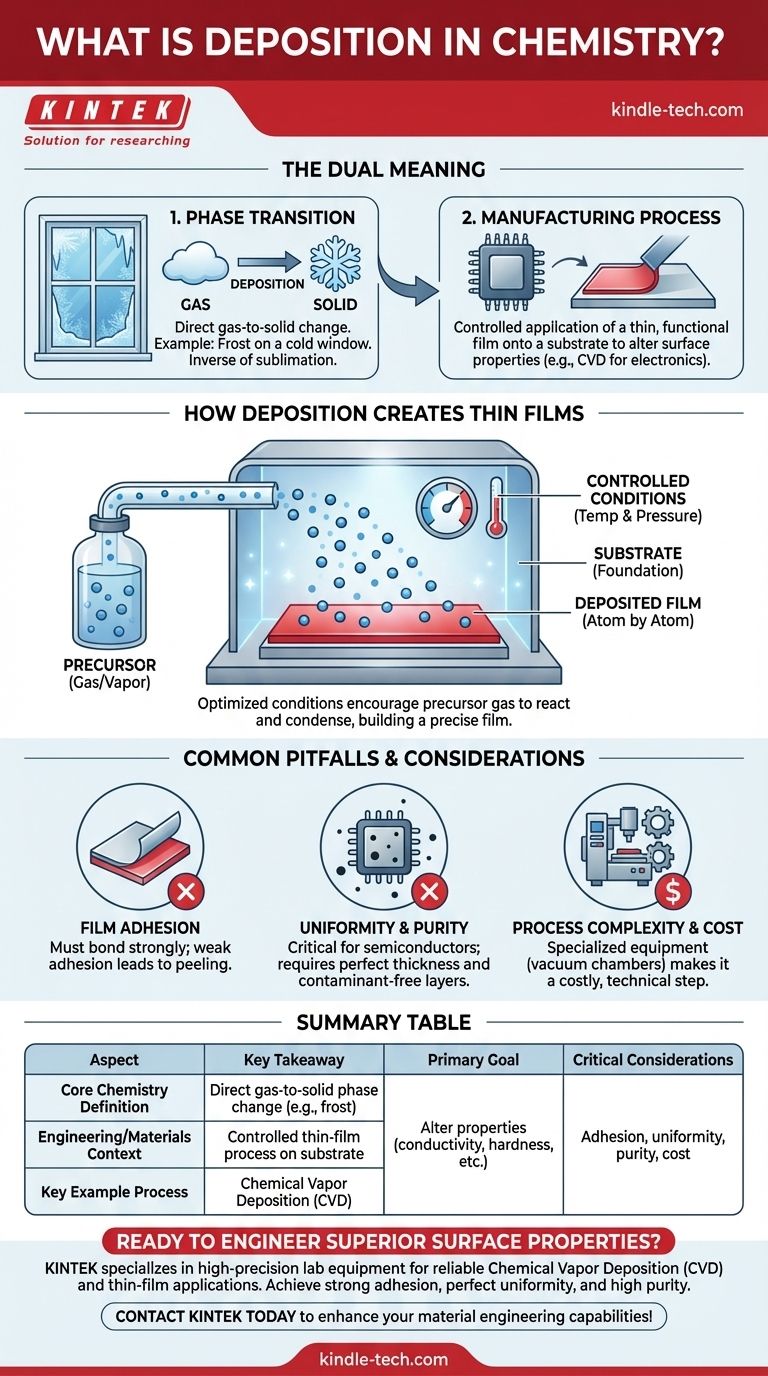
In chemistry, deposition is the process where a substance in a gaseous state transforms directly into a solid, bypassing the liquid phase. In a broader engineering and material science context, it refers to any process that deposits a layer of material onto a surface, or "substrate," to create a thin, functional film or coating.
At its core, deposition describes a change of state from gas to solid. This fundamental principle is harnessed by advanced manufacturing processes to build materials layer-by-layer, fundamentally altering the properties of a surface for technological applications.

The Two Core Meanings of Deposition
To truly understand deposition, it's essential to distinguish between its meaning as a natural phase transition and its use as a deliberate manufacturing technique.
Deposition as a Phase Transition
This is the classic textbook definition. It describes the direct transition of a substance from a gas to a solid.
The most common real-world example is frost forming on a cold window. Water vapor (a gas) in the air comes into contact with the freezing glass and turns directly into ice crystals (a solid) without first becoming liquid water.
This process is the direct opposite of sublimation, where a solid turns directly into a gas, like dry ice creating a fog.
Deposition as a Manufacturing Process
This is the application-focused meaning, particularly in fields like material science and electronics. Here, deposition is a highly controlled process used to apply a coating to a surface.
The goal is to build a thin film, often just atoms or molecules thick, on a foundation material called a substrate.
This deposited film imparts new properties to the substrate, such as electrical conductivity, hardness, or corrosion resistance. A key example is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where gases react near a surface to form a solid coating.
How Deposition Processes Create Thin Films
Controlled deposition is a cornerstone of modern technology. The process generally involves a few key elements working under precise conditions.
The Role of the Precursor
The process begins with a "precursor," which is the source material for the film. This precursor is introduced into a chamber in a gaseous or vapor state.
The Substrate as a Foundation
The substrate is the object or material that will be coated. It acts as the surface upon which the precursor gas will settle and solidify, forming the new layer.
Controlled Conditions are Key
The magic happens within a reaction chamber where variables like temperature and pressure are meticulously controlled.
These conditions are optimized to encourage the precursor gas to react and condense on the substrate, building the film atom by atom or molecule by molecule.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
While powerful, deposition is a precise science where small deviations can lead to failure. Understanding these challenges is key to appreciating the complexity of the process.
Film Adhesion
The single most common point of failure is adhesion. The deposited film must bond strongly to the substrate. If it doesn't, the coating can peel or flake off, rendering it useless.
Uniformity and Purity
For applications like semiconductors, the deposited layer must have a perfectly uniform thickness and be free of impurities. Even microscopic variations or contaminants can ruin the function of a microchip.
Process Complexity and Cost
The equipment required for high-quality deposition, such as vacuum chambers and specialized gas delivery systems, is complex and expensive. This often makes deposition a costly and highly technical step in manufacturing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding which definition of deposition matters most depends entirely on your context.
- If your primary focus is fundamental chemistry: Remember deposition as the direct phase transition from gas to solid, the inverse of sublimation.
- If your primary focus is engineering or materials: View deposition as a critical manufacturing technique for creating functional thin films and coatings on substrates.
- If your primary focus is technology: Recognize that deposition is the foundational process responsible for building the intricate layers inside the computer chips and optical lenses you use every day.
Ultimately, deposition is a perfect example of how a fundamental principle of nature is harnessed to engineer the world around us.
Summary Table:
| Aspect of Deposition | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Core Chemistry Definition | A direct phase change from a gas to a solid (e.g., frost formation). |
| Engineering/Materials Context | A controlled process to deposit a thin, functional film onto a substrate. |
| Primary Goal | To alter surface properties like conductivity, hardness, or corrosion resistance. |
| Key Example Process | Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where reactive gases form a solid coating. |
| Critical Considerations | Film adhesion, uniformity, purity, and process cost/complexity. |
Ready to Engineer Superior Surface Properties?
Whether you are developing next-generation semiconductors, durable protective coatings, or advanced optical components, the right deposition process is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-precision lab equipment and consumables needed for reliable Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and other thin-film applications.
Our solutions help you achieve the strong adhesion, perfect uniformity, and high purity your projects demand. Let our experts help you select the ideal equipment for your specific substrate and coating goals.
Contact KINTALK today to discuss your deposition needs and enhance your material engineering capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating














