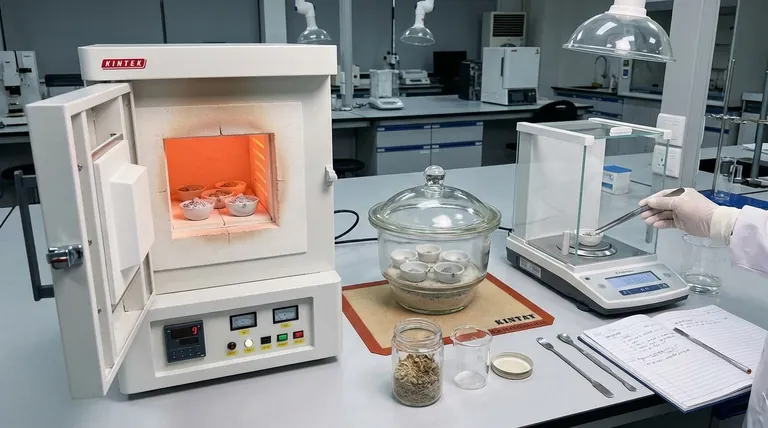
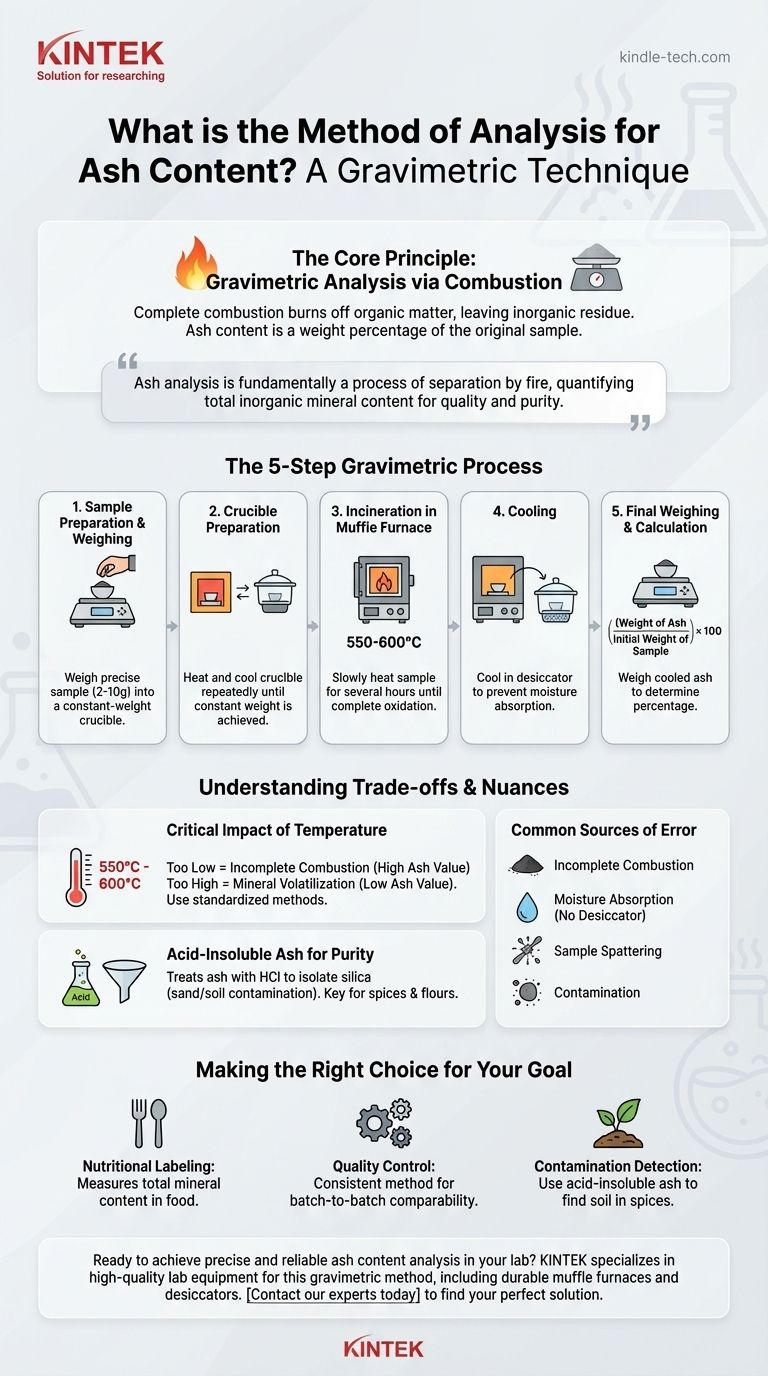
The principal method of analysis for ash content is a gravimetric technique involving the complete combustion of a sample at high temperatures. This process, known as incineration or "ashing," burns away all organic material, leaving behind only the inorganic, noncombustible residue. This residue is then weighed to determine the ash content as a percentage of the original sample's mass.
Ash analysis is fundamentally a process of separation by fire. By weighing a sample before and after controlled incineration, you can precisely quantify its total inorganic mineral content, which is a critical indicator of quality, purity, and nutritional value.

The Core Principle: Gravimetric Analysis via Combustion
The determination of ash content is one of the most fundamental analyses in food science, materials testing, and agricultural science. The entire procedure is based on a simple mass balance.
Step 1: Sample Preparation and Initial Weighing
The first step is to obtain a representative sample and homogenize it to ensure the portion being tested is indicative of the whole.
A precise, known mass of the sample (typically 2-10 grams) is weighed into a container called a crucible. The accuracy of this initial weight is critical for the final calculation.
Step 2: Preparing the Crucible
The crucible itself, usually made of porcelain or another high-temperature-resistant material, must be prepared. It is heated in the furnace at the ashing temperature, cooled in a desiccator, and weighed.
This heating and cooling cycle is repeated until the crucible reaches a constant weight. This ensures that any moisture or volatile substances in the crucible material are removed, preventing them from interfering with the final measurement.
Step 3: Incineration in a Muffle Furnace
The crucible containing the sample is placed in a muffle furnace, a specialized high-temperature oven. The temperature is slowly increased to the target, typically between 550°C and 600°C.
The sample is held at this temperature for several hours, or until the combustion is complete. The goal is the complete oxidation of all organic matter (C, H, O, N) into gaseous products like CO₂, H₂O, and NOx, leaving a light gray or white residue.
Step 4: Cooling and Final Weighing
After incineration, the crucible containing the ash is carefully removed from the furnace and placed in a desiccator.
A desiccator is a sealed container with a drying agent that prevents the hot, dry ash from absorbing moisture from the atmosphere as it cools. Reabsorbing moisture would artificially inflate the final weight.
Once cooled to room temperature, the crucible with the ash is weighed again.
The Final Calculation
The calculation is straightforward and expressed as a weight percentage.
Ash Content (%) = (Weight of Ash / Initial Weight of Sample) × 100
For example, if you started with 5.0 grams of sample and were left with 0.1 grams of ash, the ash content would be 2.0%.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
While the method is simple in principle, accuracy depends on controlling key variables. Misinterpreting the results is easy without understanding the context.
The Critical Impact of Temperature
The chosen temperature is a compromise. If it's too low, combustion may be incomplete, leaving carbon behind and leading to an artificially high ash value.
If the temperature is too high, some inorganic minerals can decompose or volatilize (e.g., chlorides and carbonates), leading to an artificially low ash value. Standardized methods (like AOAC) specify exact temperatures for different sample types to ensure reproducibility.
"Acid-Insoluble Ash" for Purity
In some applications, a further step is required. The ash is treated with hot hydrochloric acid (HCl), and the remaining insoluble material is filtered, washed, dried, and weighed.
This acid-insoluble ash value is a measure of silica content, often representing sand or soil contamination. It is a key purity test for spices, flours, and other plant-based products.
Common Sources of Error
- Incomplete Combustion: A black or dark gray ash indicates residual carbon. The sample needs more time in the furnace.
- Moisture Absorption: Failing to use a desiccator for cooling is a primary source of error, leading to falsely high results.
- Sample Spattering: Heating the sample too quickly can cause it to spatter, resulting in physical loss of material and a falsely low reading.
- Contamination: Any foreign material entering the sample or crucible will affect the final weight.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application of ash analysis dictates how you should interpret the results and which procedural details are most important.
- If your primary focus is nutritional labeling: Understand that total ash content is a direct measure of the total mineral content in a food product.
- If your primary focus is quality control for a processed good: Emphasize maintaining a consistent, documented temperature and time for all tests to ensure results are comparable batch-to-batch.
- If your primary focus is detecting contamination (like soil in spices): Use the "acid-insoluble ash" method for a more specific measurement that isolates silica-based impurities.
Mastering this fundamental technique provides a clear and reliable window into the inorganic composition of your material.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Weigh sample into a pre-weighed crucible. | Obtain a precise initial mass for calculation. |
| 2. Incineration | Heat in a muffle furnace (550-600°C). | Burn off organic matter, leaving inorganic ash. |
| 3. Cooling | Cool crucible in a desiccator. | Prevent ash from absorbing atmospheric moisture. |
| 4. Weighing | Weigh the crucible with the cooled ash. | Determine the mass of the inorganic residue. |
| 5. Calculation | (Ash Weight / Sample Weight) x 100. | Calculate the final ash content percentage. |
Ready to achieve precise and reliable ash content analysis in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in the high-quality lab equipment essential for this gravimetric method, including durable muffle furnaces for controlled incineration and desiccators for accurate cooling. Our products are designed to help your laboratory, whether in food science, materials testing, or agriculture, minimize errors and ensure consistent, reproducible results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your analytical needs and enhance your quality control processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of sintered glass? Precision Filtration and Gas Dispersion for Labs
- What are the risk factors associated with CVD? Take Control of Your Heart Health Today
- What thickness is magnetron sputtering for coating? Achieve Precise, Functional Thin Films
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of a centrifuge? Weighing Speed Against Cost and Risk
- What is the difference between traditional sintering and selective laser sintering? Choose the Right Manufacturing Path
- What is a lab oven used for? A Guide to Precise Heating, Sterilization & Drying
- How are CVD diamonds detected? Unveiling the Science Behind Lab-Grown Diamond Identification
- What is terpene distillate? A Guide to High-Potency, Flavored Cannabis Oil



















