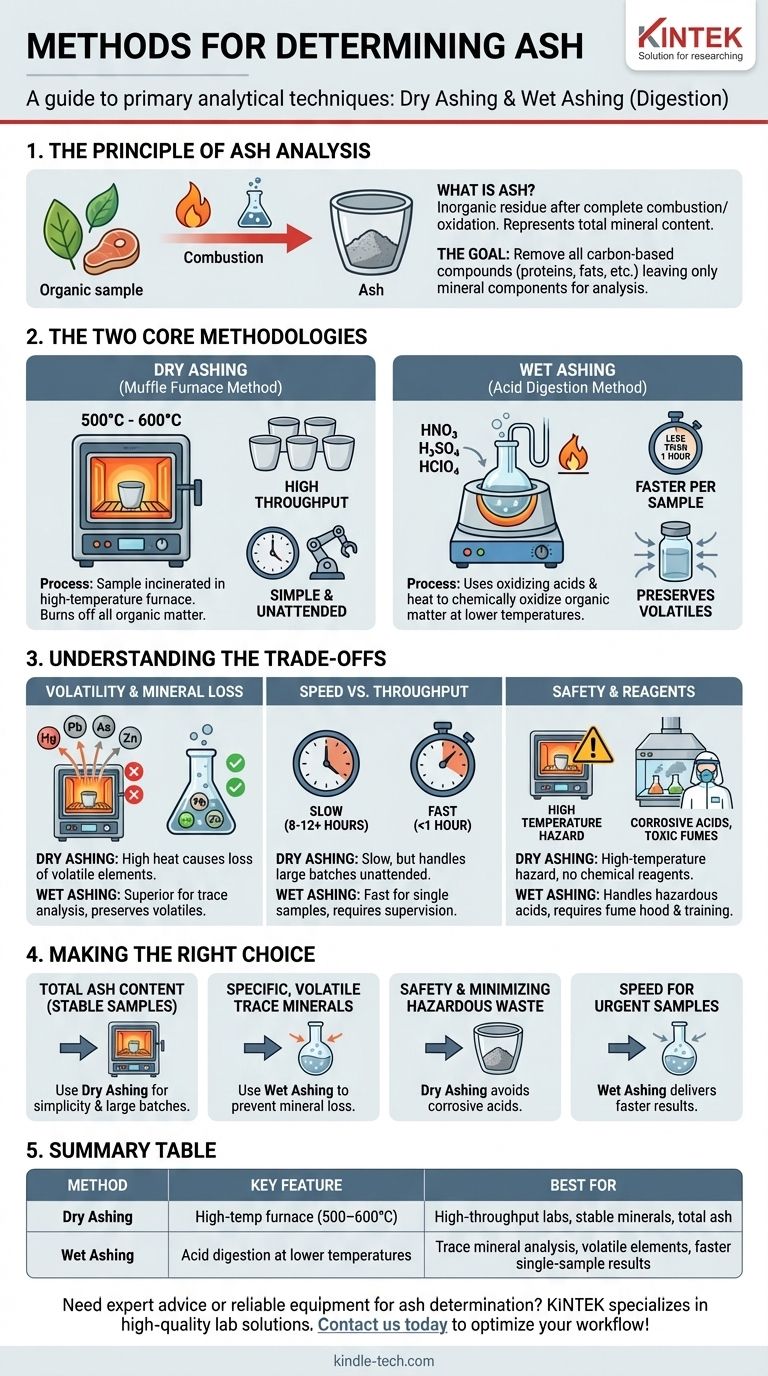
The primary methods for determining ash are dry ashing and wet ashing (also known as wet digestion). Dry ashing involves incinerating a sample at high temperatures in a muffle furnace to burn off all organic matter, while wet ashing uses oxidizing acids to achieve the same result at lower temperatures.
The choice between ashing methods is not about which is "better," but which is appropriate for your specific analytical goal. The decision hinges on the trade-offs between speed, safety, sample throughput, and the potential for losing volatile minerals during analysis.

The Principle of Ash Analysis
What is Ash?
Ash is the inorganic residue that remains after the complete combustion or oxidation of organic matter in a sample. It represents the total mineral content.
This analysis is a critical measure of quality and composition in industries ranging from food science and agriculture to materials science and environmental testing.
The Goal: Removing Organic Matter
The fundamental goal of any ashing technique is to remove all carbon-based compounds (proteins, fats, carbohydrates, plastics) while leaving the inorganic mineral components behind.
The resulting ash can then be weighed to determine the total mineral content or be further analyzed to identify specific mineral elements.
The Two Core Methodologies
Dry Ashing: The Muffle Furnace Method
Dry ashing is the most common technique. The sample is placed in a high-temperature-resistant crucible and heated in a muffle furnace, typically between 500°C and 600°C.
The extreme heat causes all organic substances to ignite and burn off, leaving only the non-combustible ash. This process is simple, requires minimal hands-on time, and is effective for processing many samples at once.
Wet Ashing: The Acid Digestion Method
Wet ashing, or wet digestion, uses a combination of strong acids (like nitric, sulfuric, or perchloric acid) and heat to chemically oxidize the organic matter.
This method is performed at much lower temperatures than dry ashing. It is significantly faster per sample and is the preferred method when analyzing for minerals that could vaporize and be lost at the high temperatures of a muffle furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Volatility and Mineral Loss
This is the most critical consideration. The high temperatures of dry ashing can cause volatile elements like arsenic, mercury, lead, zinc, and certain chlorides to turn into gas and escape, leading to an underestimation of their presence.
Wet ashing is superior for trace mineral analysis because its lower operating temperatures preserve these volatile components in the sample.
Speed vs. Throughput
Wet ashing is faster for a single sample, often taking less than an hour for complete digestion. However, it is labor-intensive and requires constant supervision.
Dry ashing is a very slow process, often taking 8-12 hours or more. Its advantage is that dozens of samples can be placed in the furnace and left unattended, making it ideal for high-throughput labs not concerned with volatile minerals.
Safety and Reagents
Dry ashing primarily involves the hazard of a high-temperature furnace. The process itself is free of chemical reagents.
Wet ashing requires the handling of extremely corrosive and hazardous acids. It must be performed in a specialized fume hood, and technicians require specific training to manage the risks of acid splatters and toxic fumes.
Other Specialized Techniques
For highly specific applications, other methods exist. Sulfated ashing uses sulfuric acid to convert metal oxides into more stable sulfates before furnace ignition. Low-temperature plasma ashing uses energized oxygen to oxidize a sample at even lower temperatures (around 150°C), providing maximum retention of volatile elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
Choosing the correct ashing method is essential for generating accurate and reliable data. Your selection should be dictated by the specific goals of your analysis and the nature of your sample.
- If your primary focus is total ash content for stable samples: Use dry ashing for its simplicity and ability to handle large batches.
- If your primary focus is analyzing for specific, volatile trace minerals: Use wet ashing to prevent mineral loss and ensure accurate quantification.
- If your primary focus is safety and minimizing hazardous waste: Dry ashing avoids the use of corrosive acids, though it presents a high-temperature hazard.
- If your primary focus is speed for a small number of urgent samples: Wet ashing will deliver results much faster than waiting for a furnace cycle.
Ultimately, aligning the method's characteristics with your analytical objective is the key to achieving trustworthy results.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Ashing | High-temperature furnace (500-600°C) | High-throughput labs, stable minerals, total ash content |
| Wet Ashing | Acid digestion at lower temperatures | Trace mineral analysis, volatile elements, faster single-sample results |
Need a reliable muffle furnace for dry ashing or expert advice on choosing the right ashing method? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution for accurate and efficient ash determination. Contact us today to optimize your analytical workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How long should a furnace take to raise the temperature? Key Factors for Optimal Heating Speed
- How does the calcination process work? Master Thermal Decomposition for Material Purification
- What do you use a muffle furnace for? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between a hot air oven and a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Tool for Your Thermal Process
- Will brazing stick to cast iron? A Low-Heat Joining Solution for Crack-Free Repairs



















