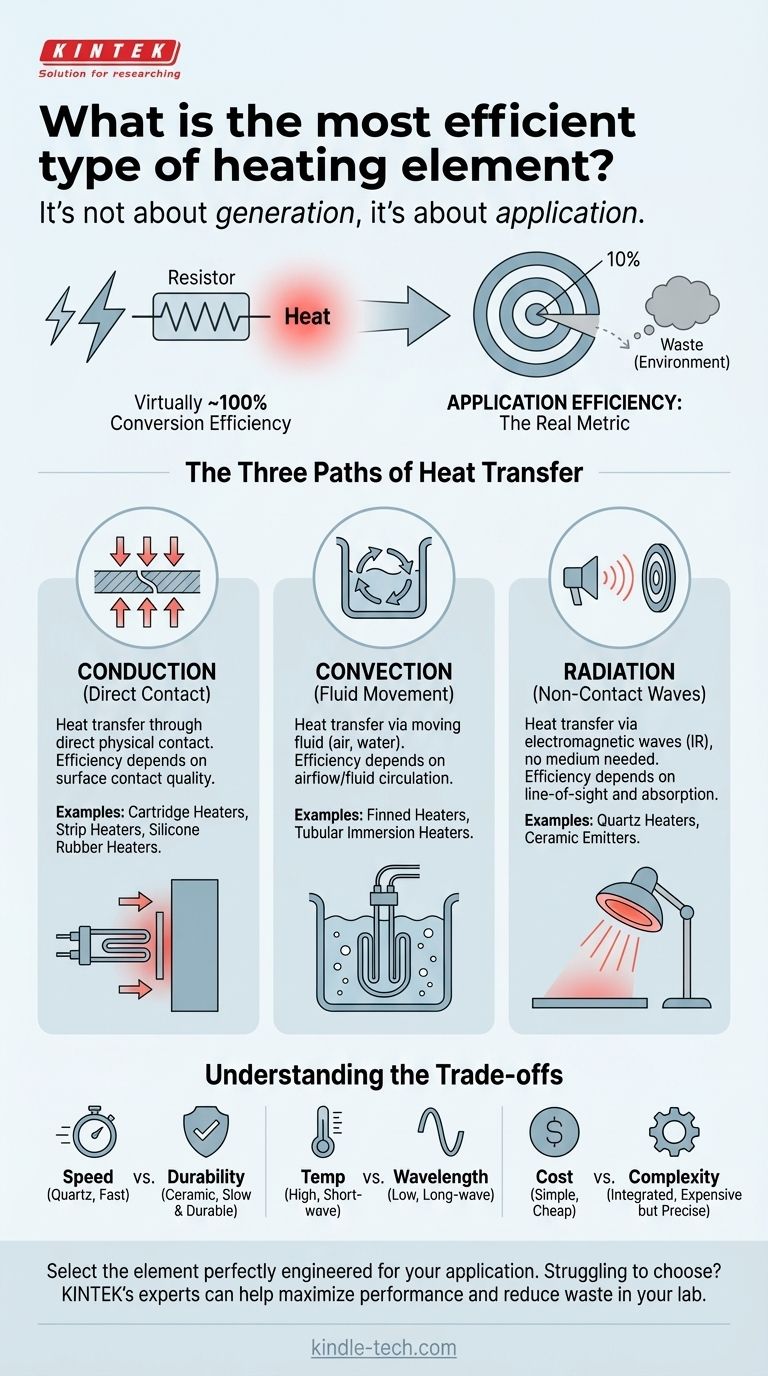
In terms of pure energy conversion, virtually all modern resistive heating elements—whether they are simple nichrome wires, quartz tubes, or advanced ceramics—are nearly 100% efficient. They operate on the principle of Joule heating, where electrical energy passing through a resistor is converted directly into thermal energy. The critical distinction is not how efficiently an element creates heat, but how effectively it transfers that heat to a specific target.
The search for the "most efficient" heating element is a misunderstanding of the core physics. The true measure of efficiency lies in the application—how well the element's heat transfer method (conduction, convection, or radiation) matches your specific heating task with minimal waste.

Redefining "Efficiency" in Heating Systems
Choosing the right heating element requires shifting your focus from heat generation to heat transfer. An element that is perfect for one task can be remarkably inefficient for another, even if both produce the same amount of heat.
The Physics of Near-100% Conversion
All resistive heaters function by impeding the flow of electricity. This electrical resistance forces the energy from the electrons to be released as heat.
According to the First Law of Thermodynamics, energy cannot be created or destroyed. Therefore, virtually every watt of electricity consumed by the resistive element is converted into a watt of heat. The 96-99% figures often cited account for trivial energy losses to light or electromagnetic fields, but for practical purposes, conversion is total.
The Real Metric: Application Efficiency
Application efficiency is the measure of how much of that generated heat successfully reaches and is absorbed by your target material or space. The rest is lost to the surrounding environment.
A 1000-watt heater warming a small part in a large, uninsulated chamber is incredibly inefficient, as most of its heat is lost. That same heater, when perfectly integrated with the part, can be highly efficient.
The Three Paths of Heat Transfer
The "best" element is simply the one that uses the optimal heat transfer method for your goal.
- Conduction: Heat transfer through direct physical contact.
- Convection: Heat transfer through the movement of a fluid (like air or water).
- Radiation: Heat transfer via electromagnetic waves (like infrared), which requires no medium.
How Heat Transfer Methods Dictate Element Choice
The type of heating element is defined by which of the three transfer methods it is designed to maximize.
Conduction Heaters: For Direct Contact
These elements excel at heating solid objects by being in direct contact with them. Examples include cartridge heaters, strip heaters, and silicone rubber heaters.
Their efficiency is almost entirely dependent on the quality of the surface contact. Any air gaps, however small, will dramatically reduce the rate of heat transfer and waste energy.
Convection Heaters: For Heating Fluids
Convection heaters are designed to heat a moving fluid, such as air or a liquid. Common examples are finned heaters and tubular immersion heaters.
The element heats the fluid in contact with it, which then circulates and transfers heat throughout the volume. Their efficiency depends on factors like airflow, fluid viscosity, and preventing heat loss from the containment vessel.
Radiation Heaters: For Non-Contact Targeting
Radiant heaters transfer energy via infrared waves, heating objects directly without needing to heat the air in between. Quartz heaters and ceramic emitters are primary examples.
Ceramic elements, like the one in your reference, are excellent at producing long-wave infrared energy. This makes them highly effective for uniformly heating surfaces, drying coatings, or thermoforming plastics, as the radiant energy can be precisely directed at the target. Their efficiency is a function of line-of-sight and the target's ability to absorb infrared energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting an element is never about a single metric. You must balance competing factors to find the optimal solution for your system.
Speed vs. Durability
Quartz tube heaters have very low thermal mass, allowing them to heat up and cool down in seconds. This makes them ideal for applications requiring rapid cycling, but they can be more fragile. In contrast, heavy-duty tubular or ceramic elements have higher thermal mass, heat up more slowly, but offer superior mechanical durability and a longer lifespan.
Temperature vs. Wavelength
The temperature of the heating element determines the wavelength of the infrared energy it emits. High-temperature quartz emitters produce short-wave IR, which is more penetrative. Lower-temperature ceramic emitters produce long-wave IR, which is more readily absorbed by the surface of many organic materials and water.
Cost vs. System Complexity
A simple open coil nichrome wire is the cheapest element, but it may require a complex and well-designed system to direct its heat effectively. An integrated ceramic or quartz emitter array is more expensive upfront but provides controlled, directional heat that can simplify system design and improve overall application efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Stop asking which element is most efficient and start asking which element is best suited for your heat transfer challenge.
- If your primary focus is heating a solid object via direct contact: Choose a conduction heater like a cartridge or strip heater and ensure excellent surface contact.
- If your primary focus is heating a volume of air or a liquid: Choose a convection heater like a finned or immersion element and manage the fluid flow.
- If your primary focus is heating a surface from a distance: Choose a radiation heater like a quartz or ceramic element and match its wavelength to your target's absorption properties.
Ultimately, the most efficient heating element is the one engineered to solve your specific heat transfer problem with the least possible waste.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Method | Best For | Common Element Types |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Heating solid objects via direct contact | Cartridge, Strip, Silicone Rubber Heaters |
| Convection | Heating volumes of air or liquid | Finned, Tubular Immersion Heaters |
| Radiation | Non-contact surface heating from a distance | Quartz Tube, Ceramic Emitter Heaters |
Struggling to choose the right heating element for your lab equipment? You're not alone. The 'most efficient' element is the one perfectly engineered for your specific application—whether it's precise temperature control for a furnace, uniform heating for a reactor, or rapid thermal cycling for a testing device.
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, and we understand that your laboratory's efficiency depends on optimal heat transfer. Our experts can help you select the ideal heating element to maximize performance, reduce energy waste, and ensure repeatable results.
Don't let inefficiency slow down your research. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how the right heating solution can transform your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Buchner Funnel and Triangular Funnel
People Also Ask
- What is the thermal expansion coefficient of molybdenum disilicide? Understanding its role in high-temperature design
- What function do molybdenum disilicide heating elements perform? Precision Heat for Pulverized Coal Research
- What are the heating elements for high temperature furnaces? Select the Right Element for Your Atmosphere
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance



















