The primary negative effect of quenching steel is the creation of extreme internal stresses as the metal rapidly and unevenly cools. These stresses are the root cause of the two most common failures: the part can physically crack, or it can warp and distort, losing its required shape and dimensional accuracy. Quenching also leaves the steel in an extremely hard but brittle state, making it unusable for most applications without further treatment.
Quenching is a controlled, violent process necessary to achieve high hardness in steel. Its negative effects—cracking, distortion, and brittleness—are not flaws to be avoided, but inherent risks that must be managed through careful process control and subsequent tempering.
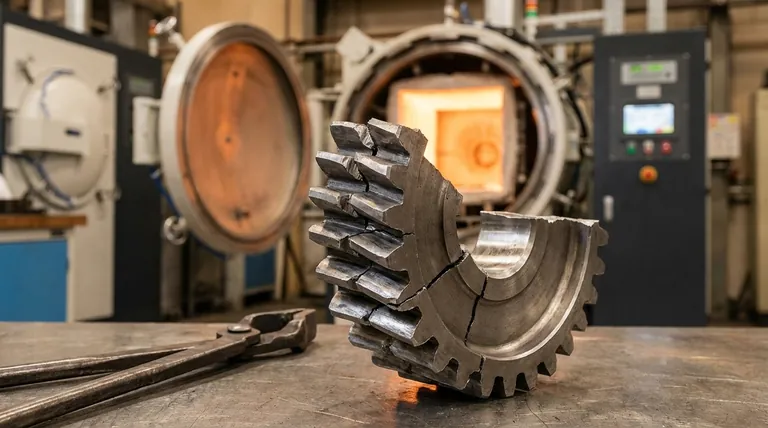

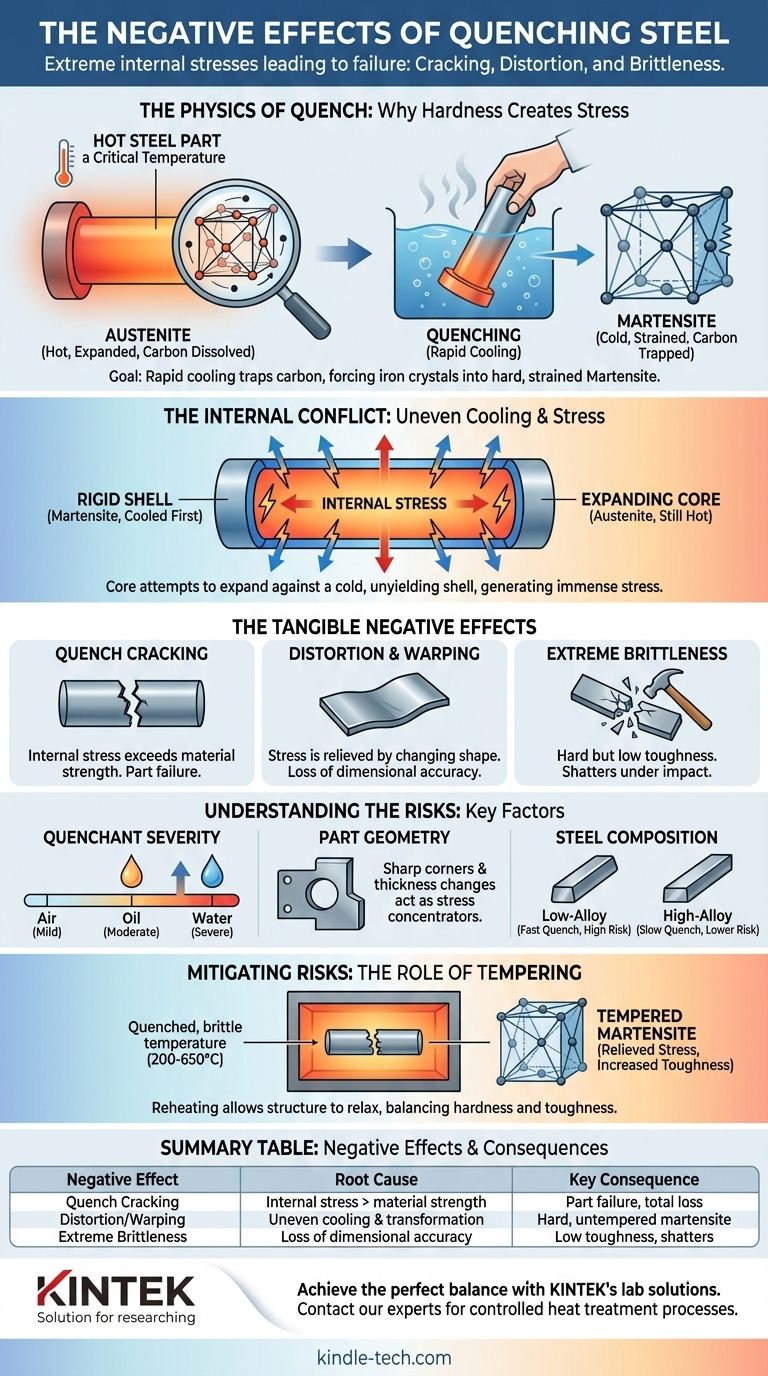
The Physics of the Quench: Why Hardness Creates Stress
To understand why quenching has negative effects, you must first understand its purpose. The goal is to rapidly cool steel from a high temperature to create a specific crystal structure.
The Goal: Creating Martensite
When steel is heated to its critical temperature (austenitizing), its carbon atoms are dissolved within a crystal structure called austenite. If cooled slowly, the carbon atoms have time to move and form softer structures.
Quenching traps these carbon atoms in place, forcing the iron crystals to contort into a new, highly strained, and very hard structure called martensite. This hardness is the desired outcome.
Uneven Cooling and Transformation
The problem begins because a steel part cannot cool instantly or uniformly. The outer surface is exposed to the quenching medium (water, oil, air) first and cools most rapidly.
This surface layer transforms to hard, rigid martensite while the core of the part is still hot, expanded, and in its softer austenitic state.
The Internal Conflict
As the core finally cools and transforms into martensite, it attempts to expand. However, it is now trapped within a cold, unyielding shell of already-formed martensite.
This creates an internal battle: the expanding core pushes outward, while the hardened shell constrains it. This conflict generates immense internal stress.
The Tangible Negative Effects
This internal stress manifests in several catastrophic or performance-degrading ways.
Quench Cracking
If the internal stress exceeds the ultimate tensile strength of the newly formed, brittle martensite, the steel will fracture. This is a quench crack.
These cracks often originate at points of high stress concentration, like sharp internal corners or abrupt changes in the part's thickness. A quench crack is a total failure of the part.
Distortion and Warping
If the internal stress is not high enough to cause a crack, it will instead relieve itself by changing the shape of the part. This is distortion or warping.
Long, thin parts may bow, flat parts may "potato chip," and round parts may go out-of-round. For precision components like gears, bearings, or molds, even minor distortion can render the part useless.
Extreme Brittleness
The as-quenched martensitic structure, while extremely hard, has very low toughness. Toughness is the ability to absorb energy and deform without fracturing.
An as-quenched part is like glass: it can resist scratching (hardness) but will shatter if dropped or struck (low toughness). This makes it unsuitable for any application that experiences impact or dynamic loads.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Factors That Increase Risk
The severity of these negative effects is not random. It is a direct result of several key variables in the material and the process.
Quenchant Severity
The faster the cooling rate, the greater the thermal shock and the higher the internal stress.
Water is a very severe quenchant, removing heat extremely quickly and creating the highest risk of cracking and distortion. Oil is less severe, and air is the mildest. The choice of quenchant must be matched to the steel's requirements.
Part Geometry
Complex shapes are inherently riskier. Sharp internal corners, holes, and sudden changes from thick to thin sections act as stress concentrators.
These features provide a natural starting point for quench cracks and are the areas most likely to distort. Good design practice calls for generous radii and uniform cross-sections where possible.
Steel Composition (Hardenability)
The alloys in steel determine its hardenability—its ability to form martensite at slower cooling rates.
Low-alloy steels (like 1095) have low hardenability and require a very fast quench (like water), increasing risk. High-alloy steels (like A2 tool steel) are "air-hardening," meaning they can achieve full hardness with a slow cool in air, dramatically reducing internal stress.
How to Mitigate the Risks: The Role of Tempering
A part is almost never used in its as-quenched state. The brittleness and high internal stress must be addressed with a subsequent heat treatment.
Why Tempering Is Essential
Tempering is the process of reheating the quenched part to a much lower temperature (e.g., 200-650°C or 400-1200°F) and holding it for a period of time.
This process allows some of the trapped carbon to precipitate and enables the crystal structure to relax, which significantly relieves internal stress and increases toughness.
The Hardness vs. Toughness Spectrum
Tempering always involves a trade-off. It reduces the steel's peak hardness, but in return, it provides a massive gain in toughness.
The specific tempering temperature is chosen to achieve the precise balance of hardness and toughness required for the final application, moving the part from a uselessly brittle state to a functional one.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these negative effects allows you to control the heat treatment process to achieve your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness: You must accept a higher risk of quench cracking and use a steel and process (like a water quench on W1 steel) that necessitates it, followed by a very low-temperature temper.
- If your primary focus is balanced strength and toughness: The quench is just the first step; your process must include a carefully controlled tempering cycle to achieve the toughness needed for tools, springs, or structural components.
- If your primary focus is dimensional stability: You must select a steel with high hardenability (an air-hardening or oil-hardening grade) that allows for a slower, less stressful quench to minimize distortion in precision parts.
Ultimately, mastering the quench is not about eliminating its negative effects, but about strategically managing them to achieve the precise properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Negative Effect | Root Cause | Key Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Quench Cracking | Internal stress exceeds material strength | Part failure, total loss |
| Distortion/Warping | Uneven cooling and transformation | Loss of dimensional accuracy |
| Extreme Brittleness | Formation of hard, untempered martensite | Low toughness, shatters under impact |
Achieve the perfect balance of hardness and toughness for your steel components.
Quenching is a critical but risky step in heat treatment. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to control this process, from selecting the right quenchant to executing accurate tempering cycles. Our expertise helps you mitigate the negative effects of quenching—like cracking and distortion—ensuring your parts meet exact specifications for strength, durability, and dimensional stability.
Let KINTEK support your laboratory's success. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your heat treatment processes and deliver reliable, high-performance results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What are the uses of vacuum furnace? Achieve Unmatched Material Purity and Performance
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the leak rate for a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Purity and Repeatability



















