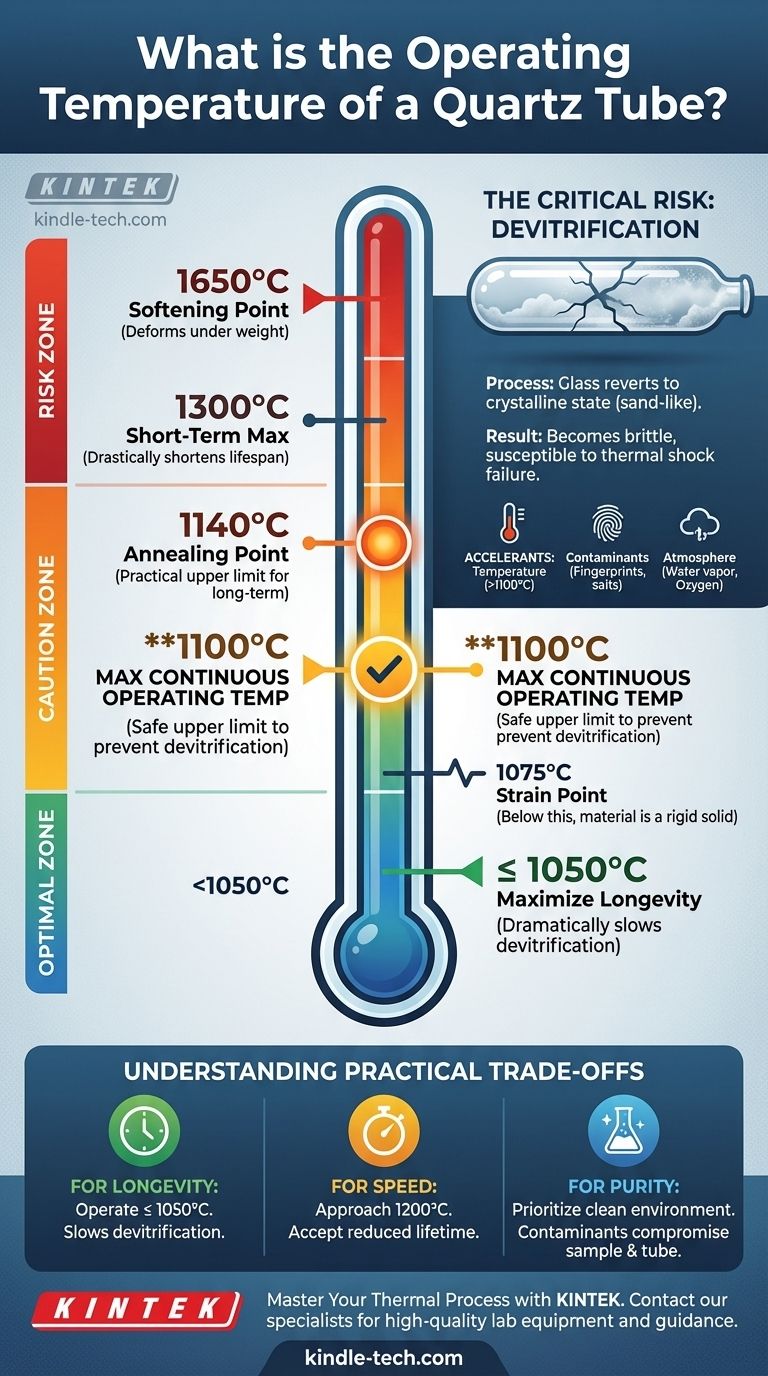
The operating temperature of a quartz tube is not a single value but a range dependent on the material's purity and the duration of heat exposure. For most high-purity fused quartz tubes, the maximum continuous operating temperature is approximately 1100°C (2012°F). While it can be used for shorter periods up to 1300°C (2372°F), exceeding the continuous limit significantly shortens its lifespan and invites material failure.
While a furnace may be rated for very high temperatures, the quartz tube itself is the limiting factor. The key to longevity is operating below the tube's annealing point to prevent devitrification—a crystallization process that renders the quartz brittle and useless.
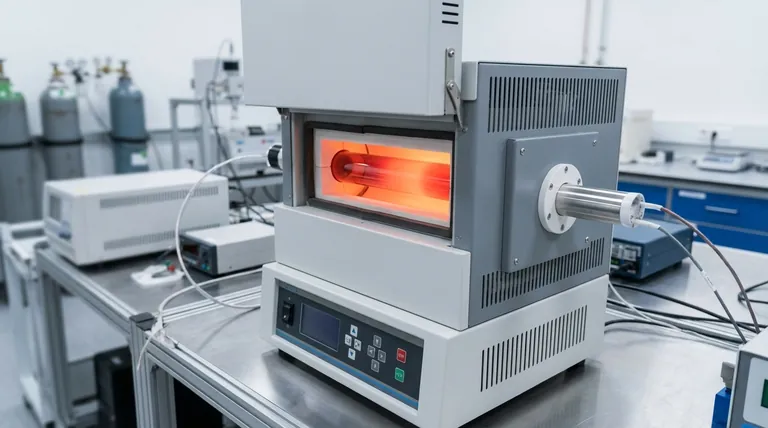

Understanding Quartz's Thermal Limits
Quartz glass, or silica glass, is prized for its excellent thermal shock resistance and high-temperature stability. However, these properties have firm physical boundaries that are critical to understand for any high-temperature application.
Key Temperature Thresholds
The behavior of quartz glass is defined by several key temperature points:
- Strain Point (approx. 1075°C): This is the temperature above which internal stresses can form but are relieved very slowly. Below this point, the material is essentially a rigid solid.
- Annealing Point (approx. 1140°C): At this temperature, internal stresses can be relieved in a matter of minutes. This is widely considered the practical upper limit for long-term, continuous operation.
- Softening Point (approx. 1650°C): This is the temperature at which the quartz begins to deform under its own weight. This is a failure point, not an operational one.
Fused Quartz vs. Fused Silica
While often used interchangeably, there is a technical difference. Fused quartz is made from melting natural quartz crystals, while fused silica is a synthetic, higher-purity material.
For most tube furnace applications, the terms are practically synonymous. However, for ultra-high purity processes, synthetic fused silica offers better performance and resistance to devitrification due to fewer impurities.
The Critical Risk: Devitrification
The primary failure mode for a quartz tube used at high temperatures is not melting, but devitrification. This process is the single most important factor limiting the tube's useful life.
What is Devitrification?
Devitrification is the process by which the amorphous, glassy structure of quartz (SiO₂) reverts to a more stable crystalline state (cristobalite). In simple terms, the glass begins to turn back into sand.
This change typically starts on the surface and appears as a hazy, opaque, or frosted layer.
Why Devitrification is a Problem
Once devitrification occurs, the material is fundamentally changed. The new crystalline structure has a different coefficient of thermal expansion.
This mismatch causes immense internal stress as the tube heats and cools. The once-durable quartz becomes extremely brittle and highly susceptible to cracking and catastrophic failure from thermal shock.
Accelerants of Devitrification
Certain conditions can dramatically speed up this process:
- Temperature: The rate of devitrification increases significantly above 1100°C.
- Contaminants: Even fingerprints, salts, or atmospheric dust contain alkali metals (like sodium and potassium) that act as powerful catalysts for crystallization.
- Atmosphere: The presence of water vapor or oxygen can also accelerate the process.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
A furnace's temperature capability is different from the tube's material limit. A furnace that can reach 1200°C or higher, as some do, does not mean you can operate a quartz tube at that temperature continuously. The reference to a 1000°C furnace is a good indicator of a common, safe operating range that balances processing speed with tube longevity.
Continuous vs. Short-Term Use
You can push a quartz tube to 1200°C or even 1250°C for brief periods. However, this comes at a steep cost to the tube's lifespan. Each cycle at these elevated temperatures will accelerate devitrification, making failure more likely.
The Importance of a Clean Environment
Because contaminants are a primary cause of devitrification, maintaining cleanliness is paramount. Always handle quartz tubes with clean, powder-free gloves. Ensure the process atmosphere is free of catalytic agents if possible, often by using an inert gas like argon.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct operating temperature is a balance between process requirements and equipment longevity.
- If your primary focus is maximizing tube life and process stability: Operate at or below 1050°C. This keeps you safely away from the annealing point and dramatically slows devitrification.
- If your primary focus is rapid processing for short-term runs: You can approach 1200°C, but you must accept a significantly reduced tube lifetime and budget for frequent replacement.
- If your primary focus is process purity: Prioritize a clean tube and a controlled atmosphere. Even at lower temperatures, contaminants can compromise both your sample and the tube itself.
Ultimately, understanding these material properties allows you to move from simply using your equipment to truly mastering your thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Point | Approx. Value (°C) | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Max Continuous Operating Temp | 1100°C | Safe upper limit for long-term use to prevent devitrification. |
| Short-Term Max Temp | 1300°C | Can be used briefly but drastically shortens tube lifespan. |
| Annealing Point | 1140°C | Practical upper limit; internal stresses are relieved quickly. |
| Strain Point | 1075°C | Temperature below which quartz is a rigid solid. |
Master Your Thermal Process with KINTEK
Understanding the precise limits of your quartz tube is crucial for the safety, efficiency, and reproducibility of your lab work. Whether you need to maximize tube longevity or push the limits for a critical short-term process, having the right equipment and expert guidance makes all the difference.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality laboratory equipment and consumables, including quartz tubes designed for superior performance and durability. Our experts can help you select the right materials and optimize your furnace settings to achieve your specific goals.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities and ensure process reliability? Contact our thermal processing specialists today via our Contact Form to discuss your application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is tantalum foil required when using graphite molds for sintering yttrium oxide? Ensure Optical Purity
- What is the purpose of a porous ceramic monolith flow restrictor in a tube furnace? Achieve Perfect Laminar Flow
- What are the primary technical functions of a mechanical stirrer and its nickel impellers? Optimize MSCC Reactions
- What is the function of combining an ultrasonic disperser and a mechanical stirrer? Achieve Flawless Slurry Dispersion
- What is the function of a mechanical stirrer in catalyst prep? Ensure Homogeneity in Mixed Oxide Catalyst Supports
- What is furnace lining? The Engineered System Protecting Your High-Temperature Processes
- Why are vacuum ball milling jars necessary for mechanical alloying? Ensure High Purity & Prevent Metal Oxidation
- What are the advantages of using zirconia grinding balls for Zr2Al-GNS? Ensure High Purity and Peak Electrical Performance



















