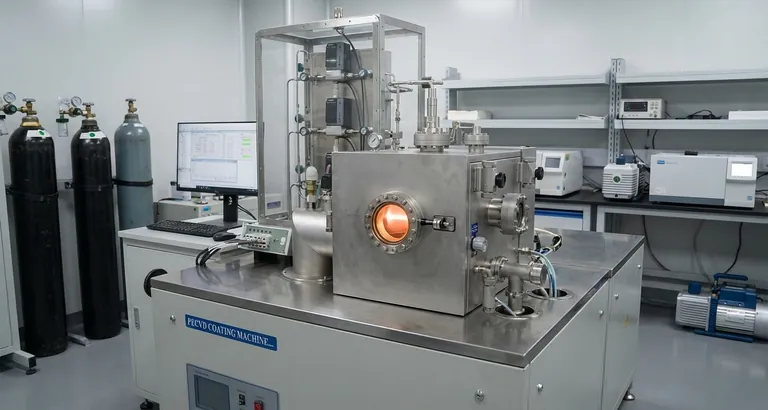
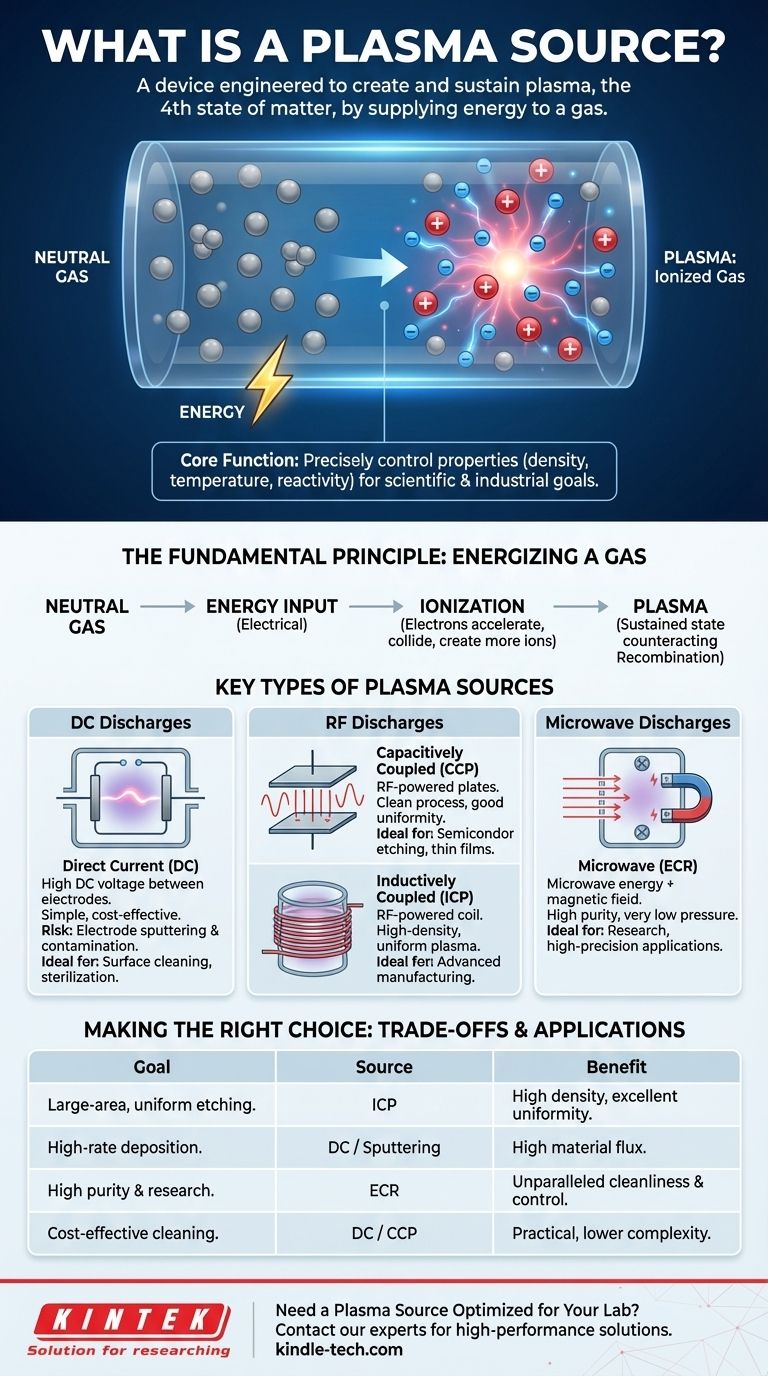
In essence, a plasma source is a device engineered to create and sustain plasma, the fourth state of matter. It works by supplying a sufficient amount of energy—typically electrical—to a neutral gas, causing its atoms or molecules to ionize into a dynamic mixture of charged ions, free electrons, and neutral particles. This controlled generation of plasma is fundamental to countless modern technologies, from manufacturing microchips to developing clean energy.
The core function of a plasma source is not merely to create this energized state of matter, but to precisely control its properties—density, temperature, and chemical reactivity—to achieve a specific scientific or industrial goal.

The Fundamental Principle: Energizing a Gas
At its heart, every plasma source operates on the same basic principle: adding energy to a gas until it changes state. This process is analogous to heating ice until it becomes water, then steam, but it involves electrical energy rather than just thermal energy.
What is Plasma? A Quick Refresher
Plasma is often called the "fourth state of matter." It's an ionized gas, meaning a significant portion of its atoms have been stripped of one or more electrons.
This process leaves behind positively charged ions and free, energetic electrons. This "soup" of charged particles is what makes plasma electrically conductive and highly responsive to electric and magnetic fields.
The Core Mechanism: Ionization
The transition from gas to plasma is achieved through ionization. A plasma source introduces energy into a low-pressure gas within a chamber.
This energy, typically from an electric field, accelerates free electrons. When these high-speed electrons collide with neutral gas atoms, they can knock other electrons loose, creating more free electrons and positive ions in a chain reaction.
Sustaining the Plasma
Creating plasma is only the first step. The source must continuously supply energy to counteract recombination, the natural tendency for electrons to rejoin with ions and return to a neutral state. A stable plasma exists in a state of equilibrium where the rate of ionization matches the rate of recombination and other particle losses.
Key Types of Plasma Sources
Plasma sources are primarily categorized by the method they use to deliver energy to the gas. Each method produces a plasma with distinct characteristics, making it suitable for different applications.
Direct Current (DC) Discharges
This is one of the simplest methods. A high DC voltage is applied between two metal electrodes inside a vacuum chamber. The resulting strong electric field accelerates electrons, initiating the plasma discharge.
DC sources are robust and cost-effective but can suffer from electrode sputtering, where ions bombard and erode the electrode material, potentially contaminating the process.
Radio Frequency (RF) Discharges
RF sources use alternating electric fields that oscillate at radio frequencies (typically 13.56 MHz) to energize the plasma. This avoids the need for direct-contact electrodes within the densest part of the plasma, leading to cleaner processes.
Capacitively Coupled Plasma (CCP) sources work like a capacitor, with the plasma forming between two parallel electrode plates. The oscillating electric field efficiently transfers energy to the electrons, making CCP a workhorse technology for etching thin films in semiconductor manufacturing.
Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) sources use an RF-powered coil, often wrapped around a ceramic chamber. The changing magnetic field from the coil induces a circular electric field inside the chamber, which accelerates electrons very efficiently. ICPs are known for producing high-density, uniform plasmas over large areas.
Microwave Discharges
These sources use microwave energy (often at 2.45 GHz) to create the plasma. When combined with a static magnetic field, they can achieve Electron Cyclotron Resonance (ECR).
At a specific magnetic field strength, electrons absorb microwave energy exceptionally efficiently, creating very high-density, high-purity plasmas at very low gas pressures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a plasma source involves a critical evaluation of competing factors. No single source is superior for all tasks; the optimal choice depends entirely on the application's requirements.
Plasma Density vs. Purity
High-density sources like ICP and ECR are powerful and enable high-rate processing, which is essential for advanced manufacturing.
However, simpler DC sources can introduce metallic impurities from the electrodes. In applications where even parts-per-billion contamination is unacceptable, "electrodeless" RF or microwave sources are required.
Operating Pressure and Uniformity
Different sources operate best at different vacuum levels. Low-pressure sources like ICP and ECR allow particles to travel farther between collisions, which can lead to more uniform processing over a large surface area.
This uniformity is absolutely critical for manufacturing semiconductor wafers, where every chip across a 300mm surface must be identical.
Cost and Complexity
There is a direct relationship between performance and complexity. A simple DC discharge system is relatively inexpensive and easy to operate.
In contrast, an ECR or advanced ICP source is a complex, expensive piece of equipment requiring sophisticated power delivery systems, vacuum technology, and control electronics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The ideal plasma source is dictated entirely by the desired outcome. Your decision should be guided by the specific process requirements of your project.
- If your primary focus is large-area, uniform semiconductor etching: Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) sources offer the best balance of high plasma density and control over a large substrate.
- If your primary focus is high-rate material deposition or surface coating: Arc discharges or magnetron sputtering (a type of DC source) provide the high flux of material needed for these tasks.
- If your primary focus is fundamental research or creating extremely pure plasma: Electron Cyclotron Resonance (ECR) sources provide unparalleled control and cleanliness, albeit at a higher cost.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective process like surface cleaning or sterilization: A basic Direct Current (DC) or Capacitively Coupled Plasma (CCP) source is often the most practical solution.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental principles transforms the plasma source from a black box into a precise tool for engineering matter at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Plasma Source Type | Key Mechanism | Ideal For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Current (DC) | High DC voltage between electrodes | Cost-effective surface cleaning, sterilization | Risk of electrode sputtering, potential contamination |
| Capacitively Coupled Plasma (CCP) | RF-powered parallel plates | Semiconductor etching, thin-film processing | Clean process, good for large-area uniformity |
| Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) | RF-powered coil inducing electric field | High-density, uniform plasma for advanced manufacturing | High plasma density, excellent uniformity |
| Microwave (ECR) | Microwave energy with magnetic field | High-purity research, low-pressure applications | Extremely high density and purity at low pressure |
Need a Plasma Source Optimized for Your Lab's Needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including plasma sources for applications ranging from semiconductor fabrication to materials research. Whether you require the high-density uniformity of an ICP source or the cost-effective simplicity of a DC system, our experts can help you select the right tool to achieve precise control over plasma density, temperature, and reactivity.
Contact us today to discuss how our plasma solutions can enhance your process efficiency and results.
Get in touch with our specialists
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
People Also Ask
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















