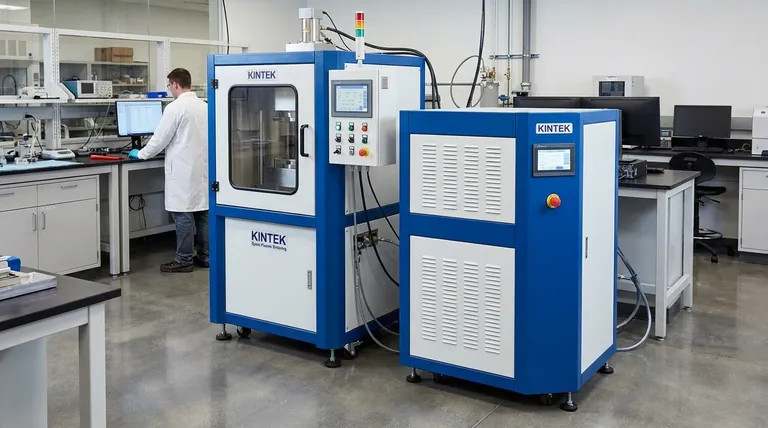
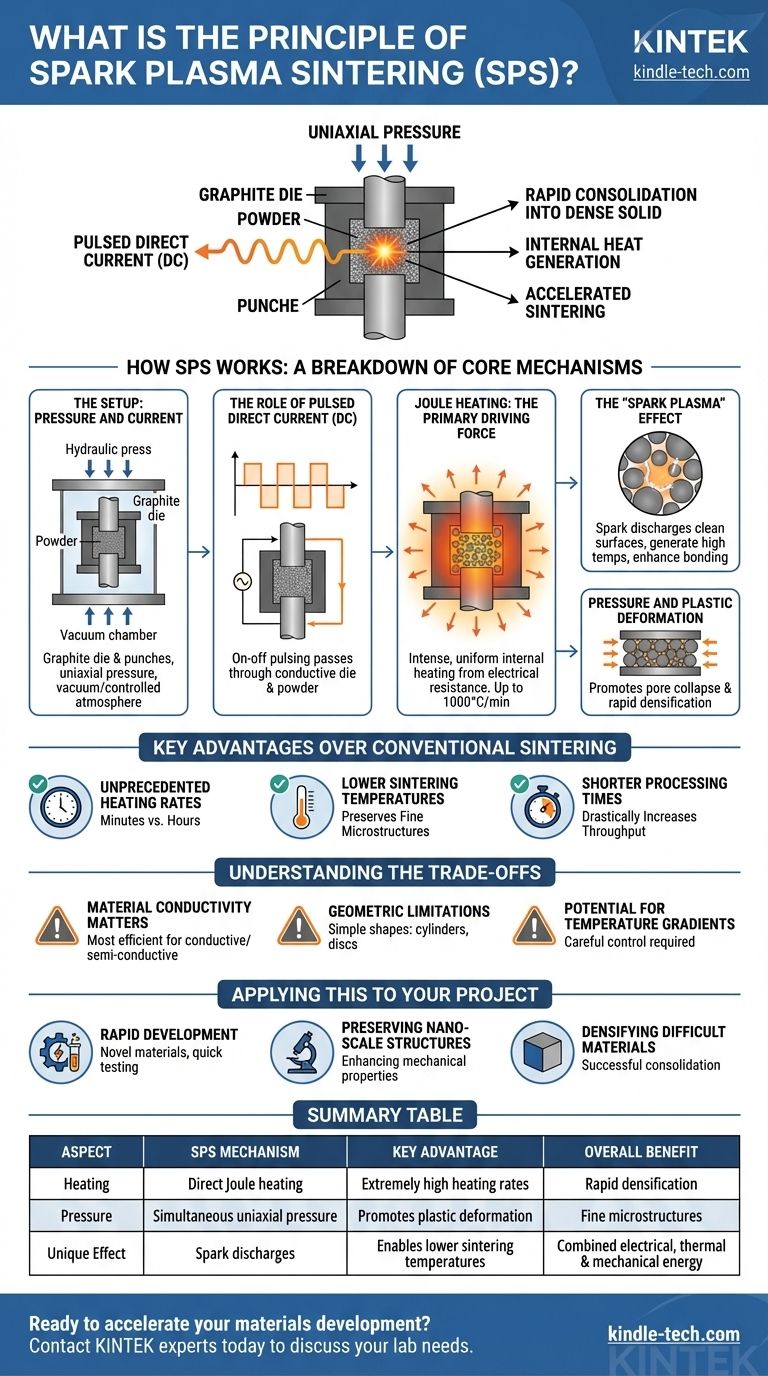
At its core, the principle of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is the use of a pulsed direct electrical current and simultaneous uniaxial pressure to rapidly consolidate powders into a dense solid. Unlike conventional furnaces that heat externally, SPS passes current directly through the conductive die and the powder itself, generating intense internal heat that dramatically accelerates the sintering process.
The central innovation of SPS is its method of heating. By using the material and its tooling as the heating element, it achieves extremely high heating rates and activates particle surfaces, allowing for full densification at lower temperatures and in significantly less time than traditional methods.

How SPS Works: A Breakdown of the Core Mechanisms
Spark Plasma Sintering, also known as Field-Assisted Sintering Technique (FAST), is a sophisticated process that integrates electrical, thermal, and mechanical energy. Understanding how these forces interact is key to grasping its effectiveness.
The Setup: Pressure and Current
The powdered material is loaded into a graphite die, which is both electrically conductive and capable of withstanding high temperatures. The die is placed between two punches that act as electrodes, and the entire assembly is put under uniaxial pressure by a hydraulic press.
This setup is housed within a vacuum or controlled atmosphere chamber to prevent oxidation and ensure the purity of the final material.
The Role of Pulsed Direct Current (DC)
Instead of a steady current, SPS uses a pulsed DC current. This on-off pulsing is a critical feature. The current is passed directly from the electrodes, through the punches, into the conductive die, and—if the powder is conductive—through the powder compact itself.
Joule Heating: The Primary Driving Force
The primary mechanism for heating is Joule heating. As the electrical current encounters resistance from the graphite die and the powder particles, it generates intense, uniform heat. This means the sample is heated from the inside out and the outside in simultaneously, a key advantage over conventional methods that rely on slow, external radiation.
This direct heating method is responsible for the extraordinary heating rates, which can reach up to 1000°C per minute.
The "Spark Plasma" Effect
The name of the process comes from a microscopic phenomenon that occurs between powder particles. The strong electric field can generate localized spark discharges across the gaps between adjacent particles.
These sparks are thought to serve two purposes. First, they clean the surfaces of the powder particles by stripping away oxide layers or other contaminants. Second, they generate extremely high temperatures in a tiny volume, creating what is theorized to be a momentary state of plasma that enhances the diffusion and bonding between particles.
Pressure and Plastic Deformation
While the electrical current heats the material, the constant uniaxial pressure plays a vital role. As the particles soften, the pressure forces them together, aiding in the collapse of pores and promoting plastic deformation to rapidly achieve a highly dense final part.
Key Advantages Over Conventional Sintering
The unique principles of SPS give it significant advantages over traditional furnace-based techniques like hot pressing.
Unprecedented Heating Rates
Because the workpiece and die act as their own heating elements, the system can reach target temperatures in minutes rather than hours. This speed is a defining characteristic of the process.
Lower Sintering Temperatures
The combination of surface cleaning from spark discharges and rapid Joule heating allows for full densification at temperatures several hundred degrees lower than required for conventional sintering. This is crucial for preserving fine-grained microstructures or processing temperature-sensitive materials.
Shorter Processing Times
The rapid heating, short holding times at temperature, and fast cooling result in total process times measured in minutes. This drastically increases throughput compared to the hours or even days required for traditional furnace cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its limitations. To apply SPS effectively, you must be aware of its constraints.
Material Conductivity Matters
The process is most efficient for electrically conductive or semi-conductive materials. While techniques exist to sinter insulating ceramics, they are more complex and may involve using a conductive powder bed or other workarounds.
Geometric Limitations
The reliance on a rigid die and uniaxial pressure generally limits SPS to producing simple shapes, such as cylinders, discs, and rectangular blocks. Complex, near-net-shape parts are challenging to fabricate directly.
Potential for Temperature Gradients
Although heating is very fast, temperature gradients can still form between the center and the surface of a large sample. Careful process design and control are required to ensure thermal uniformity and a homogenous final product.
Applying This to Your Project
The decision to use SPS should be driven by your specific material and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is rapid development of novel materials: SPS is an unparalleled tool for quickly fabricating and testing new alloys, composites, and ceramics due to its extremely short cycle times.
- If your primary focus is preserving nano-scale or fine-grained structures: The lower temperatures and short holding times of SPS are ideal for preventing grain growth, which is critical for enhancing mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is densifying difficult-to-sinter materials: The surface activation and combined effects of heat and pressure in SPS can successfully consolidate materials that fail to densify using conventional methods.
Ultimately, the principle of SPS is about using targeted electrical energy to create a superior sintering environment, unlocking new possibilities for materials processing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | SPS Mechanism | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Direct Joule heating via pulsed DC current | Extremely high heating rates (up to 1000°C/min) |
| Pressure | Simultaneous uniaxial pressure | Promotes plastic deformation and pore collapse |
| Unique Effect | Spark discharges clean particle surfaces | Enables lower sintering temperatures |
| Overall Benefit | Combined electrical, thermal, and mechanical energy | Rapid densification with fine microstructures |
Ready to accelerate your materials development with advanced sintering technology?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment, including solutions for advanced sintering processes. Whether you're developing novel alloys, composites, or need to preserve nano-scale structures, our expertise can help you achieve superior results faster and more efficiently.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs and unlock new possibilities for your research and production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum hot-pressing sintering equipment solve W-Si composition segregation? Achieve Material Homogeneity
- What is the step-by-step process for growing a diamond using the HPHT method? Master Lab-Grown Diamond Synthesis
- What is hot and cold isostatic pressing? A Guide to Forming and Densifying Materials
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Superior Densification for 2024Al/Gr/SiC Composites
- Why is a hot press used for all-solid-state batteries? Optimize Electrolyte-Cathode Interface for Peak Performance
- What is the difference between CIP and HIP? A Guide to Choosing the Right Process
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the primary function of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Mastering SiC Fiber-Reinforced Composite Fabrication



















