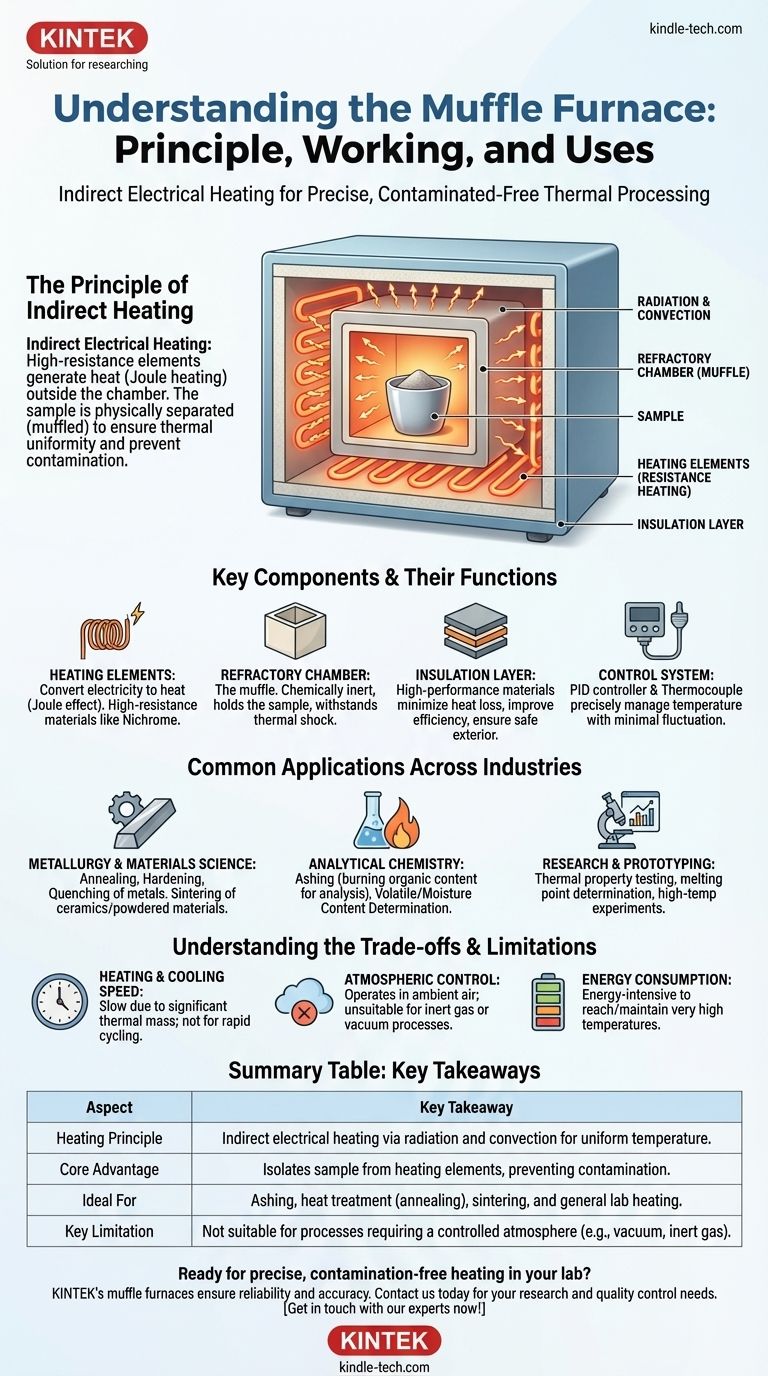
At its core, a muffle furnace operates on the principle of indirect electrical heating. It uses high-resistance heating elements to heat an insulated chamber, which then radiates uniform, high temperatures onto a sample inside. Crucially, the sample is physically separated (or "muffled") from the heating elements, which ensures thermal uniformity and prevents contamination.
The true value of a muffle furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures, but its capacity to deliver precisely controlled, uniform, and uncontaminated heat by isolating the material being heated from the direct energy source.

The Principle of Indirect Heating
A muffle furnace is fundamentally different from a simple oven. Its design is centered on providing a clean, stable heating environment, which is achieved through a multi-step energy transfer process.
How Heat is Generated
The process begins with Joule heating, also known as resistance heating. An electric current is passed through heating elements, typically made of a high-resistance material like Nichrome wire. As the current encounters this resistance, electrical energy is converted directly into heat energy, causing the elements to glow red-hot.
The Role of the Muffle
These heating elements do not directly touch the sample. Instead, they are wrapped around or embedded within the walls of an outer chamber. The inner chamber—the muffle—is a separate, sealed box made of a heat-resistant refractory material like ceramic. This muffle is what holds the sample or workpiece.
How Heat is Transferred
The hot elements heat the walls of the muffle chamber. This heat is then transferred to the sample inside primarily through radiation and convection. This indirect method ensures the entire sample is heated evenly from all sides, eliminating hot spots that could occur from direct contact with a heating element.
Key Components and Their Functions
Understanding the core components reveals how a muffle furnace achieves such precise and reliable results. Each part serves a critical function in the system.
The Heating Elements
These are the workhorses of the furnace, converting electricity into heat. Their material composition is designed to withstand extremely high temperatures and repeated heating/cooling cycles without degrading.
The Refractory Chamber
This is the muffle itself. It must be able to endure thermal shock and high temperatures while remaining chemically inert to avoid reacting with the samples being heated. It is the heart of the furnace's "uncontaminated heating" promise.
The Insulation Layer
To reach and maintain temperatures often exceeding 1000°C (1832°F) efficiently, the entire heating chamber is encased in thick layers of high-performance thermal insulation. This minimizes heat loss, improves energy efficiency, and keeps the exterior of the unit safe to touch.
The Control System
Modern furnaces rely on a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller linked to a sensor, typically a thermocouple. The thermocouple measures the internal temperature and feeds this data to the controller, which precisely adjusts the power sent to the heating elements to maintain the target temperature with minimal fluctuation.
Common Applications Across Industries
The unique capabilities of the muffle furnace make it an indispensable tool in a wide range of scientific and industrial fields.
Metallurgy and Materials Science
The furnace provides the stable, high-temperature environment required for processes like annealing, hardening, and quenching of metals. It is also essential for sintering, where powdered materials like ceramics or metals are fused together under heat without melting.
Analytical Chemistry
One of the most common laboratory uses is ashing. A sample is placed in the furnace to burn away all organic content at a controlled temperature, leaving only the inorganic ash for quantitative analysis. It is also used to determine the volatile and moisture content of materials.
Research and Prototyping
Scientists and engineers use muffle furnaces to test the thermal properties of new materials, determine melting points, and conduct various high-temperature experiments in a controlled and repeatable environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the muffle furnace is not the right tool for every job. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Limitation: Heating and Cooling Speed
Due to the significant thermal mass of the refractory materials and insulation, muffle furnaces take time to heat up and cool down. They are not designed for rapid temperature cycling.
Limitation: Atmospheric Control
A standard muffle furnace operates in ambient air. If a process requires an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon) or a vacuum to prevent oxidation, a specialized and more complex tube furnace is required.
Consideration: Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining very high temperatures is an energy-intensive process. These furnaces represent a significant electrical load, which is an important consideration for operational planning and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, align the furnace's capabilities with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is determining the inorganic content of a sample (ashing): A standard muffle furnace is the ideal tool for its ability to completely combust organic material at a stable, controlled temperature.
- If your primary focus is modifying the properties of metals (heat treatment): The furnace's uniform, radiant heat is essential for achieving consistent results in processes like annealing or hardening.
- If your primary focus is creating new ceramic or metal parts from powder (sintering): The furnace provides the stable, high-temperature environment needed to fuse powdered materials without melting them.
- If your primary focus is processing air-sensitive materials: A standard muffle furnace is unsuitable; you must use a specialized furnace with atmospheric control, such as a tube furnace.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is a foundational tool for any process requiring pure, precise, and powerful indirect heat.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Heating Principle | Indirect electrical heating via radiation and convection for uniform temperature. |
| Core Advantage | Isolates sample from heating elements, preventing contamination. |
| Ideal For | Ashing, heat treatment (annealing), sintering, and general lab heating. |
| Key Limitation | Not suitable for processes requiring a controlled atmosphere (e.g., vacuum, inert gas). |
Ready to achieve precise, contamination-free heating in your lab?
KINTEK's muffle furnaces are engineered for reliability and accuracy in critical applications like ashing, heat treatment, and materials testing. Our lab equipment ensures uniform temperatures and robust performance for your research and quality control needs.
Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your laboratory's requirements and enhance your thermal processing capabilities.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of ash analysis? Dry vs. Wet Ashing Methods Explained
- How is ash content determined using muffle furnace? Achieve Accurate Mineral Analysis
- What is the precaution for muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Lab Excellence
- How did the design of muffle furnaces change with the advent of electric heating elements? The Evolution to Precision and Purity
- What temperature should a furnace run at? From Home Comfort to Industrial Processes



















