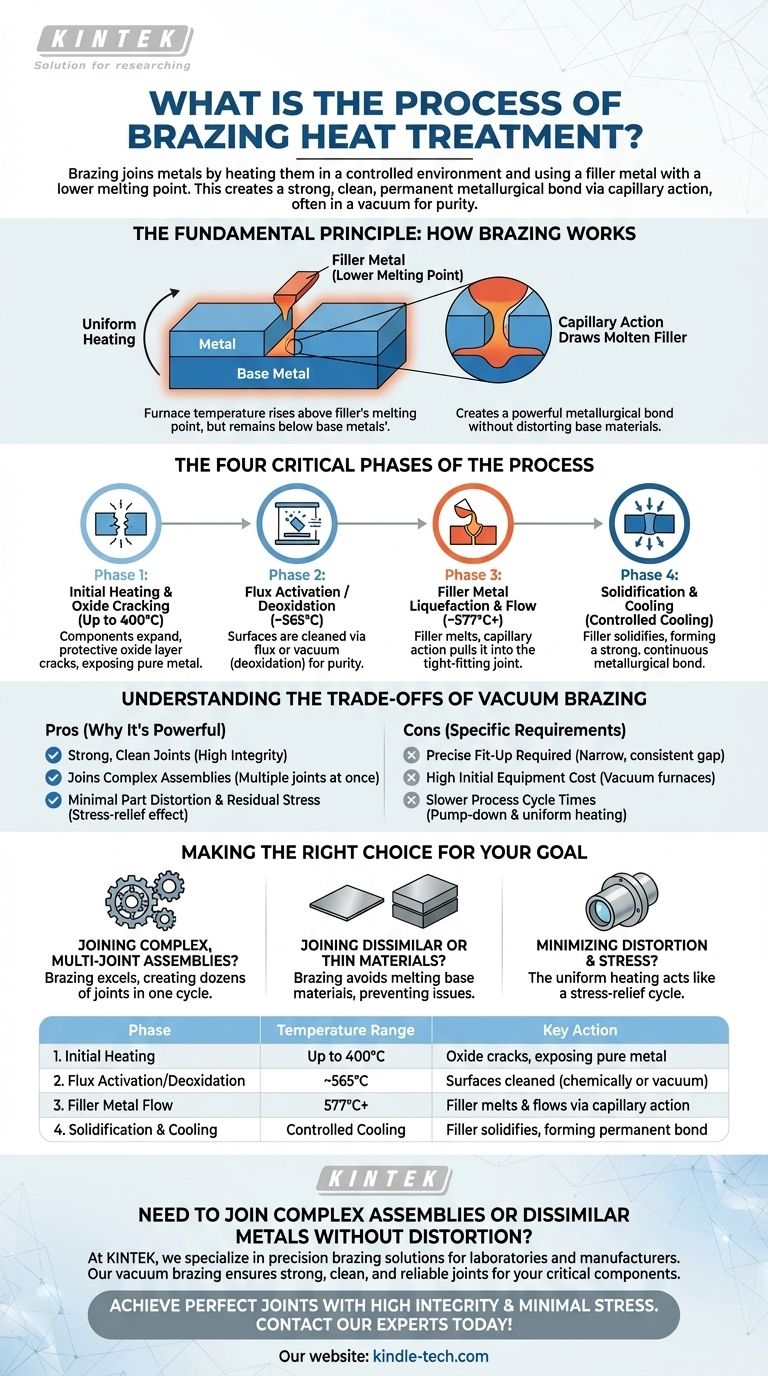
At its core, brazing heat treatment is a process for joining metals by heating them in a controlled environment and using a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the base metals. This molten filler is drawn into a tight-fitting joint by capillary action, creating a strong, clean, and permanent metallurgical bond once it cools and solidifies. The process is often performed in a vacuum to ensure the highest purity and joint integrity.
The essential principle of brazing is not to melt the components being joined, but to melt a separate filler alloy that flows between them. This creates a powerful bond without distorting or compromising the integrity of the base materials.
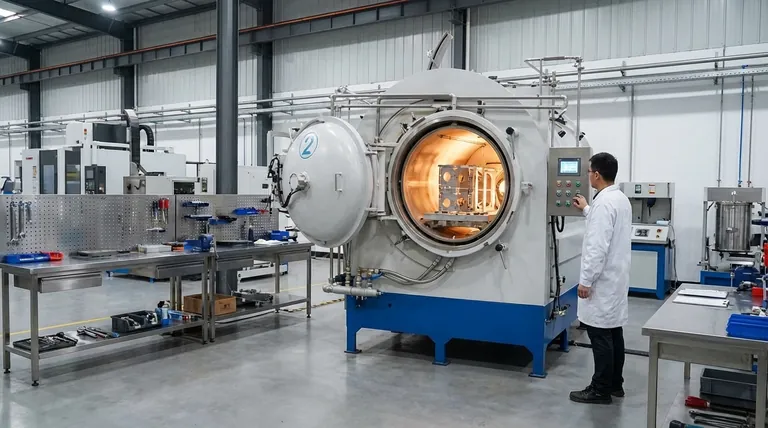

The Fundamental Principle: How Brazing Works
Brazing operates on a few key principles that distinguish it from welding or soldering. Understanding these fundamentals is crucial to appreciating its value.
Heating Below the Base Metal Melting Point
The entire assembly—the components to be joined and the filler metal—is heated uniformly. The key is that the furnace temperature rises above the melting point of the filler metal but remains safely below the melting point of the base metals.
The Critical Role of the Filler Metal
A specialized brazing alloy, or filler metal, is selected based on the base materials. This filler is designed to melt at a precise, lower temperature than the parts it is joining.
Capillary Action is the Engine
When the filler metal melts, it becomes a liquid that is naturally drawn into the narrow gap between the workpieces. This phenomenon, known as capillary action, ensures the entire joint is completely and uniformly filled.
Forming a Metallurgical Bond
As the assembly cools, the filler metal solidifies. It doesn't just act as a glue; it diffuses slightly into the surface of the base metals, forming a strong, permanent metallurgical bond that can often be as strong as the materials themselves.
The Four Critical Phases of the Process
While the principle is simple, the execution is a precise, multi-stage thermal process. Using aluminum brazing as a common example, the phases are clearly defined by temperature.
Phase 1: Initial Heating and Oxide Cracking (up to 400°C)
As the components heat up, they expand at different rates. This differential expansion causes the brittle, protective oxide layer (like aluminum oxide) on the metal's surface to crackle and break apart, exposing the pure metal underneath.
Phase 2: Flux Activation or Deoxidation (~565°C)
In traditional brazing, a chemical flux would melt at this stage to clean the surfaces. In vacuum brazing, this is the point where the high temperature and low-pressure environment work together to deoxidize the metals and remove contaminants without any chemical assistance.
Phase 3: Filler Metal Liquefaction and Flow (~577°C and above)
This is the key event. The furnace temperature surpasses the filler metal's melting point, causing it to turn to liquid. Immediately, capillary action pulls the molten alloy into the prepared joint between the workpieces.
Phase 4: Solidification and Cooling
After a set time at brazing temperature to ensure complete flow, the assembly is carefully cooled. The filler metal solidifies, creating the final, clean, and continuous brazed joint.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Vacuum Brazing
While powerful, vacuum brazing is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness depends on understanding its specific requirements and limitations.
Requirement for Precise Fit-Up
Brazing is entirely dependent on capillary action. This means the gap between the parts being joined must be extremely small and consistent, often just a few thousandths of an inch. Poor fit-up will result in an incomplete or weak joint.
High Initial Equipment Cost
Vacuum furnaces and the associated control systems represent a significant capital investment. This makes the process better suited for high-value components or high-volume production where the cost can be amortized.
Slower Process Cycle Times
The need to pump down to a deep vacuum, heat uniformly, and cool in a controlled manner means that brazing cycle times are typically longer than for processes like manual welding.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right joining process depends entirely on your application's specific demands.
- If your primary focus is joining complex, multi-joint assemblies cleanly: Brazing is ideal as it can create dozens or even hundreds of joints simultaneously in a single furnace cycle.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or very thin materials: Brazing excels because it avoids melting the base materials, preventing the common issues that make welding these materials difficult or impossible.
- If your primary focus is minimizing part distortion and residual stress: The uniform heating and cooling of the brazing process acts like a stress-relief cycle, resulting in dimensionally stable and stress-free final parts.
Ultimately, brazing is a precise thermal and metallurgical process chosen when joint integrity, cleanliness, and material preservation are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Temperature Range | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Initial Heating | Up to 400°C | Oxide layer cracks, exposing pure metal |
| 2. Flux Activation/Deoxidation | ~565°C | Surfaces are cleaned (chemically or via vacuum) |
| 3. Filler Metal Flow | 577°C+ | Filler melts & flows into joint via capillary action |
| 4. Solidification & Cooling | Controlled Cooling | Filler solidifies, forming a permanent metallurgical bond |
Need to join complex assemblies or dissimilar metals without distortion?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision brazing solutions for laboratories and manufacturers. Our expertise in vacuum brazing processes ensures strong, clean, and reliable joints for your most critical components. Whether you're working with complex multi-joint assemblies or sensitive thin materials, our lab equipment and consumables are designed to deliver superior results.
Let us help you achieve perfect joints with high integrity and minimal stress. Contact our brazing experts today to discuss your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of high-temperature furnaces in HPQ processing? Optimize Quartz Calcination & Quenching
- What are the factors that determine the strength of a brazed joint? Achieve Maximum Strength for Your Metal Assemblies
- Can stainless steel be annealed? Discover the Key to Restoring Corrosion Resistance
- What is the temperature of sintered iron? Master the 1288°C Key to Strong Parts
- What role does a high-temperature furnace play in Mn-Al-O catalysts? Expert Guide to Hexaaluminate Phase Transformation
- What is the primary function of industrial ovens in lignocellulosic waste pretreatment? Maximize Energy Efficiency
- How does the use of a vacuum drying oven affect the performance of LiMn2O4 (LMO) cathodes? Unlock Battery Stability
- What type of furnace is used for calcination? Choose the Right Heating Method for Your Process



















