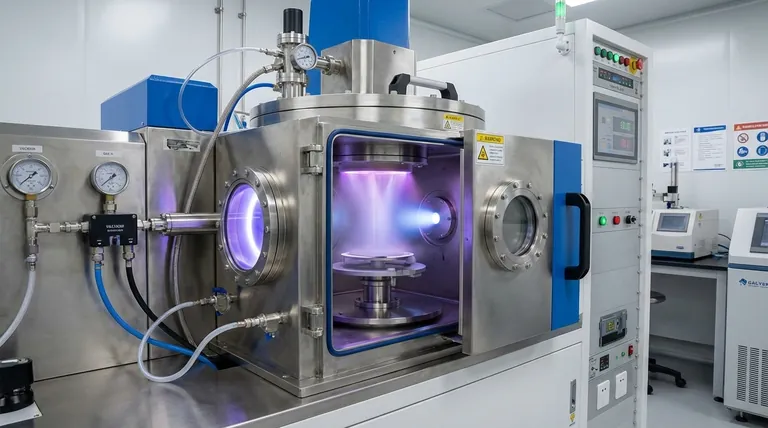
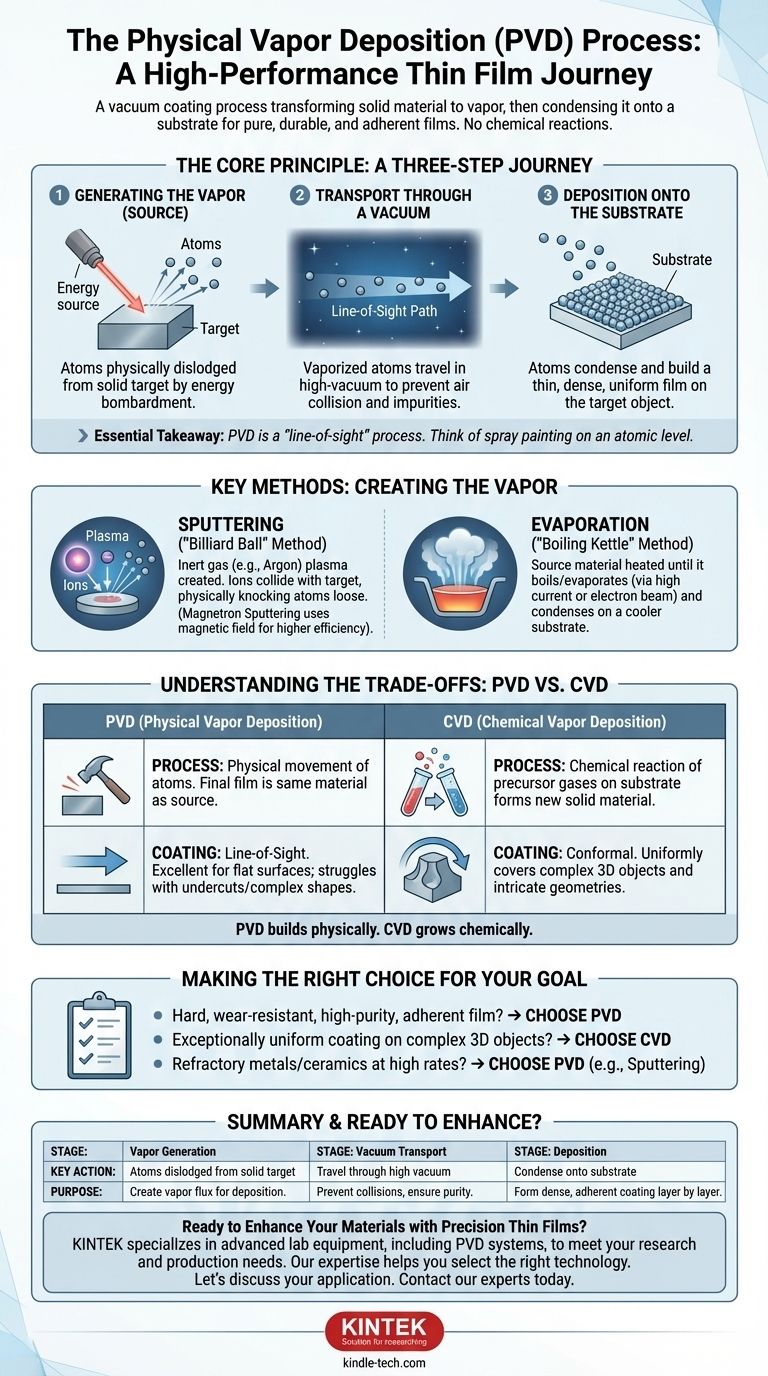
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a vacuum coating process that transforms a solid material into a vapor, transports it through a vacuum, and condenses it onto a target object’s surface to form a high-performance thin film. This entire process is purely physical, involving state changes from solid to gas and back to solid, with no chemical reactions occurring on the substrate itself.
The essential takeaway is that PVD is fundamentally a "line-of-sight" process. Think of it like spray painting on an atomic level: atoms are physically dislodged from a source and travel in a straight line through a vacuum to coat a surface, resulting in extremely pure, durable, and adherent films.

The Core Principle: A Three-Step Journey
The PVD process, regardless of the specific technique, follows a fundamental sequence of events inside a vacuum chamber. Understanding these steps is key to grasping how it achieves its unique results.
Step 1: Generating the Vapor
The first step is to create a vapor from the solid source material, often called the "target." This is achieved by bombarding the material with energy, forcing atoms or groups of atoms to break free from its surface.
Step 2: Transport Through a Vacuum
These liberated atoms travel through a high-vacuum chamber. The vacuum is critical because it eliminates air molecules that would otherwise collide with the vaporized atoms, scattering them and introducing impurities into the final film.
Step 3: Deposition onto the Substrate
When the vaporized atoms reach the target object, known as the "substrate," they condense back into a solid state. This condensation builds up, layer by layer, to form a thin, dense, and highly uniform coating on the substrate's surface.
Key Methods of Physical Vapor Deposition
While the principle is the same, there are two primary methods for generating the initial vapor. The method chosen depends on the source material and the desired film properties.
Sputtering (The "Billiard Ball" Method)
In sputtering, the chamber is filled with an inert gas, like argon. A powerful electric field energizes this gas, creating a glowing plasma of positively charged ions.
These ions are accelerated toward the negatively charged source material (the target). They collide with the target with such force that they physically knock atoms loose, much like a cue ball breaking a rack of billiard balls.
A common variant is magnetron sputtering, which uses a magnetic field to confine the plasma near the target. This dramatically increases the efficiency of the sputtering process, resulting in faster deposition rates.
Evaporation (The "Boiling Kettle" Method)
Thermal evaporation is a more straightforward method. The source material is heated in the vacuum chamber until it literally boils and turns into a vapor.
This is often done by passing a high electrical current through the material or by using an electron beam to heat it. This vapor then travels through the vacuum and condenses on the cooler substrate, much like steam from a kettle condenses on a cold window.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PVD vs. CVD
To truly understand PVD, it is useful to contrast it with its counterpart, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). While both create thin films, their mechanisms are fundamentally different.
The Process: Physical vs. Chemical
PVD physically moves atoms from the source to the substrate. The material of the final film is the same as the source material.
CVD, by contrast, introduces precursor gases into a chamber. A chemical reaction is then induced on the substrate's surface, causing the gases to decompose and form an entirely new solid material as the film.
Coating Properties: Line-of-Sight vs. Conformal
Because PVD atoms travel in straight lines, it is a line-of-sight process. It excels at coating flat surfaces or the exposed faces of an object but struggles to coat undercuts or the inside of complex shapes.
CVD gases can flow and react on all exposed surfaces, resulting in a highly conformal coating that uniformly covers even the most intricate and complex geometries.
Operating Conditions: Materials and Temperature
PVD is exceptionally good at depositing materials with very high melting points, including many metals, alloys, and ceramics, that are difficult to vaporize by heat alone.
CVD processes are versatile but often rely on the availability of suitable volatile precursor chemicals and may require high temperatures to initiate the necessary chemical reactions on the substrate's surface.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition method requires understanding the core strengths of each process in relation to the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is a hard, wear-resistant coating on a tool or a high-purity metallic film with excellent adhesion: PVD is almost always the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is creating an exceptionally uniform coating over a complex three-dimensional object, like internal tubing or microelectronics: CVD's ability to create conformal layers is essential.
- If your primary focus is depositing refractory metals or certain ceramics at high rates for industrial applications: PVD techniques like magnetron sputtering are the industry standard.
Ultimately, choosing the right technology begins with understanding that PVD physically builds a film, while CVD chemically grows one.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Vapor Generation | Atoms are physically dislodged from a solid target (source material). | To create a vapor flux for deposition. |
| 2. Vacuum Transport | Liberated atoms travel in a straight line through a high-vacuum environment. | To prevent collisions with air molecules, ensuring purity and direct travel. |
| 3. Deposition | Vaporized atoms condense onto the substrate surface, building a thin film. | To form a dense, adherent, and high-performance coating layer by layer. |
| Common Methods | Sputtering (atom knock-off) & Evaporation (thermal boiling). | Different techniques to achieve the initial vapor generation step. |
Ready to Enhance Your Materials with Precision Thin Films?
Choosing the right deposition technology is critical for achieving the desired coating properties, whether it's extreme hardness, high purity, or specific electrical characteristics. The PVD process is ideal for creating durable, wear-resistant coatings and high-purity metallic films with excellent adhesion.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including PVD systems, to meet your specific research and production needs. Our expertise helps you select the right technology—be it sputtering or evaporation—to ensure your project's success.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our experts today to find the perfect PVD solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the speed of PECVD? Achieve High-Speed, Low-Temperature Deposition for Your Lab
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition


















