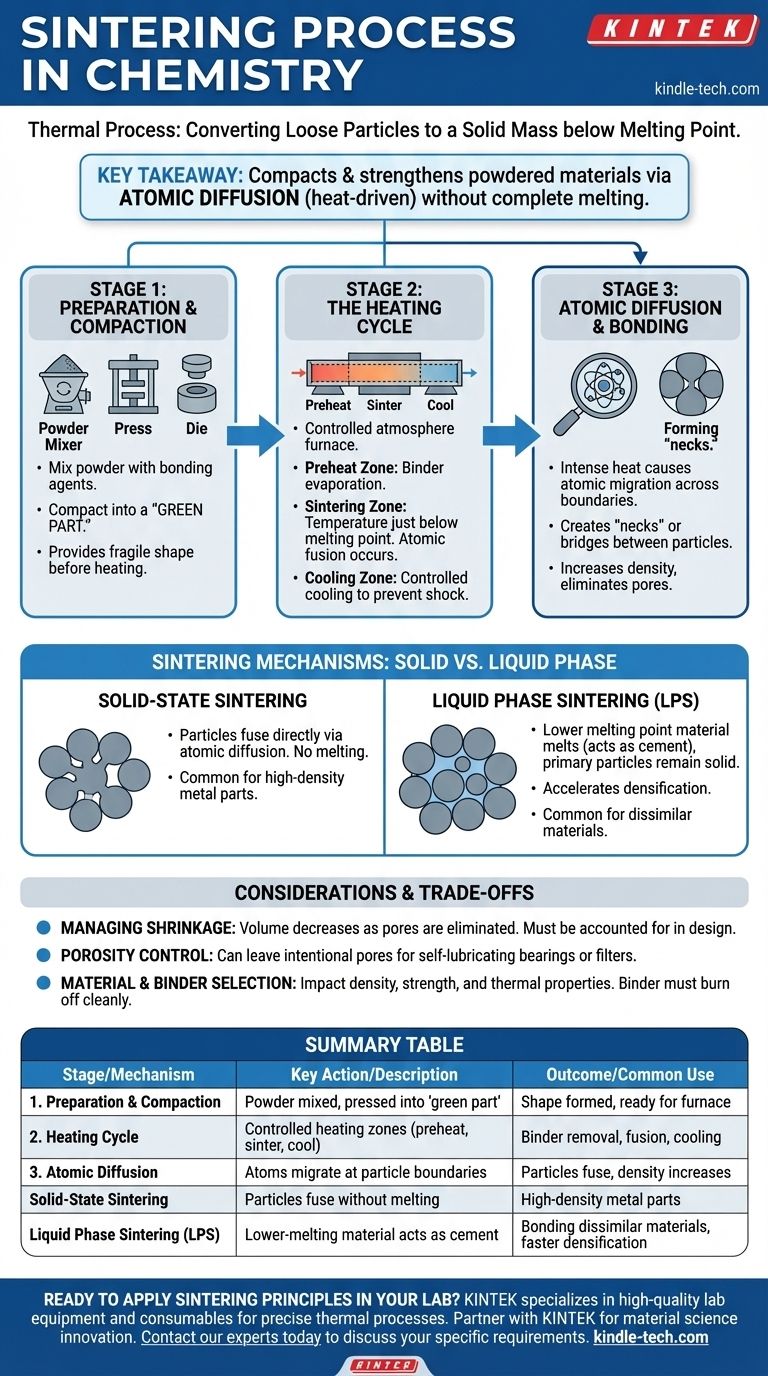
In essence, sintering is a thermal process used to convert a collection of loose particles, such as a powder, into a solid, coherent mass. This is achieved by applying heat and often pressure, but crucially, at temperatures below the material's full melting point. Instead of liquefying, the atoms at the contact points of the particles diffuse across their boundaries, fusing them together and reducing the empty space, or porosity, between them.
The central takeaway is that sintering compacts and strengthens powdered materials into a solid object without melting them completely. It relies on atomic diffusion—driven by heat—to weld particles together, transforming a loose powder into a dense, functional component.

The Core Stages of the Sintering Process
Sintering is not a single action but a controlled, multi-stage process. Each stage serves a specific purpose, from initial shaping to final solidification, ensuring the final part has the desired density and mechanical properties.
Stage 1: Preparation and Compaction
Before any heat is applied, the raw material must be prepared. This involves mixing the primary material powder with additives or bonding agents, such as wax, polymers, or water.
This mixture is then compacted into the desired shape using a die, mold, or press. The resulting fragile object is known as a "green part." The bonding agent provides just enough strength for it to hold its shape during handling before it enters the furnace.
Stage 2: The Heating Cycle
The green part is heated in a controlled atmosphere furnace, often a tunnel kiln, which has distinct temperature zones.
First, the part enters a preheat zone. Here, the temperature is raised gradually to burn off or evaporate the bonding agents and lubricants used during the compaction stage.
Next, it moves into the sintering zone, where the temperature is elevated to just below the material's melting point. This is where the critical atomic fusion occurs.
Finally, the part passes through a cooling zone. This allows the newly formed solid mass to cool down at a controlled rate, preventing thermal shock and locking in its final microstructure.
Stage 3: Atomic Diffusion and Bonding
The true work of sintering happens at a microscopic level within the high-heat sintering zone. The intense thermal energy causes atoms at the surface of each powder particle to vibrate and move.
These energized atoms migrate across the boundaries where particles touch, creating "necks" or bridges between them. As this atomic diffusion continues, these necks grow, pulling the particles closer together, increasing the part's density and eliminating pores.
Key Sintering Mechanisms: Solid vs. Liquid Phase
While the fundamental principle of atomic diffusion is always present, the specific mechanism can vary, primarily distinguished by whether the entire part remains solid or a secondary liquid is introduced.
Solid-State Sintering
This is the most direct form of the process. The primary material powder is heated, and the particles fuse directly with one another through atomic diffusion. No part of the material melts during this process.
Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS)
In this advanced method, a secondary material with a lower melting point is mixed with the primary powder. When heated, this secondary material melts and becomes a liquid, while the primary particles remain solid.
This liquid flows into the pores between the solid particles, acting like a cement. This process, known as transient liquid phase sintering, can accelerate densification and is useful for bonding materials that don't easily fuse, such as mixing copper powder with iron powder.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Sintering is a powerful manufacturing technique, but its successful application requires careful control over several variables to achieve the desired outcome.
Managing Shrinkage
As the particles fuse and the pores between them are eliminated, the overall volume of the part decreases. This shrinkage is a predictable and necessary part of the process, and it must be precisely accounted for in the initial design of the mold or die.
Porosity Control
While the goal is often to create a fully dense part, sintering can also be used to intentionally leave a certain amount of porosity. This is highly desirable for applications like self-lubricating bearings or filters, where the pores can be filled with oil or used to trap particles.
Material and Binder Selection
The choice of the primary powder, along with any additives or temporary binders, is critical. These choices directly impact the final part's density, strength, and thermal properties. The binder must burn away cleanly without leaving behind contaminants that could compromise the material's integrity.
Applying Sintering to Your Goal
Understanding the core process allows you to see how sintering can be tailored to meet specific manufacturing objectives.
- If your primary focus is high-density, complex metal parts: Standard solid-state sintering is a cost-effective method for mass-producing near-net shape components that require minimal finishing.
- If your primary focus is bonding dissimilar materials: Liquid phase sintering is the ideal approach, as it allows you to use a lower-melting-point metal to effectively "braze" the primary structural particles together.
- If your primary focus is creating controlled-porosity components: Sintering provides a unique ability to manage the final density, making it perfect for manufacturing filters or self-lubricating parts.
By controlling heat, pressure, and material composition, sintering gives engineers the power to build solid objects from the ground up, one particle at a time.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation & Compaction | Powder mixed with binder, pressed into a 'green part' | Shape is formed, ready for furnace |
| 2. Heating Cycle | Controlled heating in zones (preheat, sinter, cool) | Binder removal, particle fusion, controlled cooling |
| 3. Atomic Diffusion | Atoms migrate at particle boundaries, forming 'necks' | Particles fuse, density increases, porosity decreases |
| Mechanism | Description | Common Use |
| Solid-State Sintering | Particles fuse directly without melting | High-density metal parts |
| Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS) | A lower-melting-point material melts to act as a cement | Bonding dissimilar materials, faster densification |
Ready to apply sintering principles in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need for precise thermal processes like sintering. Whether you are developing new materials, manufacturing complex metal parts, or creating controlled-porosity components, our reliable furnaces and expert support ensure your success.
Let KINTEK be your partner in material science innovation. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory requirements and discover the right solutions for your sintering applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism of SPS process? A Deep Dive into Rapid, Low-Temperature Sintering
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- What are the advantages of SPS? Achieve Superior Material Density and Performance



















