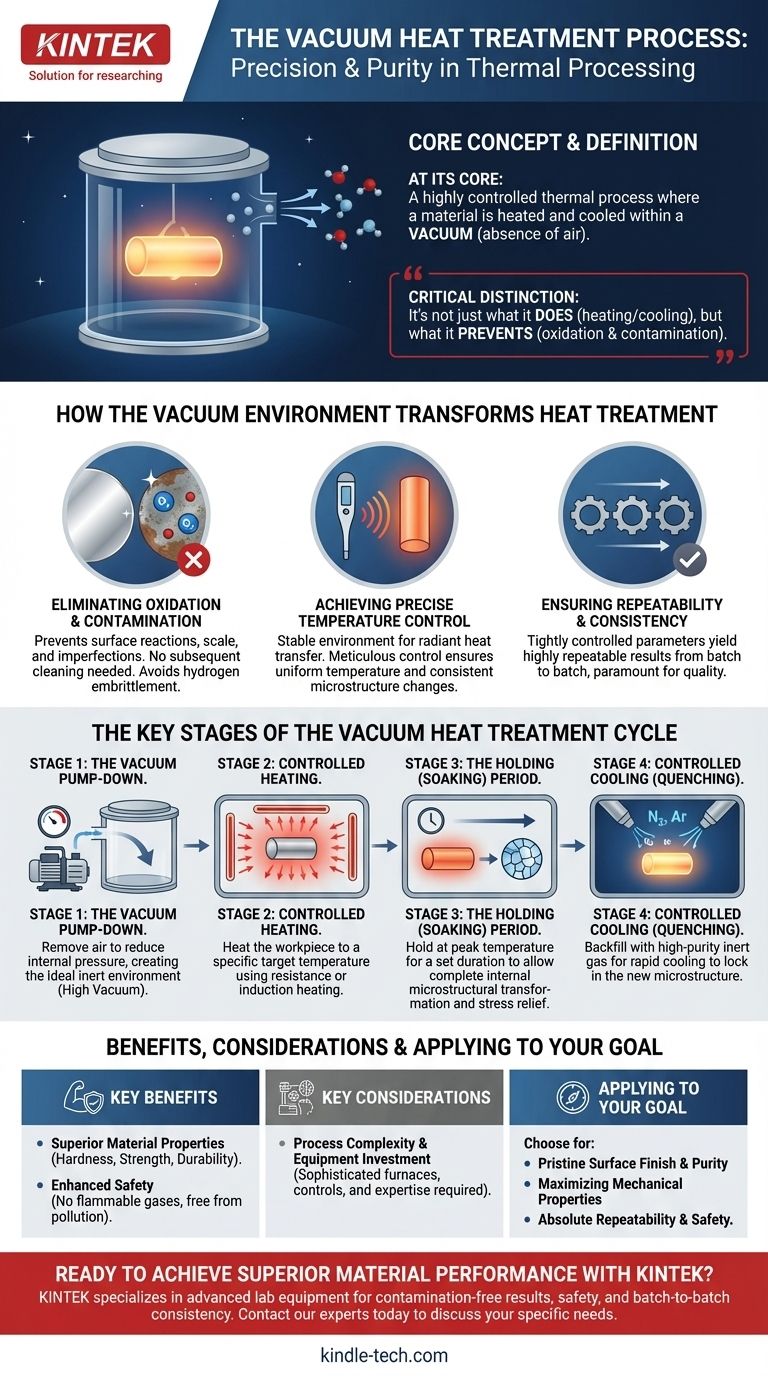
At its core, vacuum heat treatment is a highly controlled thermal process where a material is heated and cooled within a vacuum. This process involves heating the workpiece to a specific temperature, holding it for a predetermined time, and then cooling it at a controlled rate in various media. By performing these steps in the absence of air, the process fundamentally alters the material's internal microstructure, improving its performance and quality without the risk of surface oxidation or contamination.
The critical distinction of vacuum heat treatment is not just what it does—heating and cooling metal—but what it prevents. By removing air from the equation, it eliminates oxidation and contamination, granting engineers unparalleled control over the final material properties and ensuring a level of quality and consistency that conventional methods cannot match.

How the Vacuum Environment Transforms Heat Treatment
The use of a vacuum is the defining feature that provides a superior level of process control. This controlled atmosphere is the source of the method's primary advantages over traditional atmospheric heating.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
In a conventional furnace, the oxygen in the air reacts with the hot metal surface, creating scale and other imperfections. A vacuum environment is, by definition, free of oxygen.
This prevents any surface reactions from occurring, resulting in a clean, bright part that requires no subsequent cleaning. It also avoids harmful contaminants and risks like hydrogen embrittlement.
Achieving Precise Temperature Control
A vacuum provides an exceptionally stable and uniform environment for heating. The heat is transferred primarily through radiation, allowing for meticulous control over the temperature of the workpiece.
This precision ensures the entire part reaches the desired temperature uniformly, which is critical for achieving consistent changes in the material's microstructure.
Ensuring Repeatability and Consistency
Because the process parameters are so tightly controlled—from the vacuum level to the heating and cooling rates—the results are highly repeatable.
This invariability from batch to batch is a significant advantage in manufacturing, where consistent quality is paramount.
The Key Stages of the Vacuum Heat Treatment Cycle
The process follows a distinct, multi-stage cycle, with each step playing a critical role in the final outcome.
Stage 1: The Vacuum Pump-Down
The cycle begins by placing the workpiece inside a sealed furnace chamber. A vacuum pumping system then removes the air, reducing the internal pressure.
The degree of vacuum is critical; a high vacuum corresponds to a low pressure, creating the ideal inert environment for the subsequent steps.
Stage 2: Controlled Heating
Once the target vacuum level is reached, the workpiece is heated. This is typically accomplished using resistance heating elements or induction.
The material is brought up to a suitable temperature specified for the particular alloy and desired outcome.
Stage 3: The Holding (or Soaking) Period
The workpiece is held at this peak temperature for a specific duration. This "soaking" allows the material's internal structure to fully transform.
The required holding time is carefully calculated based on the material's effective thickness, shape, and the total mass of the furnace load. This is where processes like vacuum aging occur to relieve internal stress and stabilize the material.
Stage 4: Controlled Cooling (Quenching)
The final stage is cooling the part to lock in the new microstructure. In a vacuum furnace, this is often done by backfilling the chamber with a high-purity inert gas like nitrogen or argon.
This gas is blown onto the workpiece to cool it rapidly. The cooling rate can be further accelerated by using overpressure (up to 1.4 bars), which enhances the quenching effect.
Understanding the Key Benefits and Considerations
While the benefits are significant, it's important to understand the context in which this process excels.
Key Benefit: Superior Material Properties
The primary goal of any heat treatment is to improve material characteristics. Vacuum treatment excels at this by allowing for the development of improved hardness, strength, and durability while eliminating internal stresses.
Key Benefit: Enhanced Safety and Cleanliness
The process is inherently safer and cleaner than many alternatives. It does not use flammable gases and is free from pollution and oxygen.
This operational safety helps ensure compliance with regulations like OSHA and protects employees from hazardous materials.
Key Consideration: Process Complexity and Equipment
Achieving these superior results requires sophisticated equipment. Vacuum furnaces, specialized pumping systems, and advanced process controls represent a significant investment.
Furthermore, running the process effectively requires expertise in calculating holding times and managing the precise heating and cooling profiles for different materials and geometries.
Applying Vacuum Heat Treatment to Your Goal
Choosing the right thermal process depends entirely on your project's end goal.
- If your primary focus is a pristine surface finish and material purity: Vacuum treatment is the definitive choice because its oxygen-free environment prevents any surface scale or contamination.
- If your primary focus is maximizing mechanical properties and performance: The precise control over heating and quenching allows you to tailor the material's microstructure for specific hardness, strength, and ductility requirements.
- If your primary focus is process safety and absolute repeatability: The automated, contained, and highly controlled nature of vacuum treatment ensures consistent, reliable results batch after batch while eliminating the hazards of flammable gases.
Ultimately, opting for vacuum heat treatment is a deliberate choice for unparalleled control, resulting in a higher standard of quality and performance.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Pump-Down | Remove air from furnace chamber | Create an inert, oxygen-free environment |
| 2. Heating | Heat workpiece to target temperature | Initiate microstructural changes |
| 3. Soaking | Hold at peak temperature | Allow complete internal transformation |
| 4. Quenching | Cool rapidly with inert gas | Lock in new microstructure and properties |
Ready to achieve superior material performance with precision vacuum heat treatment?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for laboratories requiring the highest standards of material purity, strength, and repeatability. Our vacuum furnaces and thermal processing solutions are designed to deliver contamination-free results, enhance safety, and ensure batch-to-batch consistency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our vacuum heat treatment solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs and elevate your research and manufacturing outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment cycle? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Precision
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- What materials are used in a vacuum furnace? Selecting the Right Hot Zone for Your Process
- What are vacuum furnace parts? A Guide to the Core Systems for Precision Heat Treatment
- How to vacuum out a furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe DIY Maintenance



















