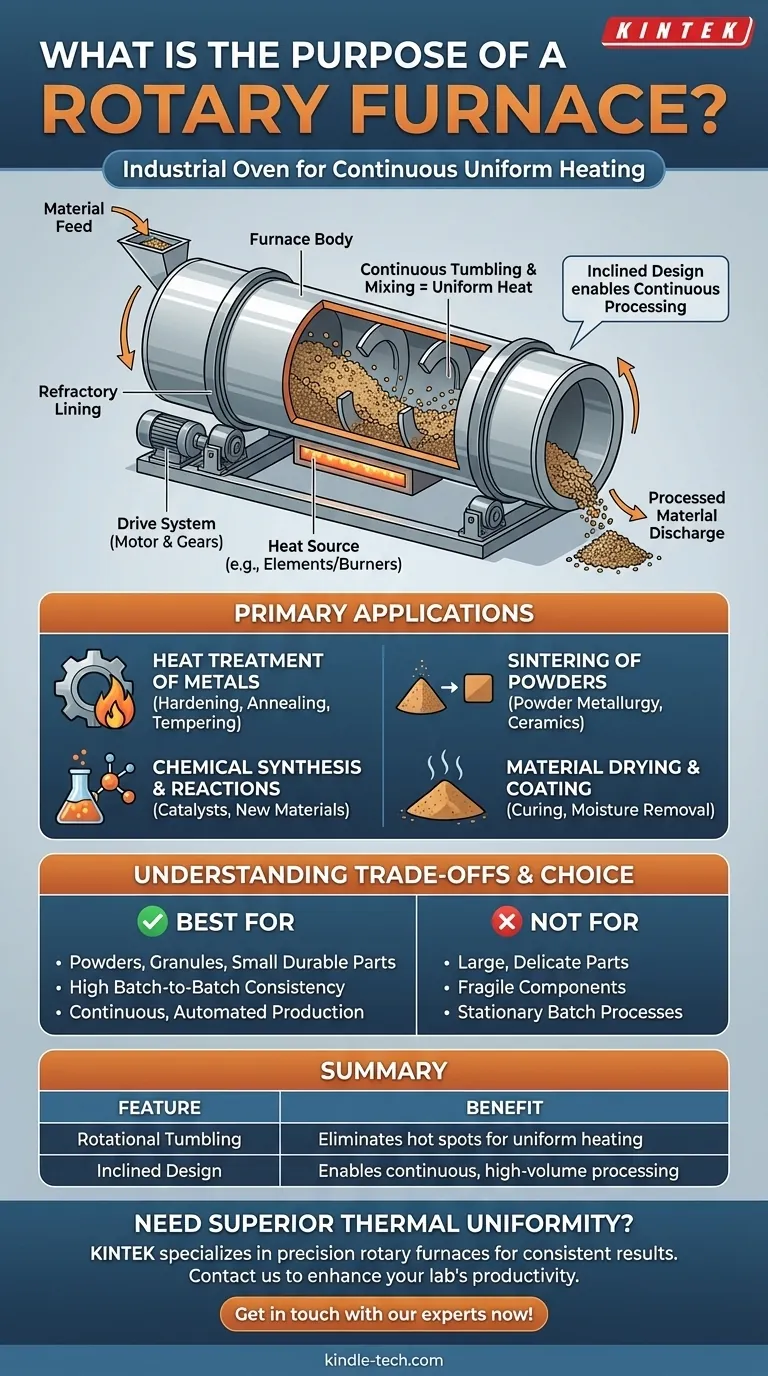
At its core, a rotary furnace is an industrial oven that continuously rotates to tumble the material inside. Its primary purpose is to apply heat with exceptional uniformity to powders, small parts, or granular substances. This method is critical for processes like material sintering, metal heat treatment, and chemical synthesis where consistent results are paramount.
The defining feature of a rotary furnace isn't just its ability to heat, but its method of doing so. By continuously tumbling the material, it eliminates hot spots and ensures every particle or surface receives the exact same thermal treatment, leading to highly consistent and predictable end-products.
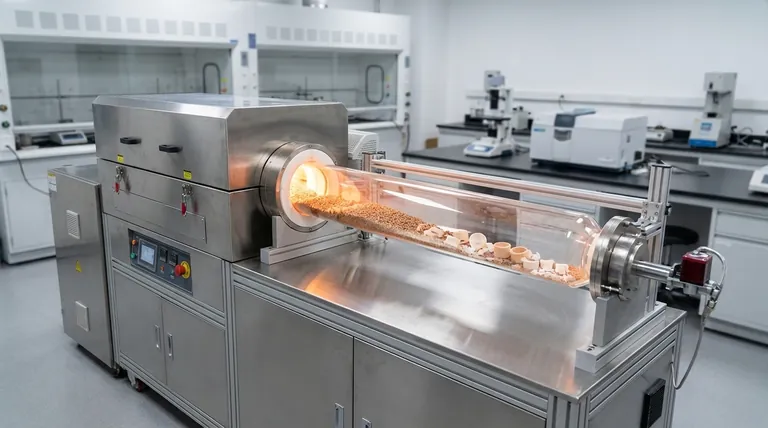

How a Rotary Furnace Achieves Uniform Heating
The genius of the rotary furnace lies in its simple, effective mechanical design. It solves the common problem of uneven heating found in stationary ovens, where some parts of the material are inevitably closer to the heat source than others.
The Principle of Rotation and Tumbling
A rotary furnace is shaped like a long cylinder or barrel. As it rotates along its horizontal axis, the material inside is lifted up the side of the cylinder before tumbling back down.
This constant mixing action ensures that no single part of the material is over-exposed or under-exposed to the heat. The result is a homogenous temperature profile throughout the entire batch.
The Role of Inclination
Most rotary furnaces are mounted on a slight angle, typically between 3 and 6 degrees. This inclination uses gravity to move the material from the entry point at the higher end to the exit point at the lower end.
This design is what enables continuous processing. New material can be fed in one end while the fully processed material is discharged from the other, making it highly efficient for high-volume production.
Core Components
A rotary furnace is constructed from a few key parts working in concert:
- Furnace Body: A long steel cylinder that contains the material.
- Refractory Lining: A heat-resistant lining inside the cylinder that protects the steel shell and insulates the process.
- Drive System: An electric motor and gears that turn the furnace body at a controlled speed.
- Heat Source: This can be electric heating elements or gas burners that provide the thermal energy.
Primary Applications Across Industries
The ability to deliver uniform heat makes the rotary furnace indispensable for a wide range of sensitive thermal processes.
Heat Treatment of Metals
Uniform heating and cooling are essential for achieving specific metallurgical properties. Rotary furnaces are used for hardening, annealing, and tempering small parts like bearings, fasteners, and ammunition casings to improve their strength and structure.
Sintering of Powders
In powder metallurgy and ceramics, sintering involves heating a compacted powder to just below its melting point. The uniform heat of a rotary furnace ensures that all particles bond together evenly, creating a dense, strong final part with consistent properties.
Chemical Synthesis and Reactions
Many chemical reactions require precise temperature control to proceed correctly. Rotary furnaces are used as reactors to synthesize new materials or prepare industrial catalysts, where consistency is key to performance and yield.
Material Drying and Coating
The furnace is highly effective for drying moisture from bulk materials or for curing coatings onto small substrates. The tumbling action exposes all surfaces for efficient and even drying or curing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a rotary furnace is a specialized tool. Understanding its limitations is as important as knowing its strengths.
Advantage: Unmatched Uniformity
For granular materials and small parts, no other furnace type can easily match the thermal consistency provided by the tumbling action of a rotary design. This is its single greatest advantage.
Advantage: Continuous Processing
The tilted design is ideal for automated, high-volume production lines where material needs to flow continuously through a heating step.
Limitation: Not for Large or Delicate Parts
The tumbling motion that is so beneficial for powders can cause damage. Large, complex, or fragile components would be broken or deformed, making a stationary batch furnace a better choice for such items.
Consideration: Simplicity vs. Complexity
While some basic smelting operations can be run by less-skilled workers, advanced applications demand precise control. High-performance processes may require sophisticated control over the furnace atmosphere (e.g., vacuum or inert gas), temperature profile, and rotation speed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct heating technology depends entirely on your material and your goal.
- If your primary focus is processing powders, pellets, or small, durable parts: A rotary furnace is the ideal choice for achieving high batch-to-batch consistency.
- If your primary focus is heat treating large, single workpieces or delicate components: You should consider a stationary chamber or batch furnace, as the tumbling action could cause damage.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, automated production: The continuous-flow design of an inclined rotary furnace makes it an exceptionally efficient option.
By understanding its core principle of rotational heating, you can effectively determine if its unique capabilities align with your material processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Rotational Tumbling | Eliminates hot spots for uniform heating of powders and small parts. |
| Inclined Design | Enables continuous, high-volume processing for automated production. |
| Key Applications | Ideal for sintering, metal heat treatment, chemical synthesis, and drying. |
| Best For | Powders, granules, and small, durable parts requiring consistent results. |
Need to achieve superior thermal uniformity in your process?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including rotary furnaces designed for consistent and efficient sintering, heat treatment, and chemical synthesis. Our expertise ensures you get the right solution for processing powders, granules, and small parts with high batch-to-batch consistency.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK rotary furnace can enhance your laboratory's productivity and results.
Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity for Your Industrial Processes
- What are the examples of the products of pyrolysis? Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Explained
- What is pyrolysis and the process of pyrolysis? Turn Waste into Valuable Resources
- What are the factors affecting plastic pyrolysis? Optimize Yield and Quality from Waste Plastic
- What apparatus is required for pyrolysis? A Guide to the Essential Components and Systems
- What is the composition of fast pyrolysis oil? A Guide to the Complex Chemical Intermediate
- Why is pyrolysis getting interesting in recent times? Unlock Waste-to-Value Solutions for a Circular Economy
- What is the composition of biomass pyrolysis gas? A Guide to Its Makeup and Energy Value



















