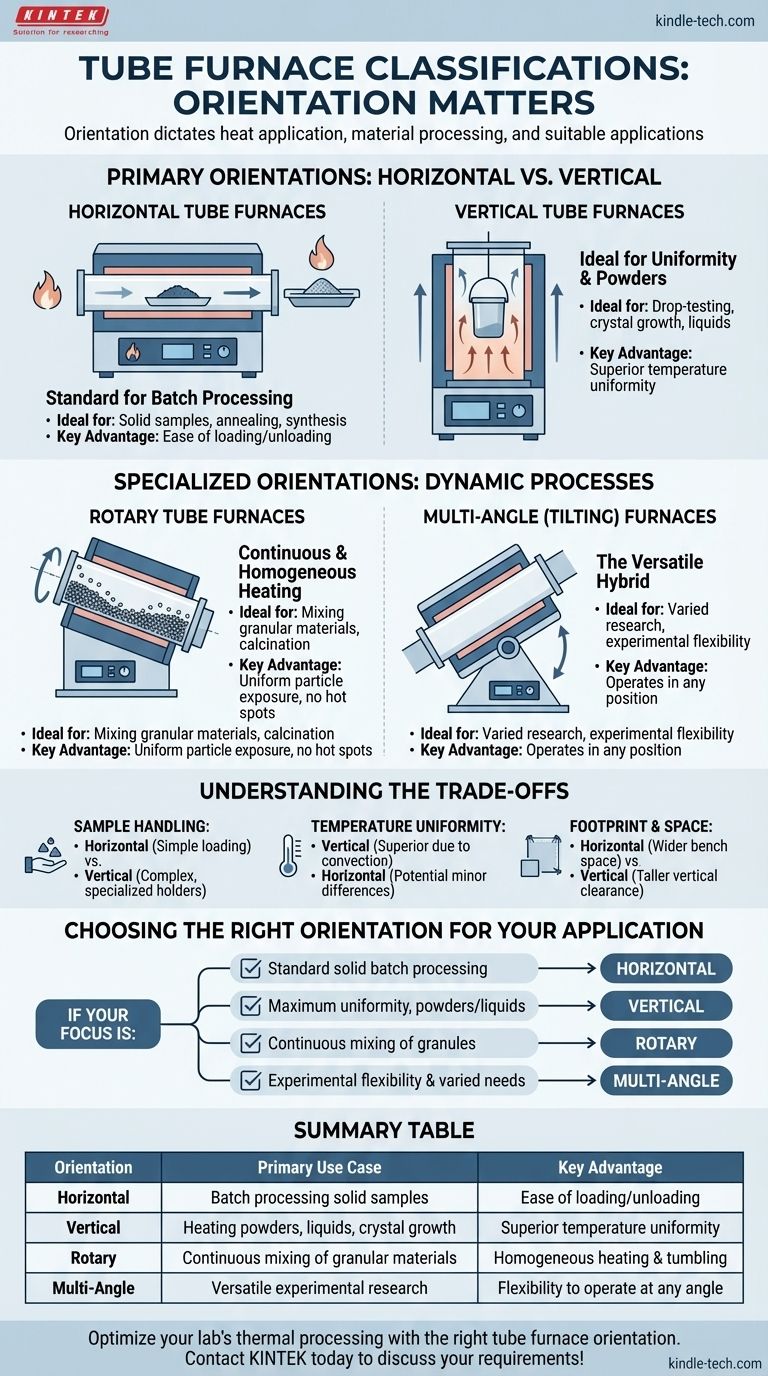
When classifying tube furnaces by the orientation of the tube, they are primarily categorized as horizontal and vertical. These two configurations represent the most common designs, but specialized applications have also led to the development of rotary and multi-angle (or tilting) furnaces, which are also defined by their operational orientation.
The orientation of a furnace's tube is not a minor design detail; it is the fundamental factor that dictates how a sample is heated, how materials can be processed, and ultimately, which scientific or industrial applications the furnace is suitable for.

The Primary Orientations: Horizontal vs. Vertical
The choice between a horizontal or vertical furnace is the most common decision researchers and engineers face. Each configuration offers distinct advantages based on the nature of the material being processed.
Horizontal Tube Furnaces: The Standard for Batch Processing
A horizontal tube furnace is the most conventional design, where the processing tube lies flat. This setup is straightforward and highly effective for general-purpose heating.
Its primary advantage is the ease of loading and unloading solid samples, which are typically placed in a ceramic or quartz "boat" and pushed into the center of the hot zone. This makes it ideal for many standard annealing, curing, and synthesis applications.
Vertical Tube Furnaces: Ideal for Uniformity and Powders
In a vertical tube furnace, the tube is oriented upright. This design leverages gravity and natural convection to its advantage.
As hot air rises, it creates a highly uniform temperature environment, often superior to that of a horizontal furnace. This configuration is essential for processes like drop-testing, crystal growth, or when heating powders and liquids in crucibles, as it prevents the sample from touching and potentially reacting with the tube walls.
Specialized Orientations for Dynamic Processes
Beyond the standard static configurations, some processes require movement and agitation to achieve the desired outcome. This need has led to more dynamic furnace designs.
Rotary Tube Furnaces: For Continuous and Homogeneous Heating
Rotary tube furnaces are designed for the continuous heating and mixing of loose, granular, or powdered materials. The tube itself rotates slowly during operation.
This constant tumbling ensures every particle is exposed to the heat source uniformly, preventing hot spots and resulting in a highly homogeneous final product. They are commonly used in industrial settings for processes like calcination or roasting.
Multi-Angle (Tilting) Furnaces: The Versatile Hybrid
A multi-angle or tilting furnace offers the ultimate flexibility. These units can be operated in a horizontal, vertical, or any intermediate angular position.
This versatility allows a single furnace to accommodate a wide variety of experimental needs, combining the benefits of different orientations. For instance, a process might involve loading a sample horizontally and then tilting the furnace to pour or mix the contents at high temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an orientation requires balancing practical considerations related to your specific process and laboratory environment.
Sample Handling and Loading
Horizontal furnaces are the simplest for handling solid samples in boats. Vertical furnaces can be more complex to load, often requiring specialized sample holders or crucibles suspended by a wire.
Temperature Uniformity
Vertical furnaces generally offer superior temperature uniformity due to natural convection. Horizontal furnaces can sometimes experience minor temperature differences between the top and bottom of the tube.
Footprint and Space
A horizontal furnace requires more benchtop width, while a vertical furnace demands more vertical clearance. This can be a critical factor in a crowded lab with limited ceiling height or bench space.
Choosing the Right Orientation for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific requirements of your material and process goal.
- If your primary focus is standard batch processing of solid samples: A horizontal tube furnace offers the simplest, most common, and most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum temperature uniformity or working with powders and liquids: A vertical tube furnace is the superior choice, leveraging gravity for cleaner and more consistent results.
- If your primary focus is continuous processing and mixing of granular materials: A rotary tube furnace is the only design built specifically for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is experimental flexibility and varied research needs: A multi-angle furnace provides the greatest versatility to adapt to future projects.
Understanding the functional impact of orientation ensures you select a furnace that is not just a tool, but a precise solution for your process.
Summary Table:
| Orientation | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Horizontal | Batch processing of solid samples | Ease of loading and unloading |
| Vertical | Heating powders, liquids, crystal growth | Superior temperature uniformity |
| Rotary | Continuous mixing of granular materials | Homogeneous heating and tumbling |
| Multi-Angle | Versatile experimental research | Flexibility to operate at any angle |
Optimize your lab's thermal processing with the right tube furnace orientation. The design of your furnace directly impacts the success of your experiments, from temperature uniformity to sample handling. KINTEK specializes in providing precise lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific laboratory needs. Let our experts help you select the ideal horizontal, vertical, rotary, or multi-angle furnace for your application. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and enhance your process efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic



















