At its core, brazing is a metal-joining process where two or more metal items are joined together by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint. The filler metal has a lower melting point than the adjoining metal, and crucially, the base materials themselves are never melted. This process creates a strong, permanent, and often leak-proof bond between the parts.
While often compared to welding or soldering, the true purpose of brazing is to create high-strength joints with minimal thermal stress. This unique characteristic makes it the ideal solution for joining delicate or dissimilar materials that cannot be welded.
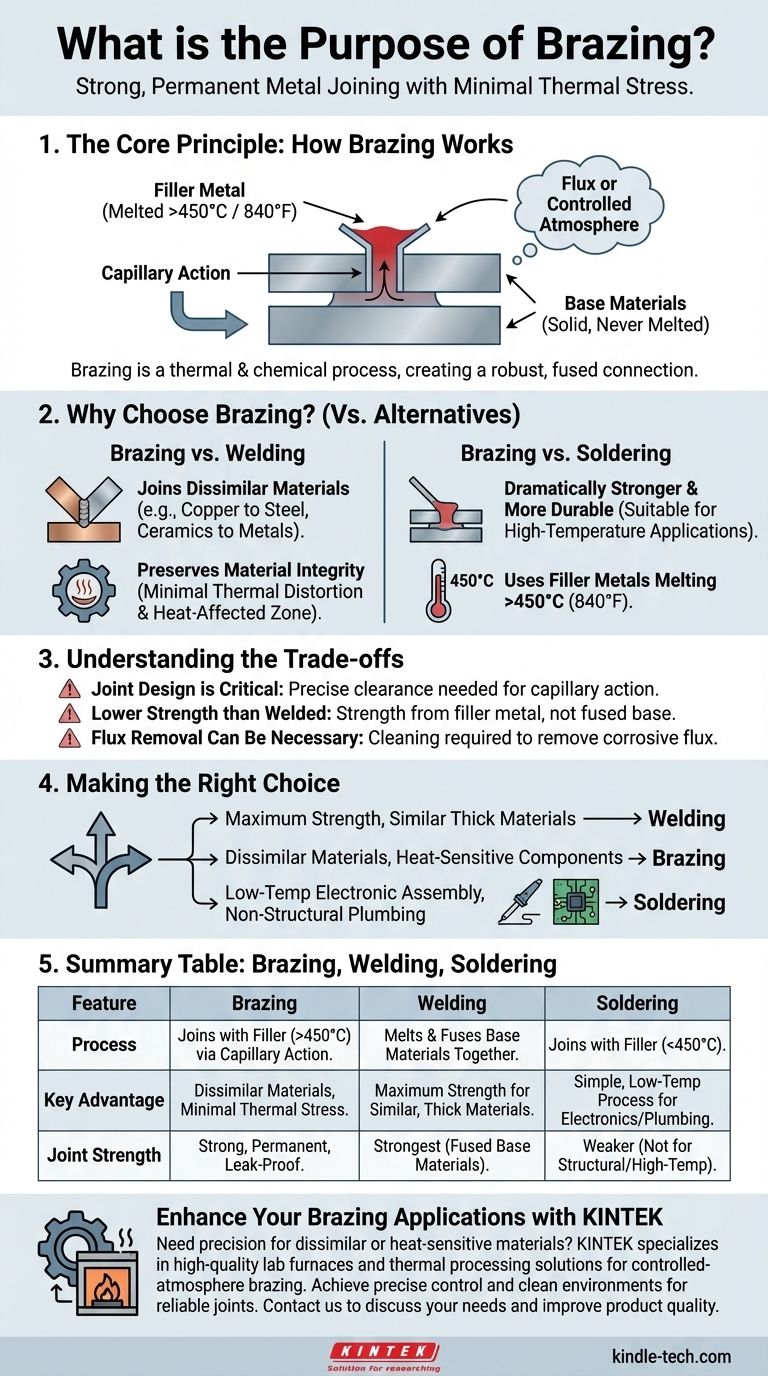
The Core Principle: How Brazing Works
Brazing relies on a simple yet powerful metallurgical principle. It is more than just "gluing" metals together; it is a thermal and chemical process that creates a robust, fused connection.
The Role of the Filler Metal
The process uses a filler metal (often called a brazing alloy) that is selected to have a melting point above 450°C (840°F) but below the melting point of the parts being joined. When heated, this filler metal becomes liquid while the base materials remain solid.
The Power of Capillary Action
Once molten, the filler metal is drawn into the tight-fitting gap between the base materials through a phenomenon called capillary action. This is the same force that draws water up a narrow tube. For this to work effectively, the joint must be designed with a specific, small clearance.
The Importance of Flux or Atmosphere
The surfaces of the metals must be clean and free of oxides for the filler metal to bond correctly. A flux is a chemical compound applied to the joint before heating that cleans the surfaces and prevents new oxidation from forming. In industrial settings, this can also be achieved by brazing inside a controlled-atmosphere furnace.
Why Choose Brazing Over Other Methods?
Understanding the purpose of brazing requires comparing it to its alternatives. The decision to braze is almost always a deliberate engineering choice based on material properties and application requirements.
Brazing vs. Welding: Joining Dissimilar Materials
Welding works by melting the base materials together, which means they must have compatible melting points and metallurgy. Brazing's greatest advantage is its ability to join dissimilar materials, such as copper to steel, or even non-metals like ceramics to metals.
Brazing vs. Welding: Preserving Material Integrity
The high heat of welding creates a large "heat-affected zone" that can distort, warp, and fundamentally change the properties of the base materials. Brazing uses significantly less heat, which minimizes thermal distortion and protects the metallurgical properties of the parent components.
Brazing vs. Soldering: A Question of Strength and Temperature
Soldering is a similar process but uses filler metals that melt below 450°C (840°F). While easier to perform, soldered joints are much weaker and cannot be used in high-temperature applications. Brazed joints are dramatically stronger and more durable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No process is perfect. Being a trusted advisor means acknowledging the limitations of brazing so you can make an informed decision.
Joint Design is Critical
Brazing is highly dependent on a proper joint design. The clearance between the parts must be tight and consistent to enable capillary action. If the gap is too large or too small, the joint will fail.
Lower Strength Than a Properly Welded Joint
For identical metals, a properly executed weld that fuses the base materials will almost always be stronger than a brazed joint. Brazing strength comes from the filler metal, whereas a weld's strength comes from the recrystallized parent material.
Flux Removal Can Be Necessary
If a chemical flux is used, it is often corrosive and must be completely cleaned from the joint after brazing. This extra step can add time and complexity to the manufacturing process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct joining method is a critical decision that impacts cost, performance, and reliability. Use these guidelines to steer your choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength joining similar thick materials: Welding is generally the superior and more direct process.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials (e.g., copper to steel) or heat-sensitive components: Brazing provides the necessary strength while protecting the integrity of the base materials.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature electronic assembly or non-structural plumbing: Soldering offers a sufficient, lower-cost, and simpler solution.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select the joining process that ensures the integrity and performance of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Welding | Soldering |
|---|---|---|---|
| Process | Joins metals with a filler metal (melts above 450°C/840°F) via capillary action. | Melts and fuses the base materials together. | Joins metals with a filler metal (melts below 450°C/840°F). |
| Key Advantage | Ideal for dissimilar materials; minimal thermal stress/distortion. | Maximum strength for similar, thick materials. | Simple, low-temperature process for electronics/plumbing. |
| Joint Strength | Strong, permanent, and often leak-proof. | Strongest, from fused base materials. | Weaker, not for structural or high-temp applications. |
Need to join dissimilar or heat-sensitive materials with precision?
Brazing is a sophisticated thermal process that requires the right equipment and expertise to ensure joint integrity and performance. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and thermal processing solutions, including models perfectly suited for controlled-atmosphere brazing.
Our equipment helps you achieve the precise temperature control and clean environments necessary for strong, reliable brazed joints. Let our experts help you select the ideal furnace for your specific materials and production goals.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss how our thermal processing solutions can enhance your brazing applications and improve your product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining



















