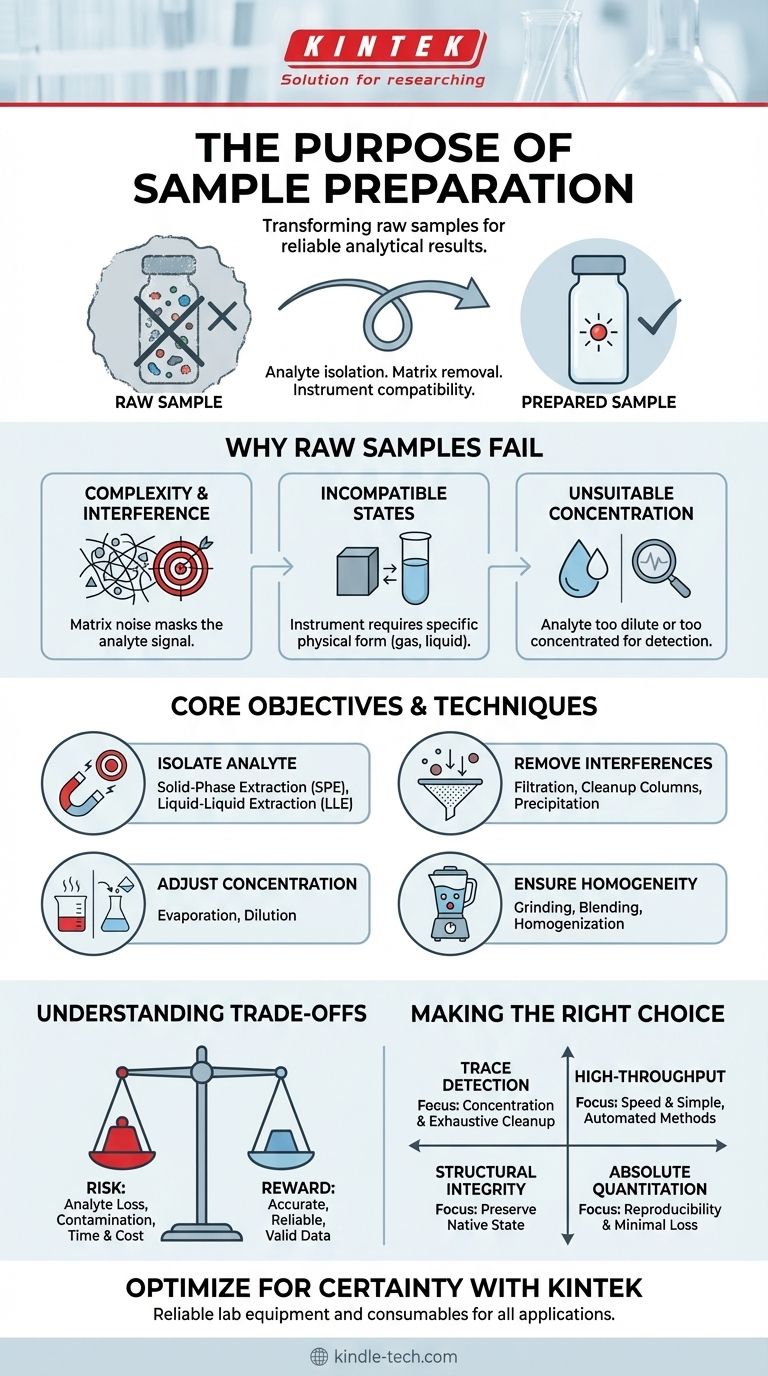
In short, the purpose of sample preparation is to transform a raw sample from its natural state into a form that is suitable for analysis by a scientific instrument. This critical process ensures that the component of interest, the analyte, can be measured accurately and reliably, free from interference from the rest of the sample material, known as the matrix.
The most advanced analytical instrument in the world will produce meaningless data if the sample is not prepared correctly. Sample preparation is not a preliminary chore; it is the foundational step that dictates the quality and validity of any analytical result.

Why Raw Samples Often Cannot Be Analyzed Directly
To understand the purpose of sample preparation, you must first recognize the inherent problems with analyzing a raw sample, whether it's a vial of blood, a soil core, or a pharmaceutical tablet.
The Problem of Complexity and Interference
A raw sample is a complex mixture. The sample matrix contains numerous compounds besides the analyte you want to measure.
These other compounds can interfere with the analysis, either by masking the analyte's signal or by creating a false signal of their own. Sample preparation is designed to clean up this "noise."
Incompatible Physical States
Analytical instruments often have strict requirements. For example, a gas chromatograph requires a volatile, gaseous sample, and a liquid chromatograph requires a sample dissolved in a compatible solvent.
Sample preparation converts the sample—whether solid, sludge, or tissue—into the correct physical state for the instrument.
Unsuitable Analyte Concentration
The analyte may be present at a concentration that is too low to be detected (trace analysis) or too high to be measured accurately by the instrument.
Preparation techniques are used to concentrate a dilute sample or dilute an overly concentrated one, bringing the analyte into the instrument's optimal detection range.
The Core Objectives of Sample Preparation
Every sample preparation protocol is designed to achieve one or more of the following fundamental goals to ensure a successful analysis.
To Isolate the Analyte of Interest
The primary goal is often to separate the analyte from the rest of the sample matrix. This is the essence of techniques like solid-phase extraction (SPE), liquid-liquid extraction (LLE), and precipitation.
To Remove Interfering Substances
This is the "cleanup" step. The goal is to eliminate any substance that could compromise the accuracy of the measurement. A well-designed preparation method is highly selective, removing interferences while leaving the analyte behind.
To Adjust Concentration for Optimal Detection
As mentioned, this involves making the analyte more concentrated or more dilute. Techniques like evaporation concentrate an analyte, while simple dilution with a pure solvent reduces its concentration.
To Ensure Sample Homogeneity
For solid or semi-solid samples, the analyte may not be distributed evenly. Homogenization (e.g., grinding, blending) ensures that the small portion of the sample taken for analysis is truly representative of the entire bulk sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While essential, sample preparation is not without its challenges and potential pitfalls. Acknowledging these trade-offs is key to developing a robust analytical method.
The Risk of Analyte Loss
Every manipulation step—from transferring a liquid to performing an extraction—carries the risk of losing some of the analyte. A good method minimizes these steps and is validated to quantify any unavoidable loss.
The Introduction of Contamination
The solvents, reagents, and equipment used in preparation can introduce contaminants that interfere with the analysis. This is a major concern in trace analysis, requiring the use of ultra-pure reagents and scrupulously clean labware.
The Cost in Time and Resources
Sample preparation is often the most time-consuming and labor-intensive part of an entire analytical procedure. It can also be the source of the majority of errors if not performed with care and consistency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" sample preparation method is entirely dependent on your analytical objective. There is no single universal protocol.
- If your primary focus is trace-level detection (e.g., environmental contaminants): Your strategy must prioritize analyte concentration and the exhaustive removal of matrix interferences, even if it is time-consuming.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput screening (e.g., drug discovery): Your methods must be simple, fast, and easily automated, accepting a lower level of cleanup in exchange for speed.
- If your primary focus is ensuring structural integrity (e.g., microscopy): Your preparation must preserve the sample's native state, focusing on techniques like fixation and sectioning rather than extraction.
- If your primary focus is absolute quantitation (e.g., pharmaceutical quality control): Your method must be exceptionally reproducible and validated to prove minimal analyte loss and no introduction of interferences.
Ultimately, investing in the development and execution of a robust sample preparation strategy is an investment in the certainty and integrity of your final results.
Summary Table:
| Objective | Key Function | Common Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Isolate Analyte | Separate target component from sample matrix | Solid-phase extraction, Liquid-liquid extraction |
| Remove Interferences | Eliminate substances that compromise accuracy | Filtration, Cleanup columns, Precipitation |
| Adjust Concentration | Bring analyte into instrument's detection range | Evaporation, Dilution |
| Ensure Homogeneity | Create a representative sample for analysis | Grinding, Blending, Homogenization |
Ready to optimize your sample preparation for reliable results?
The right equipment is fundamental to a robust sample preparation strategy. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed to minimize analyte loss, prevent contamination, and enhance reproducibility.
We serve laboratories focused on:
- Trace Analysis: Achieve the sensitivity you need with reliable homogenizers and extraction systems.
- High-Throughput Screening: Increase efficiency with our automated preparation solutions.
- Quality Control: Ensure method reproducibility and data integrity with our precision instruments.
Let us help you build a foundation for analytical certainty. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Grinding Mill Mortar Grinder for Sample Preparation
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What is the particle size for XRD analysis? Optimize Your Results with the Right Preparation
- Why is an agate mortar and pestle preferred for grinding MAX phase? Ensure Sample Purity & Zero Contamination
- Why is an alumina mortar used for grinding dried Yttrium Oxide precursor materials? Ensure Maximum Purity and Quality
- What is the function of a mortar and pestle in ZnS nanoparticle prep? Optimize Your Sample Refinement
- What is the function of an Agate Mortar and Pestle in sodium battery preparation? Ensure Contaminant-Free Mixing














