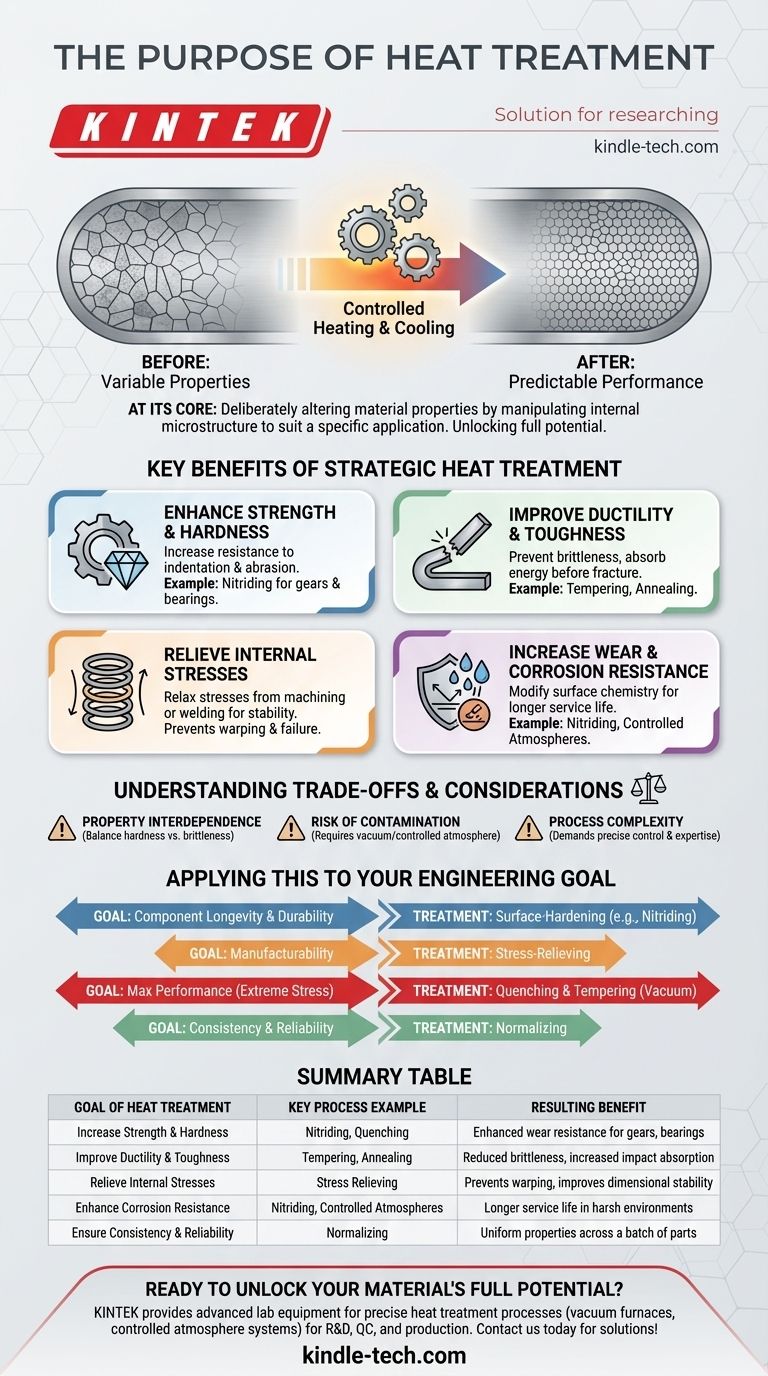
At its core, the purpose of heat treatment is to deliberately alter a material's physical and mechanical properties to suit a specific application. It is a highly controlled process of heating and cooling metals and alloys to manipulate their internal microstructure, thereby enhancing characteristics like strength, hardness, and durability, or relieving internal stresses to improve machinability.
Heat treatment is not a single action but a suite of sophisticated techniques. Its fundamental goal is to unlock the full potential of a material, tailoring its internal structure to deliver predictable and superior performance that the base material could not otherwise achieve.

The Fundamental Goal: Manipulating Microstructure
Heat treatment works by changing the crystalline structure, or microstructure, of a material. This internal change is what dictates the material's external behavior and properties.
Achieving Predictable Performance
A primary goal is to create a uniform and consistent material. Processes like normalizing are used to homogenize the internal structure, eliminating inconsistencies and ensuring that the material's mechanical properties are predictable and reliable from one part to the next.
Unlocking Latent Potential
Many alloys, particularly steel, have latent properties that can only be activated through heat treatment. By carefully controlling heating and cooling cycles, you can make a standard piece of steel significantly stronger, tougher, or more resistant to wear.
Key Benefits of Strategic Heat Treatment
Applying the right heat treatment unlocks specific, desirable outcomes that are critical for modern engineering and manufacturing.
Enhancing Strength and Hardness
One of the most common goals is to increase a material's strength and its resistance to indentation and abrasion. Surface treatments like nitriding, which introduces nitrogen, create an extremely hard outer case, crucial for gears and bearings.
Improving Ductility and Toughness
While hardness is important, so is the ability to deform without fracturing (ductility) and to absorb energy before breaking (toughness). Certain heat treatments can refine the material's grain structure to prevent brittleness.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Manufacturing processes like welding, casting, or heavy machining introduce significant internal stresses into a part. These stresses can cause warping or premature failure. Heat treatment is used to relax these stresses, making the component stable and easier to work with.
Increasing Wear and Corrosion Resistance
Specific treatments can fundamentally change a material's surface chemistry. Nitriding, for example, not only increases hardness but also significantly boosts the material's resistance to corrosion, extending its service life in harsh environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Heat treatment is a powerful tool, but it requires precision and an understanding of its inherent compromises and risks.
Property Interdependence
There is often a trade-off between properties. For example, increasing a material's hardness to its maximum level can sometimes make it more brittle and prone to cracking under sudden impact. The ideal treatment balances these competing characteristics.
The Risk of Contamination
The material's environment during treatment is critical. For high-performance alloys used in aerospace or automotive, uncontrolled atmospheres can introduce impurities that degrade the material's properties. This is why vacuum heat treatment or other controlled-atmosphere methods are essential to prevent oxidation and ensure quality.
Process Complexity
Achieving the desired outcome requires precise control over temperature, time, and cooling rates. This complexity means that proper execution demands specialized equipment and deep metallurgical expertise to avoid damaging the component.
Applying This to Your Engineering Goal
Your specific objective dictates the type of heat treatment required. Use this guide to determine your starting point.
- If your primary focus is component longevity and durability: You should investigate surface-hardening treatments like nitriding to improve wear and corrosion resistance.
- If your primary focus is manufacturability: Stress-relieving treatments are critical after welding or heavy machining to prevent distortion and ensure dimensional stability.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance under extreme stress: Look to processes like quenching and tempering, often within a vacuum environment, especially for high-performance alloys used in aerospace or automotive engines.
- If your primary focus is consistency and reliability across a batch of parts: Normalizing is the key process to ensure a homogenous microstructure and predictable mechanical properties.
Ultimately, understanding heat treatment empowers you to select not just a material, but its optimal state for the task at hand.
Summary Table:
| Goal of Heat Treatment | Key Process Example | Resulting Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Increase Strength & Hardness | Nitriding, Quenching | Enhanced wear resistance for gears, bearings |
| Improve Ductility & Toughness | Tempering, Annealing | Reduced brittleness, increased impact absorption |
| Relieve Internal Stresses | Stress Relieving | Prevents warping, improves dimensional stability |
| Enhance Corrosion Resistance | Nitriding, Controlled Atmospheres | Longer service life in harsh environments |
| Ensure Consistency & Reliability | Normalizing | Uniform properties across a batch of parts |
Ready to unlock the full potential of your materials?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise heat treatment processes. Whether you are working on R&D, quality control, or production, our solutions—including vacuum furnaces and controlled atmosphere systems—help you achieve superior material properties, consistency, and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs in material science and engineering. Get in touch via our contact form to speak with an expert!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance



















