In simple terms, the Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) process for jewelry is a high-tech vacuum coating method that molecularly bonds a durable, thin-film ceramic material onto a metal base. Unlike traditional plating, which layers a finish on top, PVD integrates the coating with the jewelry itself. This creates a surface that is exceptionally resistant to scratches, tarnishing, and corrosion, all while enabling a wide variety of colors.
The essential value of PVD is its ability to create a new, integrated surface layer, not just apply a color. By physically bonding the coating to the base metal at an atomic level, the process produces a finish that is fundamentally more durable and long-lasting than any traditional plating method.
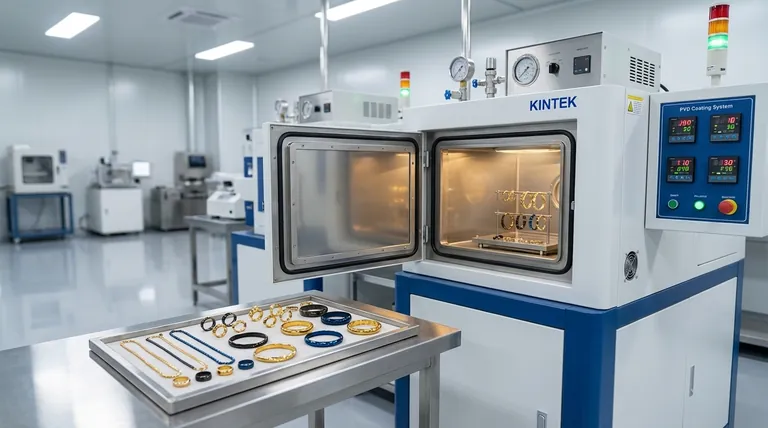

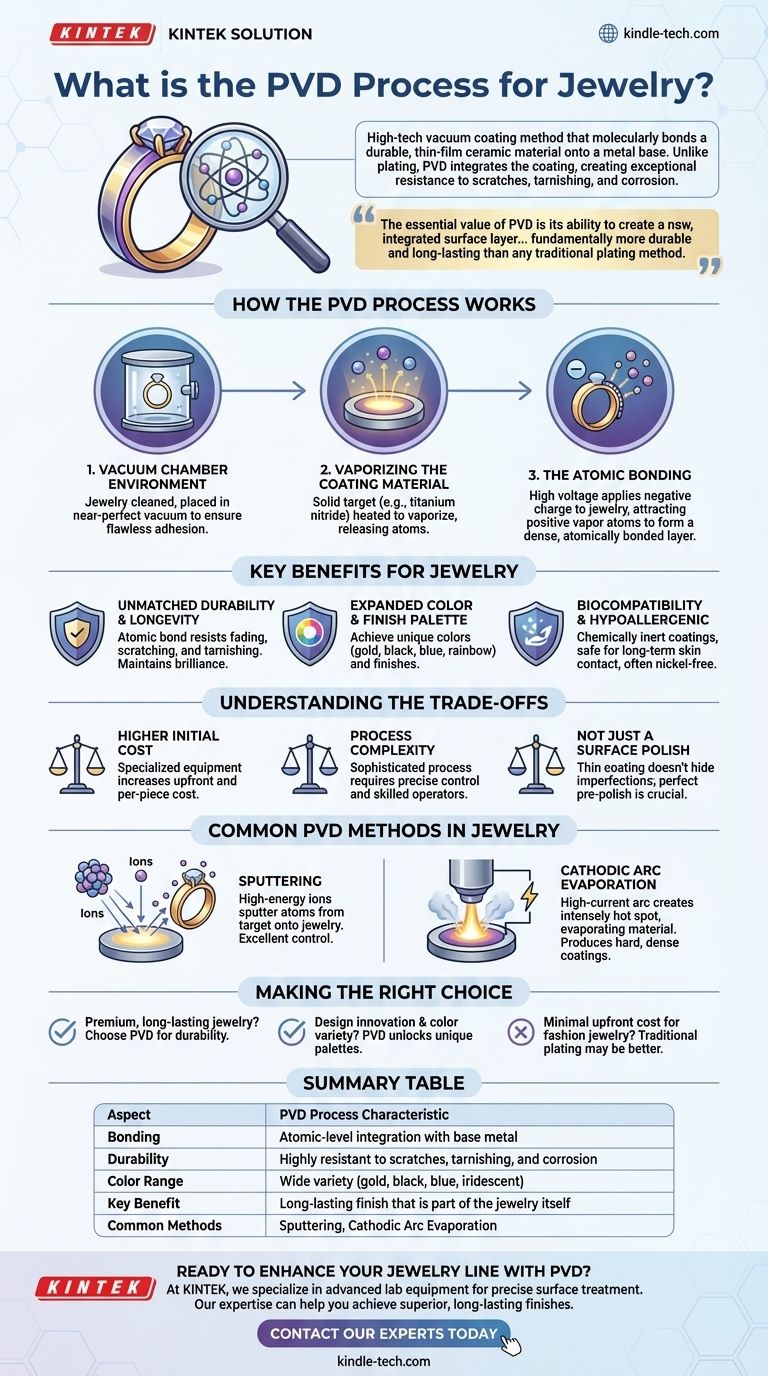
How the PVD Process Works
PVD transforms a solid coating material into a vapor, which then condenses onto the jewelry piece, forming a strong, permanent bond. This all happens within a highly controlled vacuum environment.
The Vacuum Chamber Environment
First, the jewelry is meticulously cleaned and placed inside a vacuum chamber. All the air and impurities are pumped out, creating a near-perfect vacuum. This step is critical to ensure the coating adheres flawlessly without any contaminants.
Vaporizing the Coating Material
A solid "target" material—often a ceramic like titanium nitride—is then heated to a high temperature using a high-energy source. This causes the material to evaporate, or vaporize, releasing individual atoms or molecules that disperse throughout the chamber.
The Atomic Bonding
A high voltage is applied to the jewelry, giving it a negative charge. This charge attracts the positively charged vaporized atoms, which accelerate toward the jewelry at high speed. They embed themselves into the surface of the base metal, forming a dense, hard, and atomically bonded layer.
The Key Benefits for Jewelry
The PVD process was adopted by the jewelry industry because it solves two fundamental problems: the fragility of traditional plating and the limited color palette of precious metals.
Unmatched Durability and Longevity
The atomic bond created during PVD results in a finish that is part of the jewelry itself. This makes it incredibly resistant to fading, scratching, and tarnishing from daily wear, sweat, and perfumes. PVD-coated jewelry maintains its brilliance for an extended period.
Expanded Color and Finish Palette
PVD allows designers to achieve colors that are impossible with natural metals alone. Finishes can range from classic gold and rose gold tones to black, blue, and even iridescent rainbow effects. This is achieved by using different coating materials and controlling the process variables.
Biocompatibility and Hypoallergenic Properties
Many common PVD coatings, such as titanium nitride, are chemically inert and biocompatible. This means they are hypoallergenic and safe for long-term skin contact, which is a significant advantage over plated alloys that may contain nickel or other irritants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PVD is not without its specific considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Cost
The specialized equipment required for PVD—including vacuum chambers and high-voltage power supplies—makes the initial investment and per-piece cost higher than traditional electroplating.
Process Complexity
PVD is a sophisticated process that demands precise control over temperature, pressure, and timing. It requires skilled operators and is less forgiving of errors than simpler coating methods. The quality of the finish is directly dependent on the cleanliness and preparation of the substrate.
Not Just a Surface Polish
Because the PVD coating is so thin and conforms perfectly to the surface, it will not hide underlying imperfections. The base metal must be polished to a perfect finish before the coating is applied, as any scratches or flaws will remain visible.
Common PVD Methods in Jewelry
While the principle remains the same, two main techniques are used for jewelry, each with distinct characteristics.
Sputtering
In this method, the target coating material is bombarded with high-energy ions, which "sputter" or knock atoms off its surface. These atoms then travel and deposit onto the jewelry. Sputtering is highly versatile and offers excellent control over the coating's thickness and uniformity.
Cathodic Arc Evaporation (Arc-PVD)
This technique uses a high-current electric arc to strike the target material, creating a small, intensely hot spot that evaporates the material into a highly ionized vapor. Arc-PVD is known for producing extremely hard and dense coatings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to use PVD depends entirely on your product's goals and market position.
- If your primary focus is creating premium, long-lasting jewelry: PVD is the superior choice for ensuring color and finish durability against daily wear.
- If your primary focus is design innovation and color variety: PVD unlocks a vast palette beyond traditional metals, allowing for unique and trend-setting pieces.
- If your primary focus is minimal upfront cost for fashion jewelry with a short expected lifespan: Traditional electroplating might remain a more budget-conscious alternative.
Ultimately, understanding PVD allows you to make a deliberate choice between a temporary finish and a permanently integrated surface.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PVD Process Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Bonding | Atomic-level integration with base metal |
| Durability | Highly resistant to scratches, tarnishing, and corrosion |
| Color Range | Wide variety (gold, black, blue, iridescent) |
| Key Benefit | Long-lasting finish that is part of the jewelry itself |
| Common Methods | Sputtering, Cathodic Arc Evaporation |
Ready to enhance your jewelry line with durable, vibrant PVD coatings?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise surface treatment applications. Our expertise can help you achieve the superior, long-lasting finishes that today's market demands.
We provide solutions for:
- Jewelry Manufacturers seeking durable, hypoallergenic coatings.
- Designers looking to expand their color and finish palette.
- Labs requiring reliable PVD processes for high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our equipment can bring the benefits of PVD technology to your products!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















