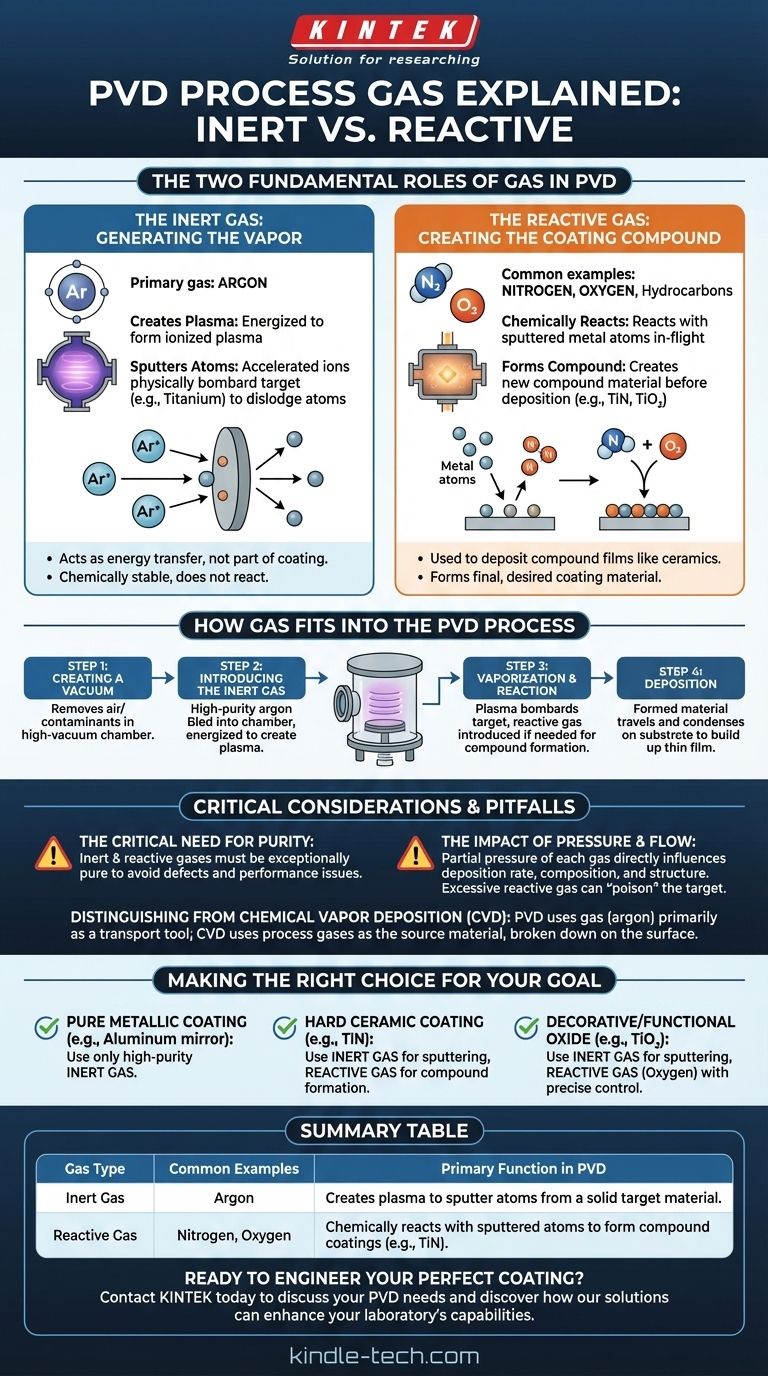
At its core, the primary process gas used in Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a chemically inert gas, most commonly argon. This gas is used to create a plasma that physically bombards a source material, dislodging atoms that will form the coating. In many cases, a second, reactive gas like nitrogen or oxygen is also introduced to chemically combine with these vaporized atoms and form a specific compound coating.
The central concept to grasp is that PVD utilizes two distinct types of gases for two different functions. An inert gas (like argon) acts as the physical force to create a vapor from a solid target, while a reactive gas (like nitrogen) is often added to chemically form the final, desired coating material.

The Two Fundamental Roles of Gas in PVD
To understand the PVD process, you must distinguish between the gas that does the physical work and the gas that becomes part of the final product.
The Inert Gas: Generating the Vapor
The process begins with an inert gas, almost always argon. Its job is not to become part of the coating, but to act as a transfer of energy.
In a vacuum chamber, the argon gas is introduced and energized, typically with a strong electric field, until it becomes an ionized plasma.
These positively charged argon ions are accelerated at high speed toward a negatively charged target, which is the solid source material for the coating (e.g., a block of pure titanium).
The forceful impact of these ions physically knocks atoms off the target in a process called sputtering. Argon is ideal for this because it is heavy enough to displace target atoms effectively but chemically stable, so it won't unintentionally react with the material.
The Reactive Gas: Creating the Coating Compound
This second gas is used only when the goal is to deposit a compound film—like a ceramic—rather than a pure metal.
After the metal atoms are sputtered from the target, they travel through the vacuum chamber toward the substrate being coated.
If a reactive gas like nitrogen, oxygen, or a hydrocarbon gas is present, it will chemically react with these traveling metal atoms.
This in-flight reaction forms a new compound. For example, vaporized titanium atoms will react with nitrogen gas to form Titanium Nitride (TiN), a very hard, gold-colored ceramic, before it deposits on the surface.
How Gas Fits Into the PVD Process
The precise control of these gases within the vacuum chamber is what defines the entire process and the final properties of the coating.
Step 1: Creating a Vacuum
The entire process occurs in a high-vacuum chamber. This removes air and other contaminants that could interfere with the process or become embedded in the coating, compromising its integrity.
Step 2: Introducing the Inert Gas
A small, precisely controlled amount of high-purity argon is bled into the chamber. It is then energized to create the sputtering plasma.
Step 3: Vaporization and Reaction
The plasma bombards the target, creating a vapor of the source material. If a compound coating is desired, the reactive gas is introduced at this stage to combine with the vapor.
Step 4: Deposition
The newly formed material—either pure metal vapor or a new compound—travels through the vacuum and condenses on the cooler substrate, building up a thin, highly adherent film layer by layer.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
Success in PVD is highly dependent on gas management. Simply using the right gas is not enough; it must be controlled with extreme precision.
The Critical Need for Purity
The inert and reactive gases must be exceptionally pure. Any contaminants, such as water vapor or oxygen (where it's not the intended reactive gas), can cause defects and negatively impact the performance of the final coating.
The Impact of Pressure and Flow
The partial pressure of each gas in the chamber is a critical control parameter. It directly influences the deposition rate, the coating's final chemical composition (stoichiometry), and its crystalline structure. Too much reactive gas, for instance, can "poison" the source target, reducing the sputtering efficiency.
Distinguishing from Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
It is important not to confuse PVD with CVD. In CVD processes, the process gases themselves (like silane, SiH₄) are the source of the coating material and are chemically broken down on the substrate surface. In PVD, the gas (argon) is primarily a tool to transport a solid source material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of process gases is dictated entirely by the desired properties of the final thin film.
- If your primary focus is a pure metallic coating (e.g., aluminum for a mirror): You will use only a high-purity inert gas like argon to physically sputter the metallic target onto your substrate.
- If your primary focus is a hard, wear-resistant ceramic coating (e.g., Titanium Nitride): You will use argon to sputter a titanium target and simultaneously introduce nitrogen as a reactive gas to form the desired compound.
- If your primary focus is a decorative or functional oxide coating (e.g., Titanium Dioxide): You will use argon to sputter the titanium target while precisely controlling the flow of oxygen as your reactive gas.
Ultimately, mastering the interplay between the inert and reactive gases is the key to engineering the exact thin-film properties your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Common Examples | Primary Function in PVD |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Gas | Argon | Creates plasma to sputter atoms from a solid target material. |
| Reactive Gas | Nitrogen, Oxygen | Chemically reacts with sputtered atoms to form compound coatings (e.g., TiN). |
Ready to Engineer Your Perfect Coating?
The precise control of PVD process gases is critical for achieving the specific properties—like hardness, durability, and appearance—that your application requires. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-purity lab equipment and consumables necessary for reliable and repeatable PVD processes.
Whether you are developing wear-resistant tools, decorative finishes, or advanced optical coatings, our expertise can help you optimize your gas parameters for superior results.
Contact KINTALK today to discuss your PVD needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition



















