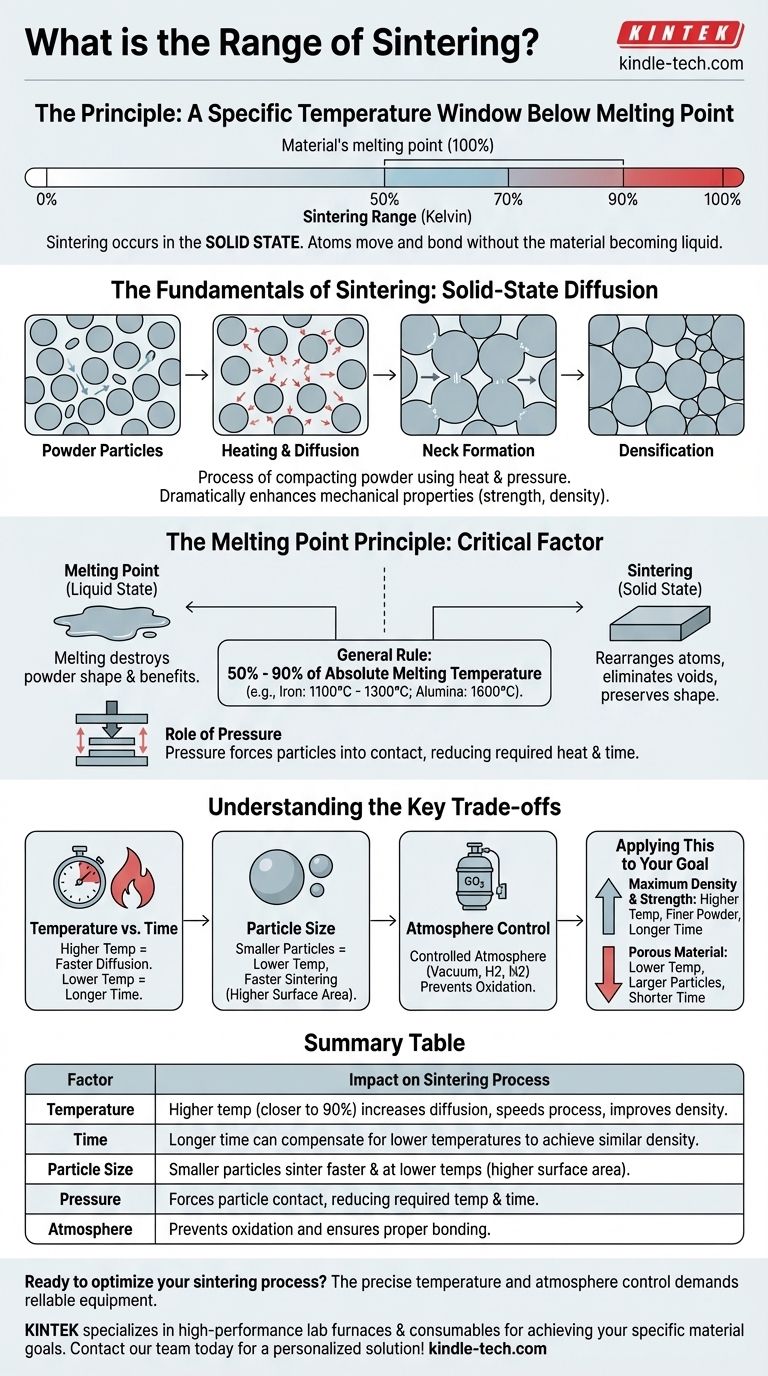
The "range" of sintering is not a single set of temperatures, but rather a principle: it is a specific temperature window relative to a material's own melting point. The process works by heating a material enough for its atoms to move and bond, but not so much that it loses its shape by turning into a liquid.
The core principle is that sintering occurs in the solid state, below a material's melting point. As a general rule, the effective sintering temperature for most materials falls between 50% and 90% of their absolute melting temperature (measured in Kelvin).

The Fundamentals of Sintering
What Sintering Accomplishes
Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material from powder using heat and pressure. Crucially, this happens without melting the material to the point of liquefaction.
The primary goal is to fuse individual particles together. This process dramatically enhances the material's mechanical properties, such as strength and density.
The Mechanism: Solid-State Diffusion
At the microscopic level, the heat applied during sintering gives atoms enough energy to move. These atoms diffuse across the boundaries of adjacent particles.
This atomic movement effectively builds "necks" or bridges between the particles. As the process continues, these bridges grow, pulling the particles closer, reducing the empty space (porosity), and fusing them into a single, coherent piece.
The Critical Factor: The Melting Point Principle
The entire process is governed by a material's melting point. Understanding this relationship is key to understanding the sintering "range."
Why Sintering Must Occur Below Melting
If you were to fully melt the material, you would lose all the benefits of the powder metallurgy process. The precisely formed shape of the compacted powder (the "green part") would be lost.
Sintering is a solid-state process. The objective is to rearrange atoms and eliminate voids between particles, not to create a cast object from a liquid.
The General Temperature Rule
While the exact temperature depends on many factors, the reliable engineering guideline is to heat the material to 50% - 90% of its absolute melting temperature.
For example, iron melts at 1538°C (1811 K). Its sintering range is therefore typically between 1100°C and 1300°C. In contrast, the ceramic alumina melts at 2072°C (2345 K), so its sintering occurs at a much higher temperature, around 1600°C.
The Role of Pressure
Pressure is the second key ingredient. It works in tandem with heat to force the particles into intimate contact.
Applying external pressure reduces the amount of heat or time needed for diffusion to occur, as the atoms don't have to travel as far to form bonds with their neighbors.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
The "correct" sintering temperature is not one number but a choice based on desired outcomes and process limitations.
Temperature vs. Time
There is an inverse relationship between sintering temperature and time. A higher temperature will achieve the desired density faster because atomic diffusion is more rapid.
Conversely, a lower temperature can achieve a similar result, but it will require a significantly longer time in the furnace.
Particle Size and Surface Area
Smaller particles will sinter at lower temperatures and faster rates than larger particles. This is because smaller particles have a much higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, which provides more contact points and energy to drive the diffusion process.
Atmosphere Control
The atmosphere inside the furnace is critical. A controlled atmosphere (such as hydrogen, nitrogen, or a vacuum) is used to prevent oxidation or other chemical reactions that would interfere with the bonding of the particles.
Applying This to Your Goal
Choosing the right parameters depends entirely on the final properties you need in your component.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: Use higher temperatures (closer to 90% of the melting point), finer powders, and sufficient time to allow for the near-complete elimination of pores.
- If your primary focus is creating a porous material (e.g., for filters or self-lubricating bearings): Use lower temperatures, larger particle sizes, and shorter cycle times to intentionally create strong bonds between particles without closing all the gaps.
Ultimately, the sintering range is a flexible window that is engineered to produce a specific microstructure and achieve the desired material performance.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Sintering Process |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Higher temperature (closer to 90% of melting point) increases diffusion, speeds up process, and improves density. |
| Time | Longer sintering time can compensate for lower temperatures to achieve similar density. |
| Particle Size | Smaller particles sinter faster and at lower temperatures due to higher surface area. |
| Pressure | Applied pressure forces particle contact, reducing required temperature and time. |
| Atmosphere | Controlled atmosphere (e.g., vacuum, hydrogen) prevents oxidation and ensures proper bonding. |
Ready to optimize your sintering process for maximum material strength and density? The precise temperature and atmosphere control required for successful sintering demands reliable equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables designed for exacting thermal processing. Our experts can help you select the right system to achieve your specific material goals, whether you need maximum density or controlled porosity. Contact our team today to discuss your application and get a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- Why Use a Quartz Tube Reactor for Y-Ti-O Phase Transformations? Achieve Absolute Purity and Precision Control
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















